Iraq War
This article may be too long to read and navigate comfortably. When this tag was added, its readable prose size was 15,530 words. (October 2023) |
| Iraq War حرب العراق (Arabic) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Iraq conflict and the war on terror | |||||||
 Clockwise from top: US troops at Uday and Qusay Hussein's hideout; insurgents in northern Iraq; the toppling of the Saddam Hussein statue in Firdos Square | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
|
Invasion (2003) |
Invasion (2003) | ||||||
|
After Invasion (2003–11) |
After Invasion (2003–11) | ||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
| Strength | |||||||
|
Coalition forces (2003) 176,000 at peak United States Forces – Iraq (2010–11) 112,000 at activation Security contractors 6,000–7,000 (estimate)[4] Iraqi security forces 805,269 (military and paramilitary: 578,269,[5][page needed] police: 227,000) ≈103,000 (2008)[6] Iraqi Kurdistan ≈400,000 (Kurdish Border Guard: 30,000,[7] Peshmerga 75,000) |
Sunni Insurgents ≈1,000 (2008) Army of the Men of the Naqshbandi Order ≈500–1,000 (2007) | ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
|
Iraqi security forces (post-Saddam) Total wounded: 117,961 |
Iraqi combatant dead (invasion period): 7,600–45,000[29][30] Insurgents (post-Saddam) Killed: 26,544+ (2003–11)[31] (4,000 foreign fighters killed by Sep. 2006)[32] Detainees: 12,000 (Iraqi-held, in 2010 only)[33] 119,752 insurgents arrested (2003–2007)[34] Total dead: 34,144–71,544 | ||||||
|
| |||||||
|
* "injured, diseased, or other medical": required medical air transport. UK number includes "aeromed evacuations". ** Total excess deaths include all additional deaths due to increased lawlessness, degraded infrastructure, poorer healthcare, etc. *** Violent deaths only – does not include excess deaths due to increased lawlessness, poorer healthcare, etc. **** Sukkariyeh, Syria were also affected (2008 Abu Kamal raid). | |||||||
| Part of a series on |
| Ba'athism |
|---|
 |
The Iraq War (Template:Lang-ar) was a protracted armed conflict in Iraq from 2003 to 2011. It began with the invasion of Iraq by the United States-led coalition that overthrew the Ba'athist government of Saddam Hussein. The conflict continued for much of the next decade as an insurgency emerged to oppose the coalition forces and the post-invasion Iraqi government. US troops were officially withdrawn in 2011. The United States became re-involved in 2014 at the head of a new coalition, and the insurgency and many dimensions of the armed conflict are ongoing. The invasion occurred as part of the George W. Bush administration's war on terror following the September 11 attacks.
In October 2002, the United States Congress passed a joint resolution which granted Bush the power to use military force against the Iraqi government. The Iraq War officially began on 20 March 2003, when the US, joined by the United Kingdom, Australia, and Poland, launched a "shock and awe" bombing campaign. Shortly following the bombing campaign, US-led forces launched a ground invasion of Iraq. Iraqi forces were quickly overwhelmed as coalition forces swept through the country. The invasion led to the collapse of the Ba'athist government; Saddam Hussein was captured during Operation Red Dawn in December of that same year and executed three years later. The power vacuum following Saddam's demise, and mismanagement by the Coalition Provisional Authority, led to widespread civil war between Shias and Sunnis, as well as a lengthy insurgency against coalition forces. The United States responded with a build-up of 170,000 troops in 2007. This build-up gave greater control to Iraq's government and military while also giving the United States a greater say in the postwar reconstruction of Iraq. In 2008, President Bush agreed to a withdrawal of all US combat troops from Iraq. The withdrawal was completed under Barack Obama in December 2011.
The United States based most of its rationale for the invasion on claims that Iraq had a weapons of mass destruction (WMD) program and posed a threat to the United States and its allies. In addition to claiming that Saddam Hussein was supporting al-Qaeda, US government also alleged that Al-Qaeda was covertly co-operating with Iraq to build weapons of mass destruction. However, in 2004 the 9/11 Commission concluded there was no evidence of any relationship between Saddam's regime and al-Qaeda. No stockpiles of WMDs or active WMD program were ever found in Iraq. Bush administration officials made numerous claims about a purported Saddam–al-Qaeda relationship and WMDs that were based on insufficient evidence rejected by intelligence officials. The rationale for the Iraq war faced heavy criticism both domestically and internationally. Kofi Annan, then the Secretary-General of the United Nations, called the invasion illegal under international law, as it violated the UN Charter. The 2016 Chilcot Report, a British inquiry into the United Kingdom's decision to go to war, concluded that not every peaceful alternative had been examined, that the UK and US had undermined the United Nations Security Council in the process of declaring war, that the process of identification for a legal basis of war was "far from satisfactory", and that, these conclusions taken together, the war was unnecessary. When interrogated by the FBI, Saddam Hussein confirmed that Iraq did not have weapons of mass destruction prior to the US invasion, although the Iraq Survey Group did find that Saddam had the aim of WMD proliferation and maintained the laboratories and scientists necessary for WMD development.
In 2005, Iraq held multi-party elections. Nouri al-Maliki became Prime Minister in 2006 and remained in office until 2014. The al-Maliki government enacted policies that alienated the country's previously dominant Sunni minority and worsened sectarian tensions.
The war killed an estimated 150,000 to 1,033,000 people, including more than 100,000 civilians (see estimates below). Most died during the initial insurgency and civil conflicts. The 2013–2017 War in Iraq, which is considered a domino effect of the invasion and occupation, caused at least 155,000 deaths and internally displaced more than 3.3 million Iraqis.
The war hurt the United States' international reputation as well as Bush's domestic popularity and public image. The war reduced Blair's popularity, leading to his resignation in 2007.
Background
Strong international opposition to the Saddam Hussein regime began following Iraq's invasion of Kuwait in 1990. The international community condemned the invasion,[43] and in 1991 a military coalition led by the United States launched the Gulf War to expel Iraqi forces from Kuwait.
Following the Gulf War, the US and its allies tried to keep Saddam Hussein in check with a policy of containment. This policy involved numerous economic sanctions by the UN Security Council; the enforcement of Iraqi no-fly zones declared by the US and the UK to protect the Kurds in Iraqi Kurdistan and Shias in the south from aerial attacks by the Iraqi government, and ongoing inspections to ensure Iraq's compliance with United Nations resolutions concerning Iraqi weapons of mass destruction.
The inspections were carried out by the United Nations Special Commission (UNSCOM). UNSCOM, in cooperation with the International Atomic Energy Agency, worked to ensure that Iraq destroyed its chemical, biological, and nuclear weapons and facilities.[44]
In the decade following the Gulf War, the United Nations passed 16 Security Council resolutions calling for the complete elimination of Iraqi weapons of mass destruction. Member states communicated their frustration over the years that Iraq was impeding the work of the special commission and failing to take seriously its disarmament obligations. Iraqi officials harassed the inspectors and obstructed their work,[44] and in August 1998, the Iraqi government suspended cooperation with the inspectors completely, alleging that the inspectors were spying for the US.[45] The spying allegations were later substantiated.[46]
In October 1998, removing the Iraqi government became official US foreign policy with the enactment of the Iraq Liberation Act. The act provided $97 million for Iraqi "democratic opposition organizations" to "establish a program to support a transition to democracy in Iraq."[47] This legislation contrasted with the terms set out in United Nations Security Council Resolution 687, which focused on weapons and weapons programs and made no mention of regime change.[48]
One month after the passage of the Iraq Liberation Act, the US and UK launched a bombardment campaign of Iraq called Operation Desert Fox. The campaign's express rationale was to hamper Saddam Hussein's government's ability to produce chemical, biological, and nuclear weapons, but US intelligence personnel also hoped it would help weaken Saddam's grip on power.[49]
Following the election of George W. Bush as president in 2000, the US moved towards a more aggressive Iraq policy. The Republican Party's campaign platform in the 2000 election called for "full implementation" of the Iraq Liberation Act as "a starting point" in a plan to "remove" Saddam.[50]
Little formal movement towards an invasion occurred until the September 11 attacks although plans were drafted and meetings were held from the first days of his administration.[51][52]
Pre-war events

Following 9/11, the Bush administration's national security team actively debated an invasion of Iraq. On the day of the attacks, Secretary of Defense Donald Rumsfeld asked his aides for: "best info fast. Judge whether good enough hit Saddam Hussein at the same time. Not only Osama bin Laden."[54] President Bush spoke with Rumsfeld on 21 November and instructed him to conduct a confidential review of OPLAN 1003, the war plan for invading Iraq.[55][56] Rumsfeld met with General Tommy Franks, the commander of US Central Command, on 27 November to go over the plans. A record of the meeting includes the question "How start?", listing multiple possible justifications for a US–Iraq War.[53][57] The rationale for invading Iraq as a response to 9/11 has been refuted, as there was no cooperation between Saddam Hussein and al-Qaeda.[58][59][60][61][62][63]
President Bush began laying the public groundwork for an invasion of Iraq in January 2002 State of the Union address, calling Iraq a member of the Axis of Evil, and saying "The United States of America will not permit the world's most dangerous regimes to threaten us with the world's most destructive weapons."[64] Bush said this and made many other dire allegations about the threat of Iraqi weapons of mass destruction despite the fact that the Bush administration knew that Iraq had no nuclear weapons and had no information about whether Iraq had biological weapons.[65][66][67][68][69] He began formally making his case to the international community for an invasion of Iraq in his 12 September 2002 address to the UN Security Council.[70] However, a 5 September 2002 report from Major General Glen Shaffer revealed that the Joint Chiefs of Staff's J2 Intelligence Directorate had concluded that the United States' knowledge on different aspects of the Iraqi WMD program ranged from essentially zero to about 75%, and that knowledge was particularly weak on aspects of a possible nuclear weapons program: "Our knowledge of the Iraqi nuclear weapons program is based largely – perhaps 90% – on analysis of imprecise intelligence," they concluded. "Our assessments rely heavily on analytic assumptions and judgment rather than hard evidence. The evidentiary base is particularly sparse for Iraqi nuclear programs."[71][72] Similarly, the British government found no evidence that Iraq possessed nuclear weapons or any other weapons of mass destruction and that Iraq posed no threat to the West, a conclusion British diplomats shared with the US government.[73]

Key US allies in NATO, such as the United Kingdom, agreed with the US actions, while France and Germany were critical of plans to invade Iraq, arguing instead for continued diplomacy and weapons inspections. After considerable debate, the UN Security Council adopted a compromise resolution, UN Security Council Resolution 1441, which authorized the resumption of weapons inspections and promised "serious consequences" for non-compliance. Security Council members France and Russia made clear that they did not consider these consequences to include the use of force to overthrow the Iraqi government.[74] The US and UK ambassadors to the UN publicly confirmed this reading of the resolution.[75]
Resolution 1441 set up inspections by the United Nations Monitoring, Verification and Inspection Commission (UNMOVIC) and the International Atomic Energy Agency. Saddam accepted the resolution on 13 November and inspectors returned to Iraq under the direction of UNMOVIC chairman Hans Blix and IAEA Director General Mohamed ElBaradei. As of February 2003, the IAEA "found no evidence or plausible indication of the revival of a nuclear weapons program in Iraq"; the IAEA concluded that certain items which could have been used in nuclear enrichment centrifuges, such as aluminum tubes, were in fact intended for other uses.[76] In March 2003, Blix said progress had been made in inspections, and no evidence of WMD had been found.[77]
In October 2002, the US Congress passed the "Iraq Resolution",[78] which authorized the President to "use any means necessary" against Iraq. Americans polled in January 2003 widely favored further diplomacy over an invasion. Later that year, however, Americans began to agree with Bush's plan (see popular opinion in the United States on the invasion of Iraq). The US government engaged in an elaborate domestic public relations campaign to promote the war to its citizens. Americans overwhelmingly believed Saddam did have weapons of mass destruction: 85% said so, even though the inspectors had not uncovered those weapons. By February 2003, 64% of Americans supported taking military action to remove Saddam from power.[79]

On 5 February 2003, Secretary of State Colin Powell appeared before the UN to present evidence that Iraq was hiding unconventional weapons. However, despite warnings from the German Federal Intelligence Service and the British Secret Intelligence Service that the source was untrustworthy, Powell's presentation included information based on the claims of Rafid Ahmed Alwan al-Janabi, codenamed "Curveball", an Iraqi emigrant living in Germany who also later admitted that his claims had been false.[80] Powell also claimed that Iraq was covertly harbouring and supporting al-Qaeda networks. Additionally, Powell alleged that al-Qaeda was attempting to acquire weapons of mass destruction from Iraq:
"Al-Qaida continues to have a deep interest in acquiring weapons of mass destruction. As with the story of Zarqawi and his network, I can trace the story of a senior terrorist operative telling how Iraq provided training in these weapons to al-Qaida. Fortunately, this operative is now detained and he has told his story. ... The support that this detainee describes included Iraq offering chemical or biological weapons training for two al-Qaida associates beginning in December 2000. He says that a militant known as Abdallah al-Iraqi had been sent to Iraq several times between 1997 and 2000 for help in acquiring poisons and gasses. Abdallah al-Iraqi characterized the relationship he forged with Iraqi officials as successful."[81]
As a follow-up to Powell's presentation, the United States, the United Kingdom, Poland, Italy, Australia, Denmark, Japan, and Spain proposed a resolution authorizing the use of force in Iraq, but NATO members like Canada, France, and Germany, together with Russia, strongly urged continued diplomacy. Facing a losing vote as well as a likely veto from France and Russia, the US, the UK, Poland, Spain, Denmark, Italy, Japan, and Australia eventually withdrew their resolution.[82][83]
In March 2003, the United States, the United Kingdom, Poland, Australia, Spain, Denmark, and Italy began preparing for the invasion of Iraq with a host of public relations and military moves. In an address to the nation on 17 March 2003, Bush demanded that Saddam and his two sons, Uday and Qusay, surrender and leave Iraq, giving them a 48-hour deadline.[84]
The UK House of Commons held a debate on going to war on 18 March 2003 where the government motion was approved 412 to 149.[85] The vote was a key moment in the history of the Blair government, as the number of government MPs who rebelled against the vote was the greatest since the repeal of the Corn Laws in 1846. Three government ministers resigned in protest at the war, John Denham, Lord Hunt of Kings Heath, and the then Leader of the House of Commons Robin Cook.
Opposition to invasion
In October 2002, former US President Bill Clinton warned about the possible dangers of pre-emptive military action against Iraq. Speaking in the UK at a Labour Party conference he said: "As a preemptive action today, however well-justified, may come back with unwelcome consequences in the future... I don't care how precise your bombs and your weapons are when you set them off, innocent people will die."[86][87] Of 209 House Democrats in Congress, 126 voted against the Authorization for Use of Military Force Against Iraq Resolution of 2002, although 29 of 50 Democrats in the Senate voted in favor of it. Only one Republican Senator, Lincoln Chafee, voted against it. The Senate's lone Independent, Jim Jeffords, voted against it. Retired US Marine, former Navy Secretary and future US senator Jim Webb wrote shortly before the vote, "Those who are pushing for a unilateral war in Iraq know full well that there is no exit strategy if we invade."[88]
In the same period, Pope John Paul II publicly condemned the military intervention. During a private meeting, he also said directly to George W. Bush: "Mr. President, you know my opinion about the war in Iraq. Let's talk about something else. Every violence, against one or a million, is a blasphemy addressed to the image and likeness of God."[89]

On 20 January 2003, French Foreign Minister Dominique de Villepin declared "we believe that military intervention would be the worst solution".[91] Meanwhile, anti-war groups across the world organized public protests. According to French academic Dominique Reynié, between 3 January and 12 April 2003, 36 million people across the globe took part in almost 3,000 protests against the war in Iraq, with demonstrations on 15 February 2003 being the largest.[92] Nelson Mandela voiced his opposition in late January, stating "All that (Mr. Bush) wants is Iraqi oil," and questioning if Bush deliberately undermined the U.N. "because the secretary-general of the United Nations [was] a black man".[93]
In February 2003, the US Army's top general, Eric Shinseki, told the Senate Armed Services Committee that it would take "several hundred thousand soldiers" to secure Iraq.[94] Two days later, US Defense Secretary Donald Rumsfeld said the post-war troop commitment would be less than the number of troops required to win the war, and that "the idea that it would take several hundred thousand US forces is far from the mark." Deputy Defense Secretary Paul Wolfowitz said Shinseki's estimate was "way off the mark," because other countries would take part in an occupying force.[95]
Germany's Foreign Secretary Joschka Fischer, although having been in favor of stationing German troops in Afghanistan, advised Federal Chancellor Schröder not to join the war in Iraq. Fischer famously confronted United States Defense Secretary Donald Rumsfeld at the 39th Munich Security Conference in 2003 on the secretary's purported evidence for Iraq's possession of weapons of mass destruction: "Excuse me, I am not convinced!"[96] Fischer also cautioned the United States about biting off more than it could chew by assuming that democracy would easily take root post-invasion; "You're going to have to occupy Iraq for years and years, the idea that democracy will suddenly blossom is something that I can't share. … Are Americans ready for this?"[97]
There were serious legal questions surrounding the launching of the war against Iraq and the Bush Doctrine of preemptive war in general. On 16 September 2004, Kofi Annan, the Secretary-General of the United Nations, said of the invasion "...was not in conformity with the UN Charter. From our point of view, from the Charter point of view, it was illegal."[98]
Course of the war
2003: Invasion

The first Central Intelligence Agency team entered Iraq on 10 July 2002.[99] This team was composed of members of the CIA's Special Activities Division and was later joined by members of the US military's elite Joint Special Operations Command (JSOC).[100] Together, they prepared for an invasion by conventional forces. These efforts consisted of persuading the commanders of several Iraqi military divisions to surrender rather than oppose the invasion, and identifying all the initial leadership targets during very high risk reconnaissance missions.[100]

Most importantly, their efforts organized the Kurdish Peshmerga to become the northern front of the invasion. Together this force defeated Ansar al-Islam in Iraqi Kurdistan before the invasion and then defeated the Iraqi army in the north.[100][101] The battle against Ansar al-Islam, known as Operation Viking Hammer, led to the death of a substantial number of militants and the uncovering of a chemical weapons facility at Sargat.[99][102]

At 5:34 am Baghdad time on 20 March 2003[103] (9:34 pm, 19 March EST) the surprise[104] military invasion of Iraq began.[citation needed] There was no declaration of war.[105] The 2003 invasion of Iraq was led by US Army General Tommy Franks, under the code-name Operation Iraqi Freedom,[106] the UK code-name Operation Telic, and the Australian code-name Operation Falconer. Coalition forces also cooperated with Kurdish Peshmerga forces in the north. Approximately forty other governments, the "Coalition of the Willing", participated by providing troops, equipment, services, security, and special forces, with 248,000 soldiers from the United States, 45,000 British soldiers, 2,000 Australian soldiers and 194 Polish soldiers from Special Forces unit GROM sent to Kuwait for the invasion.[107] The invasion force was also supported by Iraqi Kurdish militia troops, estimated to number upwards of 70,000.[108]
According to General Franks, there were eight objectives of the invasion:
"First, ending the regime of Saddam Hussein. Second, to identify, isolate, and eliminate Iraq's weapons of mass destruction. Third, to search for, to capture, and to drive out terrorists from that country. Fourth, to collect such intelligence as we can relate to terrorist networks. Fifth, to collect such intelligence as we can relate to the global network of illicit weapons of mass destruction. Sixth, to end sanctions and to immediately deliver humanitarian support to the displaced and to many needy Iraqi citizens. Seventh, to secure Iraq's oil fields and resources, which belong to the Iraqi people. And last, to help the Iraqi people create conditions for a transition to representative self-government."[109]
The invasion was a quick and decisive operation encountering major resistance, though not what the US, British and other forces expected. The Iraqi regime had prepared to fight both a conventional and irregular, asymmetric warfare at the same time, conceding territory when faced with superior conventional forces, largely armored, but launching smaller-scale attacks in the rear using fighters dressed in civilian and paramilitary clothes.
Coalition troops launched air and amphibious assaults on the al-Faw Peninsula to secure the oil fields there and the important ports, supported by warships of the Royal Navy, Polish Navy, and Royal Australian Navy. The United States Marine Corps' 15th Marine Expeditionary Unit, attached to 3 Commando Brigade and the Polish Special Forces unit GROM, attacked the port of Umm Qasr, while the British Army's 16 Air Assault Brigade secured the oil fields in southern Iraq.[110][111]
The heavy armor of the US 3rd Infantry Division moved westward and then northward through the western desert toward Baghdad, while the 1st Marine Expeditionary Force moved more easterly along Highway 1 through the center of the country, and 1 (UK) Armoured Division moved northward through the eastern marshland.[112] The American 1st Marine Division fought through Nasiriyah in a battle to seize the major road junction.[113] The United States Army 3rd Infantry Division defeated Iraqi forces entrenched in and around Talil Airfield.[114]
With the Nasiriyah and Talil Airfields secured in its rear, the 3rd Infantry Division supported by the 101st Airborne Division continued its attack north toward Najaf and Karbala, but a severe sand storm slowed the coalition advance and there was a halt to consolidate and make sure the supply lines were secure.[115] When they started again they secured the Karbala Gap, a key approach to Baghdad, then secured the bridges over the Euphrates River, and US Army forces poured through the gap on to Baghdad. In the middle of Iraq, the 1st Marine Division fought its way to the eastern side of Baghdad and prepared for the attack to seize the city.[116]
On 9 April, Baghdad fell, ending Saddam's 24‑year rule. US forces seized the deserted Ba'ath Party ministries and, according to some reports later disputed by the Marines on the ground, stage-managed[117] the tearing down of a huge iron statue of Saddam, photos and video of which became symbolic of the event, although later controversial. Allegedly, though not seen in the photos or heard on the videos, shot with a zoom lens, was the chant of the inflamed crowd for Muqtada al-Sadr, the radical Shiite cleric.[118] The abrupt fall of Baghdad was accompanied by a widespread outpouring of gratitude toward the invaders, but also massive civil disorder, including the looting of public and government buildings and drastically increased crime.[119][120]
According to the Pentagon, 250,000 short tons (230,000 t) (of 650,000 short tons (590,000 t) total) of ordnance was looted, providing a significant source of ammunition for the Iraqi insurgency. The invasion phase concluded when Tikrit, Saddam's home town, fell with little resistance to the US Marines of Task Force Tripoli on 15 April.
In the invasion phase of the war (19 March – 30 April), an estimated 9,200 Iraqi combatants were killed by coalition forces along with an estimated 3,750 non-combatants, i.e. civilians who did not take up arms.[121] Coalition forces reported the death in combat of 139 US military personnel[122] and 33 UK military personnel.[123]
Post-invasion phase
2003: Beginnings of insurgency




On 1 May 2003, President Bush visited the aircraft carrier USS Abraham Lincoln operating a few miles west of San Diego, California. At sunset, he held his nationally televised "Mission Accomplished" speech, delivered before the sailors and airmen on the flight deck. Bush declared the end of major combat operations in Iraq, due to the defeat of Iraq's conventional forces, while maintaining that much still needed to be done.[56]
Nevertheless, Saddam Hussein remained at large, and significant pockets of resistance remained. After Bush's speech, coalition forces noticed a flurry of attacks on its troops began to gradually increase in various regions, such as the "Sunni Triangle".[citation needed] The initial Iraqi insurgents were supplied by hundreds of weapons caches created before the invasion by the Iraqi army and Republican Guard.
Initially, Iraqi resistance (described by the coalition as "Anti-Iraqi Forces") largely stemmed from fedayeen and Saddam/Ba'ath Party loyalists, but soon religious radicals and Iraqis angered by the occupation contributed to the insurgency. The three governorates with the highest number of attacks were Baghdad, Al Anbar, and Saladin. Those three governorates account for 35% of the population, but by December 2006 they were responsible for 73% of US military deaths and an even higher percentage of recent US military deaths (about 80%).[124]
Insurgents used various guerrilla tactics, including mortars, missiles, suicide attacks, snipers, improvised explosive devices (IEDs), car bombs, small arms fire (usually with assault rifles), and RPGs (rocket-propelled grenades), as well as sabotage against the petroleum, water, and electrical infrastructures.
Coalition efforts to establish post-invasion Iraq commenced after the fall of Saddam's regime. The coalition nations, together with the United Nations, began to work to establish a stable, compliant democratic state capable of defending itself from non-coalition forces, as well as overcoming internal divisions.[125]
Meanwhile, coalition military forces launched several operations around the Tigris River peninsula and in the Sunni Triangle. A series of similar operations were launched throughout the summer in the Sunni Triangle. In late 2003, the intensity and pace of insurgent attacks began to increase. A sharp surge in guerrilla attacks ushered in an insurgent effort that was termed the "Ramadan Offensive", as it coincided with the beginning of the Muslim holy month of Ramadan.
To counter this offensive, coalition forces began to use air power and artillery again for the first time since the end of the invasion, by striking suspected ambush sites and mortar launching positions. Surveillance of major routes, patrols, and raids on suspected insurgents was stepped up. In addition, two villages, including Saddam's birthplace of al-Auja and the small town of Abu Hishma, were surrounded by barbed wire and carefully monitored.
Coalition Provisional Authority and the Iraq Survey Group
Shortly after the invasion, the multinational coalition created the Coalition Provisional Authority (CPA; Template:Lang-ar), based in the Green Zone, as a transitional government of Iraq until the establishment of a democratic government. Citing United Nations Security Council Resolution 1483 (22 May 2003) and the laws of war, the CPA vested itself with executive, legislative, and judicial authority over the Iraqi government from the period of the CPA's inception on 21 April 2003 until its dissolution on 28 June 2004.

The CPA was originally headed by Jay Garner, a former US military officer, but his appointment lasted only until 11 May 2003, when President Bush appointed L. Paul Bremer. On 16 May 2003, his first day on the job, Paul Bremer issued Coalition Provisional Authority Order 1 to exclude from the new Iraqi government and administration members of the Baathist party. This policy, known as De-Ba'athification, eventually led to the removal of 85,000 to 100,000 Iraqi people from their jobs,[126] including 40,000 school teachers who had joined the Baath Party simply to stay employed. US army general Ricardo Sanchez called the decision a "catastrophic failure".[127] Bremer served until the CPA's dissolution in June 2004.
In May 2003, the US Advisor to Iraq Ministry of Defense within the CPA, Walter B. Slocombe, advocated changing the pre-war Bush policy to employ the former Iraq Army after hostilities on the ground ceased.[128] At the time, hundreds of thousands of former Iraq soldiers who had not been paid for months were waiting for the CPA to hire them back to work to help secure and rebuild Iraq. Despite advice from US Military Staff working within the CPA, Bremer met with President Bush, via video conference, and asked for authority to change the US policy. Bush gave Bremer and Slocombe authority to change the pre-war policy. Slocombe announced the policy change in the Spring of 2003. The decision led to the alienation of hundreds of thousands of former armed Iraq soldiers, who subsequently aligned themselves with various occupation resistance movements all over Iraq. In the week before the order to dissolve the Iraq Army, no coalition forces were killed by hostile action in Iraq; the week after, five US soldiers were killed. Then, on 18 June 2003, coalition forces opened fire on former Iraq soldiers protesting in Baghdad who were throwing rocks at coalition forces. The policy to disband the Iraq Army was reversed by the CPA only days after it was implemented. But it was too late; the former Iraq Army shifted their alliance from one that was ready and willing to work with the CPA to one of armed resistance against the CPA and the coalition forces.[129]
Another group created by the multinational force in Iraq post-invasion was the 1,400-member international Iraq Survey Group, who conducted a fact-finding mission to find Iraq's weapons of mass destruction (WMD) programs. In 2004, the ISG's Duelfer Report stated that Iraq did not have a viable WMD program.[130][131][132][133][134][135]
Capturing former government leaders

In the summer of 2003, the multinational forces focused on capturing the remaining leaders of the former government. On 22 July, a raid by the US 101st Airborne Division and soldiers from Task Force 20 killed Saddam's sons (Uday and Qusay) along with one of his grandsons. In all, over 300 top leaders of the former government were killed or captured, as well as numerous lesser functionaries and military personnel.
Most significantly, Saddam Hussein himself was captured on 13 December 2003, on a farm near Tikrit in Operation Red Dawn.[136] The operation was conducted by the United States Army's 4th Infantry Division and members of Task Force 121. Intelligence on Saddam's whereabouts came from his family members and former bodyguards.[137]
With the capture of Saddam and a drop in the number of insurgent attacks, some concluded that multinational forces were prevailing in the fight against the insurgency. The provisional government began training the new Iraqi security forces intended to police the country, and the United States promised over $20 billion in reconstruction money in the form of a credit against Iraq's future oil revenues. Oil revenue was also used for rebuilding schools and for work on the electrical and refining infrastructure.
Shortly after the capture of Saddam, elements left out of the Coalition Provisional Authority began to agitate for elections and the formation of an Iraqi Interim Government. Most prominent among these was the Shia cleric Grand Ayatollah Ali al-Sistani. The Coalition Provisional Authority opposed allowing democratic elections at this time.[138] The insurgents stepped up their activities. The two most turbulent centers were the area around Fallujah and the poor Shia sections of cities from Baghdad (Sadr City) to Basra in the south.
Looting of artifacts from Iraqi museums
Following the United States' invasion of Iraq in 2003, large numbers of antiquities including the Gilgamesh Dream Tablet were stolen, both from museums, such as the Iraq National Museum, but also because of illegal excavations at archeological sites throughout the country. Many of them were smuggled into the United States through the United Arab Emirates (UAE) and Israel, contrary to federal law. Donald Rumsfeld rejected the claim that they were removed by US military personnel. In the 2020s, about 17,000 artifacts were returned to Iraq from the U.S. and Middle Eastern countries. But according to an Iraqi archeology professor at the University of Baghdad, the repatriation of these items was only a partial success; the Baghdad office of the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) continues to search for the loot worldwide. Many Iraqis blame the United States for the loss of so many pieces of their country's history.[139][140]
2004: Insurgency expands

The start of 2004 was marked by a relative lull in violence. Insurgent forces reorganised during this time, studying the multinational forces' tactics and planning a renewed offensive. However, violence did increase during the Iraq Spring Fighting of 2004 with foreign fighters from around the Middle East as well as Jama'at al-Tawhid wal-Jihad, an al-Qaeda-linked group led by Abu Musab al-Zarqawi, helping to drive the insurgency.[141]
As the insurgency grew there was a distinct change in targeting from the coalition forces towards the new Iraqi Security Forces, as hundreds of Iraqi civilians and police were killed over the next few months in a series of massive bombings. An organized Sunni insurgency, with deep roots and both nationalist and Islamist motivations, was becoming more powerful throughout Iraq. The Shia Mahdi Army also began launching attacks on coalition targets in an attempt to seize control from Iraqi security forces. The southern and central portions of Iraq were beginning to erupt in urban guerrilla combat as multinational forces attempted to keep control and prepared for a counteroffensive.

The most serious fighting of the war so far began on 31 March 2004, when Iraqi insurgents in Fallujah ambushed a Blackwater USA convoy led by four US private military contractors who were providing security for food caterers Eurest Support Services.[142] The four armed contractors, Scott Helvenston, Jerko Zovko, Wesley Batalona, and Michael Teague, were killed with grenades and small arms fire. Subsequently, their bodies were dragged from their vehicles by local people, beaten, set ablaze, and their burned corpses hung over a bridge crossing the Euphrates.[143] Photos of the event were released to news agencies worldwide, causing a great deal of indignation and moral outrage in the United States, and prompting an unsuccessful "pacification" of the city: the First Battle of Fallujah in April 2004.
The offensive was resumed in November 2004 in the bloodiest battle of the war: the Second Battle of Fallujah, described by the US military as "the heaviest urban combat (that they had been involved in) since the Battle of Hue City in Vietnam."[144] During the assault, US forces used white phosphorus as an incendiary weapon against insurgent personnel, attracting controversy. The 46‑day battle resulted in a victory for the coalition, with 95 US soldiers killed along with approximately 1,350 insurgents. Fallujah was totally devastated during the fighting, though civilian casualties were low, as they had mostly fled before the battle.[145]
Another major event of that year was the revelation of widespread prisoner abuse at Abu Ghraib, which received international media attention in April 2004. First reports of the Abu Ghraib prisoner abuse, as well as graphic pictures showing US military personnel taunting and abusing Iraqi prisoners, came to public attention from a 60 Minutes II news report (28 April) and a Seymour M. Hersh article in The New Yorker (posted online on 30 April).[146] Military correspondent Thomas Ricks claimed that these revelations dealt a blow to the moral justifications for the occupation in the eyes of many people, especially Iraqis, and was a turning point in the war.[147]
2004 also marked the beginning of Military Transition Teams in Iraq, which were teams of US military advisors assigned directly to New Iraqi Army units.
2005: Elections and transitional government

On 31 January, Iraqis elected the Iraqi Transitional Government in order to draft a permanent constitution. Although some violence and a widespread Sunni boycott marred the event, most of the eligible Kurd and Shia populace participated. On 4 February, Paul Wolfowitz announced that 15,000 US troops whose tours of duty had been extended in order to provide election security would be pulled out of Iraq by the next month.[148] February to April proved to be relatively peaceful months compared to the carnage of November and January, with insurgent attacks averaging 30 a day from the prior average of 70.
The Battle of Abu Ghraib on 2 April 2005 was an attack on United States forces at Abu Ghraib prison, which consisted of heavy mortar and rocket fire, under which an estimated 80–120 armed insurgents attacked with grenades, small arms, and two vehicle-borne improvised explosive devices (VBIED). The US force's munitions ran so low that orders to fix bayonets were given in preparation for hand-to-hand fighting. It was considered to be the largest coordinated assault on a US base since the Vietnam War.[149]
Hopes for a quick end to the insurgency and a withdrawal of US troops were dashed in May, Iraq's bloodiest month since the invasion. Suicide bombers, believed to be mainly disheartened Iraqi Sunni Arabs, Syrians and Saudis, tore through Iraq. Their targets were often Shia gatherings or civilian concentrations of Shias. As a result, over 700 Iraqi civilians died in that month, as well as 79 US soldiers.
The summer of 2005 saw fighting around Baghdad and at Tall Afar in northwestern Iraq as US forces tried to seal off the Syrian border. This led to fighting in the autumn in the small towns of the Euphrates valley between the capital and that border.[150]
A referendum was held on 15 October in which the new Iraqi constitution was ratified. An Iraqi National Assembly was elected in December, with participation from the Sunnis as well as the Kurds and Shia.[150]
Insurgent attacks increased in 2005 with 34,131 recorded incidents, compared to a total 26,496 for the previous year.[151]
2006: Civil war and permanent Iraqi government

The beginning of 2006 was marked by government creation talks, growing sectarian violence, and continuous anti-coalition attacks. Sectarian violence expanded to a new level of intensity following the al-Askari Mosque bombing in the Iraqi city of Samarra, on 22 February 2006. The explosion at the mosque, one of the holiest sites in Shi'a Islam, is believed to have been caused by a bomb planted by al-Qaeda.
Although no injuries occurred in the blast, the mosque was severely damaged and the bombing resulted in violence over the following days. Over 100 dead bodies with bullet holes were found on 23 February, and at least 165 people are thought to have been killed. In the aftermath of this attack, the US military calculated that the average homicide rate in Baghdad tripled from 11 to 33 deaths per day. In 2006 the UN described the environment in Iraq as a "civil war-like situation".[152]
On 12 March, five United States Army soldiers of the 502nd Infantry Regiment raped the 14-year-old Iraqi girl Abeer Qassim Hamza al-Janabi, and then murdered her, her father, her mother Fakhriya Taha Muhasen, and her six-year-old sister Hadeel Qassim Hamza al-Janabi. The soldiers then set fire to the girl's body to conceal evidence of the crime.[153] Four of the soldiers were convicted of rape and murder and the fifth was convicted of lesser crimes for their involvement in the events, which became known as the Mahmudiyah rape and killings.[154][155]
On 6 June 2006, the United States was successful in tracking Abu Musab al-Zarqawi, the leader of al-Qaeda in Iraq who was killed in a targeted killing, while attending a meeting in an isolated safehouse approximately 8 km (5.0 mi) north of Baqubah. Having been tracked by a British UAV, radio contact was made between the controller and two United States Air Force F-16C jets, which identified the house and at 14:15 GMT, the lead jet dropped two 500‑pound (230 kg) guided bombs, a laser-guided GBU‑12 and GPS-guided GBU‑38 on the building where he was located. Six others – three male and three female individuals – were also reported killed. Among those killed were one of his wives and their child.
The government of Iraq took office on 20 May 2006, following approval by the members of the Iraqi National Assembly. This followed the general election in December 2005. The government succeeded the Iraqi Transitional Government, which had continued in office in a caretaker capacity until the formation of the permanent government.
Iraq Study Group report and Saddam's execution
The Iraq Study Group Report was released on 6 December 2006. The Iraq Study Group made up of people from both of the major US parties, was led by co-chairs James Baker, a former Secretary of State (Republican), and Lee H. Hamilton, a former US Representative (Democrat). It concluded that "the situation in Iraq is grave and deteriorating" and "US forces seem to be caught in a mission that has no foreseeable end." The report's 79 recommendations include increasing diplomatic measures with Iran and Syria and intensifying efforts to train Iraqi troops. On 18 December, a Pentagon report found that insurgent attacks were averaging about 960 attacks per week, the highest since the reports had begun in 2005.[156]
Coalition forces formally transferred control of a governorate to the Iraqi government, the first since the war. Military prosecutors charged eight US Marines with the murders of 24 Iraqi civilians in Haditha in November 2005, 10 of them women and children. Four officers were also charged with dereliction of duty in relation to the event.[157]
Saddam Hussein was hanged on 30 December 2006, after being found guilty of crimes against humanity by an Iraqi court after a year-long trial.[158]
2007: US troops surge

On 10 January 2007, in a televised address to the US public, Bush proposed 21,500 more troops for Iraq, a job program for Iraqis, more reconstruction proposals, and $1.2 billion for these programs.[159] On 23 January 2007, in the 2007 State of the Union Address, Bush announced he was "deploying reinforcements of more than 20,000 additional soldiers and Marines to Iraq".
On 10 February 2007, David Petraeus was made commander of Multi-National Force – Iraq (MNF-I), the four-star post that oversees all coalition forces in the country, replacing General George Casey. In his new position, Petraeus oversaw all coalition forces in Iraq and employed them in the new "Surge" strategy outlined by the Bush administration.[160][161]
On 10 May 2007, 144 Iraqi Parliamentary lawmakers signed onto a legislative petition calling on the United States to set a timetable for withdrawal.[162] On 3 June 2007, the Iraqi Parliament voted 85 to 59 to require the Iraqi government to consult with Parliament before requesting additional extensions of the UN Security Council Mandate for Coalition operations in Iraq.[163]
Pressures on US troops were compounded by the continuing withdrawal of coalition forces.[citation needed] In early 2007, British Prime Minister Blair announced that following Operation Sinbad, British troops would begin to withdraw from Basra Governorate, handing security over to the Iraqis.[164] In July Danish Prime Minister Anders Fogh Rasmussen also announced the withdrawal of 441 Danish troops from Iraq, leaving only a unit of nine soldiers manning four observational helicopters.[165] In October 2019, the new Danish government said it would not re-open an official probe into the country's participation in the US-led military coalition in 2003 Iraqi war.[166]
Planned troop reduction
In a speech made to Congress on 10 September 2007, Petraeus "envisioned the withdrawal of roughly 30,000 US troops by next summer, beginning with a Marine contingent [in September]."[167] On 13 September, Bush backed a limited withdrawal of troops from Iraq.[168] Bush said 5,700 personnel would be home by Christmas 2007, and expected thousands more to return by July 2008. The plan would take troop numbers back to their level before the surge at the beginning of 2007.
Effects of the surge on security
By March 2008, violence in Iraq was reportedly curtailed by 40–80%, according to a Pentagon report.[169] Independent reports[170][171] raised questions about those assessments. An Iraqi military spokesman claimed that civilian deaths since the start of the troop surge plan were 265 in Baghdad, down from 1,440 in the four previous weeks. The New York Times counted more than 450 Iraqi civilians killed during the same 28‑day period, based on initial daily reports from Iraqi Interior Ministry and hospital officials.

Historically, the daily counts tallied by The New York Times underestimated the total death toll by 50% or more when compared to studies by the United Nations, which rely upon figures from the Iraqi Health Ministry and morgue figures.[172]
The rate of US combat deaths in Baghdad nearly doubled to 3.14 per day in the first seven weeks of the "surge" in security activity, compared to the previous period. Across the rest of Iraq, it decreased slightly.[173][174]
On 14 August 2007, the deadliest single attack of the whole war occurred. Nearly 800 civilians were killed by a series of coordinated suicide bomb attacks on the northern Iraqi settlement of Kahtaniya. More than 100 homes and shops were destroyed in the blasts. US officials blamed al‑Qaeda. The targeted villagers belonged to the non-Muslim Yazidi ethnic minority. The attack may have represented the latest in a feud that erupted earlier that year when members of the Yazidi community stoned to death a teenage girl called Du'a Khalil Aswad accused of dating a Sunni Arab man and converting to Islam. The killing of the girl was recorded on camera-mobiles and the video was uploaded onto the internet.[175][176][177][178]
On 13 September 2007, Abdul Sattar Abu Risha was killed in a bomb attack in the city of Ramadi.[179] He was an important US ally because he led the "Anbar Awakening", an alliance of Sunni Arab tribes that opposed al-Qaeda. The latter organization claimed responsibility for the attack.[180] A statement posted on the Internet by the shadowy Islamic State of Iraq called Abu Risha "one of the dogs of Bush" and described Thursday's killing as a "heroic operation that took over a month to prepare".[181]

There was a reported trend of decreasing US troop deaths after May 2007,[citation needed] and violence against coalition troops had fallen to the "lowest levels since the first year of the American invasion".[182] These, and several other positive developments, were attributed to the surge by many analysts.[183]
Data from the Pentagon and other US agencies such as the Government Accountability Office (GAO) found that daily attacks against civilians in Iraq remained "about the same" since February. The GAO also stated that there was no discernible trend in sectarian violence.[184] However, this report ran counter to reports to Congress, which showed a general downward trend in civilian deaths and ethno-sectarian violence since December 2006.[185] By late 2007, as the US troop surge began to wind down, violence in Iraq had begun to decrease from its 2006 highs.[186]
Entire neighborhoods in Baghdad were ethnically cleansed by Shia and Sunni militias and sectarian violence broke out in every Iraqi city where there was a mixed population.[187][188][189] Investigative reporter Bob Woodward cited US government sources according to which the US "surge" was not the primary reason for the drop in violence in 2007–08. Instead, according to that view, the reduction of violence was due to newer covert techniques by US military and intelligence officials to find, target, and kill insurgents, including working closely with former insurgents.[190]
In the Shia region near Basra, British forces turned over security for the region to Iraqi Security Forces. Basra was the ninth governorate of Iraq's 18 governorates to be returned to local security forces' control since the beginning of the occupation.[191]
Political developments
More than half of the members of Iraq's parliament rejected the continuing occupation of their country for the first time. 144 of the 275 lawmakers signed onto a legislative petition that would require the Iraqi government to seek approval from Parliament before it requests an extension of the UN mandate for foreign forces to be in Iraq, which expires at the end of 2008. It also calls for a timetable for troop withdrawal and a freeze on the size of foreign forces. The UN Security Council mandate for US‑led forces in Iraq will terminate "if requested by the government of Iraq."[192] 59% of those polled in the US support a timetable for withdrawal.[193]
In mid-2007, the Coalition began a controversial program to recruit Iraqi Sunnis (often former insurgents) for the formation of "Guardian" militias. These Guardian militias are intended to support and secure various Sunni neighborhoods against the Islamists.[194]
Tensions with Iran
In 2007, tensions increased greatly between Iran and Iraqi Kurdistan due to the latter's giving sanctuary to the militant Kurdish secessionist group Party for a Free Life in Kurdistan (PEJAK). According to reports, Iran had been shelling PEJAK positions in Iraqi Kurdistan since 16 August. These tensions further increased with an alleged border incursion on 23 August by Iranian troops who attacked several Kurdish villages killing an unknown number of civilians and militants.[195]
Coalition forces also began to target alleged Iranian Quds force operatives in Iraq, either arresting or killing suspected members. The Bush administration and coalition leaders began to publicly state that Iran was supplying weapons, particularly EFP devices, to Iraqi insurgents and militias although to date have failed to provide any proof for these allegations. Further sanctions on Iranian organizations were also announced by the Bush administration in the autumn of 2007. On 21 November 2007, Lieutenant General James Dubik, who is in charge of training Iraqi security forces, praised Iran for its "contribution to the reduction of violence" in Iraq by upholding its pledge to stop the flow of weapons, explosives, and training of extremists in Iraq.[196]
Tensions with Turkey
Border incursions by PKK militants based in Northern Iraq have continued to harass Turkish forces, with casualties on both sides. In the fall of 2007, the Turkish military stated their right to cross the Iraqi Kurdistan border in "hot pursuit" of PKK militants and began shelling Kurdish areas in Iraq and attacking PKK bases in the Mount Cudi region with aircraft.[197][198] The Turkish parliament approved a resolution permitting the military to pursue the PKK in Iraqi Kurdistan.[199] In November, Turkish gunships attacked parts of northern Iraq in the first such attack by Turkish aircraft since the border tensions escalated.[200] Another series of attacks in mid-December hit PKK targets in the Qandil, Zap, Avashin and Hakurk regions. The latest series of attacks involved at least 50 aircraft and artillery and Kurdish officials reported one civilian killed and two wounded.[201]
Additionally, weapons that were given to Iraqi security forces by the US military were being recovered by authorities in Turkey after being used by PKK in that state.[202]
Blackwater private security controversy
On 17 September 2007, the Iraqi government announced that it was revoking the license of the US security firm Blackwater USA over the firm's involvement in the killing of eight civilians, including a woman and an infant,[203] in a firefight that followed a car bomb explosion near a State Department motorcade.
2008: Civil war continues

Throughout 2008, US officials and independent think tanks began to point to improvements in the security situation, as measured by key statistics. According to the US Defense Department, in December 2008 the "overall level of violence" in the country had dropped 80% since before the surge began in January 2007, and the country's murder rate had dropped to prewar levels. They also pointed out that the casualty figure for US forces in 2008 was 314 against a figure of 904 in 2007.[204]
According to the Brookings Institution, Iraqi civilian fatalities numbered 490 in November 2008 as against 3,500 in January 2007, whereas attacks against the coalition numbered somewhere between 200 and 300 per week in the latter half of 2008, as opposed to a peak of nearly 1,600 in summer 2007. The number of Iraqi security forces killed was under 100 per month in the second half of 2008, from a high of 200 to 300 in the summer of 2007.[205]
Meanwhile, the proficiency of the Iraqi military increased as it launched a spring offensive against Shia militias, which Prime Minister Nouri al-Maliki had previously been criticized for allowing to operate. This began with a March operation against the Mahdi Army in Basra, which led to fighting in Shia areas up and down the country, especially in the Sadr City district of Baghdad. By October, the British officer in charge of Basra said that since the operation, the town had become "secure" and had a murder rate comparable to Manchester in England.[206] The US military also said there had been a decrease of about a quarter in the quantity of Iranian-made explosives found in Iraq in 2008, possibly indicating a change in Iranian policy.[207]
Progress in Sunni areas continued after members of the Awakening movement were transferred from US military to Iraqi control.[208] In May, the Iraqi army – backed by coalition support – launched an offensive in Mosul, the last major Iraqi stronghold of al-Qaeda. Despite detaining thousands of individuals, the offensive failed to lead to major long-term security improvements in Mosul. At the end of the year, the city remained a major flashpoint.[209][210]
In the regional dimension, the ongoing conflict between Turkey and PKK[211][212][213] intensified on 21 February, when Turkey launched a ground attack into the Quandeel Mountains of Northern Iraq. In the nine-day-long operation, around 10,000 Turkish troops advanced up to 25 km into Northern Iraq. This was the first substantial ground incursion by Turkish forces since 1995.[214][215]
Shortly after the incursion began, both the Iraqi cabinet and the Kurdistan regional government condemned Turkey's actions and called for the immediate withdrawal of Turkish troops from the region.[216] Turkish troops withdrew on 29 February.[217] The fate of the Kurds and the future of the ethnically diverse city of Kirkuk remained a contentious issue in Iraqi politics.
US military officials met these trends with cautious optimism as they approached what they described as the "transition" embodied in the US–Iraq Status of Forces Agreement, which was negotiated throughout 2008.[204] The commander of the coalition, US General Raymond T. Odierno, noted that "in military terms, transitions are the most dangerous time" in December 2008.[204]
Spring offensives on Shiite militias

At the end of March, the Iraqi Army, with Coalition air support, launched an offensive, dubbed "Charge of the Knights", in Basra to secure the area from militias. This was the first major operation where the Iraqi Army did not have direct combat support from conventional coalition ground troops. The offensive was opposed by the Mahdi Army, one of the militias, which controlled much of the region.[218][219] Fighting quickly spread to other parts of Iraq: including Sadr City, Al Kut, Al Hillah and others. During the fighting Iraqi forces met stiff resistance from militiamen in Basra to the point that the Iraqi military offensive slowed to a crawl, with the high attrition rates finally forcing the Sadrists to the negotiating table.
Following intercession by the Iranian government, al‑Sadr ordered a ceasefire on 30 March 2008.[220] The militiamen kept their weapons.
By 12 May 2008, Basra "residents overwhelmingly reported a substantial improvement in their everyday lives" according to The New York Times. "Government forces have now taken over Islamic militants' headquarters and halted the death squads and 'vice enforcers' who attacked women, Christians, musicians, alcohol sellers and anyone suspected of collaborating with Westerners", according to the report; however, when asked how long it would take for lawlessness to resume if the Iraqi army left, one resident replied, "one day".[219]
In late April roadside bombings continued to rise from a low in January – from 114 bombings to more than 250, surpassing the May 2007 high.
Congressional testimony

Speaking before Congress on 8 April 2008, General David Petraeus urged delaying troop withdrawals, saying, "I've repeatedly noted that we haven't turned any corners, we haven't seen any lights at the end of the tunnel," referencing the comments of then-President Bush and former Vietnam-era General William Westmoreland.[221] When asked by the Senate if reasonable people could disagree on the way forward, Petraeus said, "We fight for the right of people to have other opinions."[222]
Upon questioning by then Senate committee chair Joe Biden, Ambassador Crocker admitted that Al‑Qaeda in Iraq was less important than the Al Qaeda organization led by Osama bin Laden along the Afghan-Pakistani border.[223] Lawmakers from both parties complained that US taxpayers are carrying Iraq's burden as it earns billions of dollars in oil revenues.
Iraqi security forces rearm
Iraq became one of the top purchasers of US military equipment with their army trading its AK‑47 assault rifles for the US M‑16 and M‑4 rifles, among other equipment.[224] In 2008 alone, Iraq accounted for more than $12.5 billion of the $34 billion US weapon sales to foreign countries (not including the potential F-16 fighter planes.).[225]
Iraq sought 36 F‑16s, the most sophisticated weapons system Iraq has attempted to purchase. The Pentagon notified Congress that it had approved the sale of 24 American attack helicopters to Iraq, valued at as much as $2.4 billion. Including the helicopters, Iraq announced plans to purchase at least $10 billion in US tanks and armored vehicles, transport planes, and other battlefield equipment and services. Over the summer, the Defense Department announced that the Iraqi government wanted to order more than 400 armored vehicles and other equipment worth up to $3 billion, and six C-130J transport planes, worth up to $1.5 billion.[226][227] From 2005 to 2008, the United States had completed approximately $20 billion in arms sales agreements with Iraq.[228]
Status of forces agreement
The US–Iraq Status of Forces Agreement was approved by the Iraqi government on 4 December 2008.[229] It established that US combat forces would withdraw from Iraqi cities by 30 June 2009, and that all US forces would be completely out of Iraq by 31 December 2011. The pact was subject to possible negotiations which could have delayed withdrawal and a referendum scheduled for mid-2009 in Iraq, which might have required all US forces to completely leave by the middle of 2010.[230][231] The pact required criminal charges for holding prisoners over 24 hours, and required a warrant for searches of homes and buildings that are not related to combat.[232]

US contractors working for US forces were to be subject to Iraqi criminal law, while contractors working for the State Department and other US agencies may retain their immunity. If US forces commit still undecided "major premeditated felonies" while off-duty and off-base, they will be subject to the still undecided procedures laid out by a joint US‑Iraq committee if the United States certifies the forces were off-duty.[233][234][235][236]
Some Americans have discussed "loopholes"[237] and some Iraqis have said they believe parts of the pact remain a "mystery".[238] US Secretary of Defense Robert Gates predicted that after 2011 he expected to see "perhaps several tens of thousands of American troops" as part of a residual force in Iraq.[239]
Several groups of Iraqis protested the passing of the SOFA accord[240][241][242] as prolonging and legitimizing the occupation. Tens of thousands of Iraqis burned an effigy of George W. Bush in a central Baghdad square where US troops five years previously organized a tearing down of a statue of Saddam Hussein.[117][238][243] Some Iraqis expressed skeptical optimism that the US would completely end its presence by 2011.[244] On 4 December 2008, Iraq's presidential council approved the security pact.[229]
A representative of Grand Ayatollah Ali Husseini al‑Sistani expressed concern with the ratified version of the pact and noted that the government of Iraq has no authority to control the transfer of occupier forces into and out of Iraq, no control of shipments and that the pact grants the occupiers immunity from prosecution in Iraqi courts. He said that Iraqi rule in the country is not complete while the occupiers are present, but that ultimately the Iraqi people would judge the pact in a referendum.[243] Thousands of Iraqis have gathered weekly after Friday prayers and shouted anti‑US and anti-Israeli slogans protesting the security pact between Baghdad and Washington. A protester said that despite the approval of the Interim Security pact, the Iraqi people would break it in a referendum next year.[245]
2009: Coalition redeployment
Transfer of the Green Zone

On 1 January 2009, the United States handed control of the Green Zone and Saddam Hussein's presidential palace to the Iraqi government in a ceremonial move described by the country's prime minister as a restoration of Iraq's sovereignty. Iraqi Prime Minister Nouri al-Maliki said he would propose 1 January be declared national "Sovereignty Day". "This palace is the symbol of Iraqi sovereignty and by restoring it, a real message is directed to all Iraqi people that Iraqi sovereignty has returned to its natural status", al‑Maliki said.[citation needed]
The US military attributed a decline in reported civilian deaths to several factors including the US‑led "troop surge", the growth of US-funded Awakening Councils, and Shiite cleric Muqtada al-Sadr's call for his militia to abide by a cease fire.[246]
Provincial elections
On 31 January, Iraq held provincial elections.[247] Provincial candidates and those close to them faced some political assassinations and attempted assassinations, and there was also some other violence related to the election.[248][249][250][251]
Iraqi voter turnout failed to meet the original expectations which were set and was the lowest on record in Iraq,[252] but US Ambassador Ryan Crocker characterized the turnout as "large".[253] Of those who turned out to vote, some groups complained of disenfranchisement and fraud.[252][254][255] After the post-election curfew was lifted, some groups made threats about what would happen if they were unhappy with the results.[256]
Exit strategy announcement
On 27 February, United States President Barack Obama gave a speech at Marine Corps Base Camp Lejeune in the US state of North Carolina announcing that the US combat mission in Iraq would end by 31 August 2010. A "transitional force" of up to 50,000 troops tasked with training the Iraqi Security Forces, conducting counterterrorism operations, and providing general support may remain until the end of 2011, the president added. However, the insurgency in 2011 and the rise of ISIL in 2014 caused the war to continue.[257]
The day before Obama's speech, Prime Minister of Iraq Nouri al‑Maliki said at a press conference that the government of Iraq had "no worries" over the impending departure of US forces and expressed confidence in the ability of the Iraqi Security Forces and police to maintain order without US military support.[258]
Sixth anniversary protests
On 9 April, the 6th anniversary of Baghdad's fall to coalition forces, tens of thousands of Iraqis thronged Baghdad to mark the anniversary and demand the immediate departure of coalition forces. The crowds of Iraqis stretched from the Sadr City slum in northeast Baghdad to the square around 5 km (3.1 mi) away, where protesters burned an effigy featuring the face of US President George W. Bush.[259] There were also Sunni Muslims in the crowd. Police said many Sunnis, including prominent leaders such as a founding sheikh from the Sons of Iraq, took part.[260]
Coalition forces withdraw
On 30 April, the United Kingdom formally ended combat operations. Prime Minister Gordon Brown characterized the operation in Iraq as a "success story" because of UK troops' efforts. Britain handed control of Basra to the United States Armed Forces.[261]
The withdrawal of US forces began at the end of June, with 38 bases to be handed over to Iraqi forces. On 29 June 2009, US forces withdrew from Baghdad. On 30 November 2009, Iraqi Interior Ministry officials reported that the civilian death toll in Iraq fell to its lowest level in November since the 2003 invasion.[262]
On 28 July, Australia withdrew its combat forces as the Australian military presence in Iraq ended, per an agreement with the Iraqi government.
Iraq awards oil contracts

On 30 June and 11 December 2009, the Iraqi ministry of oil awarded contracts to international oil companies for some of Iraq's many oil fields. The winning oil companies entered joint ventures with the Iraqi ministry of oil, and the terms of the awarded contracts included extraction of oil for a fixed fee of approximately $1.40 per barrel.[263][264][265] The fees will only be paid once a production threshold set by the Iraqi ministry of oil is reached.
2010: US drawdown and Operation New Dawn
On 17 February 2010, US Secretary of Defense Robert Gates announced that as of 1 September, the name "Operation Iraqi Freedom" would be replaced by "Operation New Dawn".[266]
On 18 April, US and Iraqi forces killed Abu Ayyub al-Masri the leader of al-Qaeda in Iraq in a joint American and Iraqi operation near Tikrit, Iraq.[267] The coalition forces believed al-Masri to be wearing a suicide vest and proceeded cautiously. After the lengthy exchange of fire and bombing of the house, the Iraqi troops stormed inside and found two women still alive, one of whom was al-Masri's wife, and four dead men, identified as al-Masri, Abu Abdullah al-Rashid al-Baghdadi, an assistant to al-Masri, and al-Baghdadi's son. A suicide vest was indeed found on al-Masri's corpse, as the Iraqi Army subsequently stated.[268] Iraqi Prime Minister Nouri al-Maliki announced the killings of Abu Omar al-Baghdadi and Abu Ayyub al-Masri at a news conference in Baghdad and showed reporters photographs of their bloody corpses. "The attack was carried out by ground forces which surrounded the house, and also through the use of missiles," Maliki said. "During the operation computers were seized with e-mails and messages to the two biggest terrorists, Osama bin Laden and [his deputy] Ayman al-Zawahiri", Maliki added. US forces commander Gen. Raymond Odierno praised the operation. "The death of these terrorists is potentially the most significant blow to al‑Qaeda in Iraq since the beginning of the insurgency", he said. "There is still work to do but this is a significant step forward in ridding Iraq of terrorists."
US Vice President Joe Biden stated that the deaths of the top two al‑Qaeda figures in Iraq are "potentially devastating" blows to the terror network there and proof that Iraqi security forces are gaining ground.[269]
On 20 June, Iraq's Central Bank was bombed in an attack that left 15 people dead and brought much of downtown Baghdad to a standstill. The attack was claimed to have been carried out by the Islamic State of Iraq. This attack was followed by another attack on Iraq's Bank of Trade building that killed 26 and wounded 52 people.[270]

In late August 2010, insurgents conducted a major attack with at least 12 car bombs simultaneously detonating from Mosul to Basra and killing at least 51. These attacks coincided with the US plans for a withdrawal of combat troops.[271]
From the end of August 2010, the United States attempted to dramatically cut its combat role in Iraq, with the withdrawal of all US ground forces designated for active combat operations. The last US combat brigades departed Iraq in the early morning of 19 August. Convoys of US troops had been moving out of Iraq to Kuwait for several days, and NBC News broadcast live from Iraq as the last convoy crossed the border. While all combat brigades left the country, an additional 50,000 personnel (including Advise and Assist Brigades) remained in the country to provide support for the Iraqi military.[272][273] These troops were required to leave Iraq by 31 December 2011 under an agreement between the US and Iraqi governments.[274]
The desire to step back from an active counter-insurgency role did not however mean that the Advise and Assist Brigades and other remaining US forces would not be caught up in combat. A standards memo from the Associated Press reiterated "combat in Iraq is not over, and we should not uncritically repeat suggestions that it is, even if they come from senior officials".[275]
State Department spokesman P. J. Crowley stated "... we are not ending our work in Iraq, We have a long-term commitment to Iraq."[276] On 31 August, from the Oval Office, Barack Obama announced his intent to end the combat mission in Iraq. In his address, he covered the role of the United States' soft power, the effect the war had on the United States economy, and the legacy of the Afghanistan and Iraq wars.[277]
On the same day in Iraq, at a ceremony at one of Saddam Hussein's former residences at Al-Faw Palace in Baghdad, a number of US dignitaries spoke in a ceremony for television cameras, avoiding overtones of the triumphalism present in US announcements made earlier in the war. Vice President Joe Biden expressed concerns regarding the ongoing lack of progress in forming a new Iraqi government, saying of the Iraqi people that "they expect a government that reflects the results of the votes they cast". Gen. Ray Odierno stated that the new era "in no way signals the end of our commitment to the people of Iraq". Speaking in Ramadi earlier in the day, Gates said that US forces "have accomplished something really quite extraordinary here, [but] how it all weighs in the balance over time I think remains to be seen". When asked by reporters if the seven-year war was worth doing, Gates commented that "It really requires a historian's perspective in terms of what happens here in the long run". He noted the Iraq War "will always be clouded by how it began" regarding Saddam Hussein's supposed weapons of mass destruction, which were never confirmed to have existed. Gates continued, "This is one of the reasons that this war remains so controversial at home".[278] On the same day Gen. Ray Odierno was replaced by Lloyd Austin as Commander of US forces in Iraq.

On 7 September, two US troops were killed and nine wounded in an incident at an Iraqi military base. The incident is under investigation by Iraqi and US forces, but it is believed that an Iraqi soldier opened fire on US forces.[279]
On 8 September, the US Army announced the arrival in Iraq of the first specifically designated Advise and Assist Brigade, the 3d Armored Cavalry Regiment. It was announced that the unit would assume responsibilities in five southern governorates.[280] From 10 to 13 September, Second Advise and Assist Brigade, 25th Infantry Division fought Iraqi insurgents near Diyala.
According to reports from Iraq, hundreds of members of the Sunni Awakening Councils may have switched allegiance back to the Iraqi insurgency or al-Qaeda.[281]
In October, WikiLeaks disclosed 391,832 classified US military documents on the Iraq War.[282][283][284] Approximately, 58 people were killed with another 40 wounded in an attack on the Sayidat al‑Nejat church, a Chaldean Catholic church in Baghdad. Responsibility for the attack was claimed by the Islamic State in Iraq organization.[285]
Coordinated attacks in primarily Shia areas struck throughout Baghdad on 2 November, killing approximately 113 and wounding 250 with around 17 bombs.[286]
Iraqi arms purchases

As US forces departed the country, the Iraq Defense Ministry solidified plans to purchase advanced military equipment from the United States. Plans in 2010 called for $13 billion of purchases, to include 140 M1 Abrams main battle tanks.[287] In addition to the $13 billion purchase, the Iraqis also requested 18 F-16 Fighting Falcons as part of a $4.2 billion program that also included aircraft training and maintenance, AIM‑9 Sidewinder air-to-air missiles, laser-guided bombs and reconnaissance equipment.[288] All Abrams tanks were delivered by the end of 2011,[289] but the first F-16s did not arrive in Iraq until 2015, due to concerns that the Islamic State might overrun Balad Air Base.[290]
The Iraqi Navy also purchased 12 US‑built Swift-class patrol boats, at a cost of $20 million each. Delivery was completed in 2013.[291] The vessels are used to protect the oil terminals at Basra and Khor al-Amiya.[288] Two US‑built offshore support vessels, each costing $70 million, were delivered in 2011.[292]
The UN lifts restrictions on Iraq
In a move to legitimize the existing Iraqi government, the United Nations lifted the Saddam Hussein-era UN restrictions on Iraq. These included allowing Iraq to have a civilian nuclear program, permitting the participation of Iraq in international nuclear and chemical weapons treaties, as well as returning control of Iraq's oil and gas revenue to the government and ending the Oil-for-Food Programme.[293]
2011: US withdrawal
Muqtada al-Sadr returned to Iraq in the holy city of Najaf to lead the Sadrist movement after being in exile since 2007.[294]
On 15 January 2011, three US troops were killed in Iraq. One of the troops was killed on a military operation in central Iraq, while the other two troops were deliberately shot by one or two Iraqi soldiers during a training exercise.[295]
On 6 June, five US troops were killed in an apparent rocket attack on JSS Loyalty.[296] A sixth soldier, who was wounded in the attack, died 10 days later of his wounds.[297]
On 13 June 2011, two US troops were killed in an IED attack located in Wasit Governorate.[298]

On 26 June 2011, a US soldier was killed.[299] Sergeant Brent McBride was sentenced to four years, two months for his involvement in the death.[300]
On 29 June, three US troops were killed in a rocket attack on a US base located near the border with Iran. It was speculated that the militant group responsible for the attack was the same one which attacked JSS Loyalty just over three weeks before.[301] With the three deaths, June 2011, became the bloodiest month in Iraq for the US military since June 2009, with 15 US soldiers killed, only one of them outside combat.[302]
On 7 July, two US troops were killed and one seriously injured in an IED attack at Victory Base Complex outside Baghdad. They were members of the 145th Brigade Support Battalion, 116th Cavalry Heavy Brigade Combat Team, an Idaho Army National Guard unit base in Post Falls, Idaho. Spc. Nathan R. Beyers, 24, and Spc. Nicholas W. Newby, 20, were killed in the attack, Staff Sgt. Jazon Rzepa, 30, was seriously injured.[303]
In September, Iraq signed a contract to buy 18 Lockheed Martin F-16 warplanes, becoming the 26th nation to operate the F-16. Because of windfall profits from oil, the Iraqi government is planning to double this originally planned 18, to 36 F-16s. Iraq is relying on the US military for air support as it rebuilds its forces and battles a stubborn Islamist insurgency.[304]
With the collapse of the discussions about extending the stay of any US troops beyond 2011, where they would not be granted any immunity from the Iraqi government, on 21 October 2011, President Obama announced at a White House press conference that all remaining US troops and trainers would leave Iraq by the end of the year as previously scheduled, bringing the US mission in Iraq to an end.[305][306][307][308][309][310] The last American soldier to die in Iraq before the withdrawal, SPC. David Hickman, was killed by a roadside bomb in Baghdad on 14 November.[311]
In November 2011, the US Senate voted down a resolution to formally end the war by bringing its authorization by Congress to an end.[312]

On 15 December, an American military ceremony was held in Baghdad putting a formal end to the US mission in Iraq.[313]
The last US combat troops withdrew from Iraq on 18 December 2011, although the US embassy and consulates continue to maintain a staff of more than 20,000 including 100+ military personnel within the Office of Security Cooperation-Iraq (OSC-I),[314] US Marine Embassy Guards and between 4,000 and 5,000 private military contractors.[315][316] The next day, Iraqi officials issued an arrest warrant for the Sunni Vice-President Tariq al-Hashimi. He has been accused of involvement in assassinations and fled to the Kurdish part of Iraq.[317]
Aftermath
Emerging conflict and insurgency

The invasion and occupation led to sectarian violence, which caused widespread displacement among Iraqi civilians. Since the beginning of the war, the first parliamentary elections were held in 2005 which brought greater representation and autonomy to Iraqi Kurds. By 2007 the Iraqi Red Crescent estimated 2.3 million Iraqis were internally displaced, with an estimated 2 million Iraqis fleeing to neighboring countries, mostly to Syria and Jordan.[318]
Sectarian violence continued in the first half of 2013. At least 56 people died in April when a Sunni protest in Hawija was interrupted by a government-supported helicopter raid and a series of violent incidents occurred in May. On 20 May 2013, at least 95 people died in a wave of car bomb attacks that was preceded by a car bombing on 15 May that led to 33 deaths; also, on 18 May 76 people were killed in the Sunni areas of Baghdad. Some experts have stated that Iraq could return to the brutal sectarian conflict of 2006.[319][320]
On 22 July 2013, at least five hundred convicts, most of whom were senior members of al-Qaida who had received death sentences, were freed from Abu Ghraib jail in an insurgent attack, which began with a suicide bomb attack on the prison gates.[321] James F. Jeffrey, the United States ambassador in Baghdad when the last American troops exited, said the assault and resulting escape "will provide seasoned leadership and a morale boost to Al Qaeda and its allies in both Iraq and Syria ... it is likely to have an electrifying impact on the Sunni population in Iraq, which has been sitting on the fence."[322]
By mid-2014 Iraq was in chaos with a new government yet to be formed following national elections, and the insurgency reaching new heights. In early June 2014 the Islamic State in Iraq and the Levant (ISIL) took over the cities of Mosul and Tikrit and said it was ready to march on Baghdad, while Iraqi Kurdish forces took control of key military installations in the major oil city of Kirkuk. The al-Qaida breakaway group formally declared the creation of an Islamic state on 29 June 2014, in the territory under its control.[323]
Prime Minister Nouri al-Maliki unsuccessfully asked his parliament to declare a state of emergency that would give him increased powers.[324] On 14 August 2014, Prime Minister Nouri al-Maliki succumbed to pressure at home and abroad to step down. This paved the way for Haidar al-Abadi to take over on 19 August 2014.
In September 2014, President Obama acknowledged that the US underestimated the rise of the Islamic State and overestimated the Iraqi military's ability to fight ISIL.[325] Obama announced the return of US forces, in the form of aerial support, in an effort to halt the advance of ISIL forces, render humanitarian aid to stranded refugees and stabilize the political situation.[326]
A civil war between ISIL and the central government continued for the next three years. Following the election of Donald Trump, the United States intensified its campaign against the Islamic State by January 2017.[327] Defense Secretary Jim Mattis said a tactical shift to surrounding Islamic State strongholds in Mosul, Iraq, and Raqqa, Syria, was devised not only to "annihilate" ISIL fighters hunkered down there, but also to prevent them from returning to their home nations in Europe, Africa, and the Middle East. In 2017, US-backed Kurdish forces captured Raqqa, which had served as the ISIL capital.[328] The Iraqi government declared victory against ISIL in December 2017.[329] By 2018, violence in Iraq was at its lowest level in ten years. This was greatly a result of the defeat of ISIL forces and the subsequent calming-down of the insurgency.[330]
In January 2020, after the assassination of Qasem Soleimani, the Iraqi parliament voted for all foreign troops to leave the country. This would end its standing agreement with the United States to station 5,200 soldiers in Iraq. Then-President Trump objected to withdrawing troops and threatened Iraq with sanctions over this decision.[331] In 2023, Iraqi Prime Minister Mohammed Shia' Al Sudani indicated his support for an indefinite U.S. military presence in Iraq.[332]
Casualties
Casualty estimates

For coalition death totals see the infobox at the top right. See also Casualties of the Iraq War, which has casualty numbers for coalition nations, contractors, non-Iraqi civilians, journalists, media helpers, aid workers, and the wounded. Casualty figures, especially Iraqi ones, are highly disputed.
There have been several attempts by the media, coalition governments and others to estimate the Iraqi casualties. The table below summarizes some of these estimates and methods.
| Source | Iraqi casualties | March 2003 to ... |
|---|---|---|
| Iraq Family Health Survey | 151,000 violent deaths | June 2006 |
| Lancet survey | 601,027 violent deaths out of 654,965 excess deaths | June 2006 |
| PLOS Medicine Study | 460,000 excess deaths including 132,000 violent deaths from the conflict[42] | June 2011 |
| Opinion Research Business survey | 1,033,000 violent deaths from the conflict | August 2007 |
| Iraqi Health Ministry | 87,215 violent deaths per death certificates issued Deaths prior to January 2005 unrecorded Ministry estimates up to 20% more deaths are undocumented. |
January 2005 to February 2009 |
| Associated Press | 110,600 violent deaths Health Ministry death certificates plus AP estimate of casualties for 2003–04 |
April 2009 |
| Iraq Body Count | 105,052–114,731 violent civilian deaths compiled from commercial news media, NGO and official reports Over 162,000 civilian and combatant deaths |
January 2012 |
| WikiLeaks. Classified Iraq War Logs | 109,032 violent deaths including 66,081 civilian deaths | January 2004 to December 2009 |
Impacts
Financial cost

In March 2013, the total cost of the Iraq War to date was estimated at $1.7 trillion by the Watson Institute for International and Public Affairs at Brown University.[333] Some argue that the total cost of the war to the US economy will range from $3 trillion[334] to $6 trillion,[335] including interest rates, by 2053, as described in the Watson Institute's report. The upper ranges of these estimates include long-term veterans costs and economic impacts. For example, Harvard's public finance expert Linda J. Bilmes has estimated that the long-term cost of providing disability compensation and medical care to US troops injured in the Iraq conflict will reach nearly $1 trillion over the next 40 years,[336] and that the war in Iraq diverted resources from the war in Afghanistan, led to rising oil prices, increased the federal debt, and contributed to a global financial crisis.[337]
A CNN report noted that the United States–led interim government, the Coalition Provisional Authority lasting until 2004 in Iraq had lost $8.8 billion in the Development Fund for Iraq. In June 2011, it was reported by CBS News that $6 billion in neatly packaged blocks of $100 bills was air-lifted into Iraq by the George W. Bush administration, which flew it into Baghdad aboard C‑130 military cargo planes. In total, the Times says $12 billion in cash was flown into Iraq in 21 separate flights by May 2004, all of which has disappeared. An inspector general's report mentioned that "'Severe inefficiencies and poor management' by the Coalition Provisional Authority would leave no guarantee that the money was properly used", said Stuart W. Bowen, Jr., director of the Office of the Special Inspector General for Iraq Reconstruction. "The CPA did not establish or implement sufficient managerial, financial, and contractual controls to ensure that funds were used in a transparent manner."[338] Bowen told the Times the missing money may represent "the largest theft of funds in national history."[339]
Reparations
By 2013, some human rights groups in both Iraq and the U.S. had begun campaigning for reparations from the US for the devastation and health effects suffered by Iraqis during the war.[340][341]
Economic recession in 2021
As of 2021, Iraq had fallen into an economic depression, caused by the ongoing COVID pandemic and falling oil and gas prices, which economists described as the country's biggest financial threat since the rule of Saddam Hussein. Iraq suffered from currency devaluation in 2021 for the first time in decades and was unable to import crucial products, including medicines and food, and had a lack of foreign currency to pay off the national debt.[342]
Humanitarian crisis
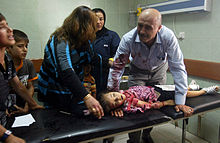
According to a 2007 Oxfam report, the child malnutrition rate had risen to 28%, and the rate of people without access to clean drinking water had risen to 70%.[343] In 2007, Nasser Muhssin, a researcher on family and children's affairs affiliated to the University of Baghdad claimed that 60–70% of Iraqi children suffered from psychological problems.[344] A 2007 cholera outbreak in northern Iraq was thought to be the result of poor water quality.[345] As many as half of Iraqi doctors left the country between 2003 and 2006.[346]
By the end of 2015, according to the Office of the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees, 4.4 million Iraqis had been internally displaced.[347] The population of Iraqi Christians dropped dramatically during the war, from 1.5 million in 2003 to 500,000 in 2015,[348] and perhaps only 275,000 in 2016.
The Foreign Policy Association reported that: "Perhaps the most perplexing component of the Iraq refugee crisis ... has been the inability for the United States to absorb more Iraqis following the 2003 invasion of the country. To date, the United States has granted around 84,000 Iraqis refugee status, of the more than two million global Iraqi refugees. By contrast, the United States granted asylum to more than 100,000 South Vietnamese refugees during the Vietnam War."[349][350][351]
Environmental impact
Oil pollution
The war has led to oil spills, which increased carbon emissions and contaminated the surrounding water resources. During the invasion period, the retreating Iraqi army damaged the oil infrastructure and destroyed more than 736 oil wells in southern Iraq, resulting in massive oil spills and the ignition of fires.[352] In 2003, more than 50 billion tonnes of carbon emissions were produced from burning oil fields and released into the atmosphere.[353] Also, over 130 million gallons of oil leaked into surrounding water resources, such as Sawa Lake.[354] Between 2003 and 2010, more than 5,000 birds from three species died around Sawa Lake.[354]
Radioactive contamination

The U.S.-led coalition used depleted uranium (DU) munitions during the war to pierce tank armour.[355] 1,000 to 2,000 tonnes (2,200,000 to 4,400,000 lb) of DU munitions were fired, which caused ammunition fragments containing radioactive material to spread across the country. According to a United Nations Environment Programme report, radioactive material contaminated air and soil; with the radioactive concentration found in Iraqi soil at 709.52 Bq in 2003 compared to 143.22 Bq in 2002.[356] The report states that high levels of radiation prevented plants, especially crop seeds, from sprouting; with about 22% (9.5 million ha) of the farmland in Iraq unable to grow barley.[354]
In addition, radiation contamination may have had harmful public health outcomes through poisoning and increased incidence of various cancers and birth defects.[356] Several studies have identified increased occurrence of deformities, cancers, and other serious health problems in areas where DU shells were used.[357] Some Iraqi doctors attributed these malformations to possible long-term effects of depleted uranium.[358] Studies disagree on whether DU ammunition has any measurable detrimental health effects.[359][356] According to research from the UK Atomic Energy Authority in 2005, the cancer rate had increased by 35% since 2003. As of 2013, 140,000 Iraqis were suffering from cancer, with between 7,000 and 8,000 new cases yearly.[356] According to a 2012 journal article by Al-Hadithi et al., existing studies and research evidence does not show a "clear increase in birth defects" or a "clear indication of a possible environmental exposure including depleted uranium". The article further states that "there is actually no substantial evidence that genetic defects can arise from parental exposure to DU in any circumstances."[360]
Ecosystem destruction

The war has also led to damage to ecosystems though pollution and physical destruction. Approximately 25,000 tons of bombs were dropped by the U.S. military during the war.[352] More than 250 chemical and armament factories were destroyed, which caused over 50,000 cubic meters of hazardous chemicals, such as fertilizer, and raw sewage to leak into water,[361] leading to surrounding freshwater ecosystem becoming polluted and species' habitat being impacted.[352] According to the World Wide Fund for Nature, 33 Iraqi wetlands, especially the Mesopotamian Marshland, have been contaminated by chemicals, which has caused 60 types of mammal species to lose their habitats, and more than 45 types of plants to become extinct.[354]
Impact on the Global War on Terrorism
Though explicitly stating that Iraq had "nothing" to do with 9/11,[362] erstwhile President George W. Bush consistently referred to the Iraq War as "the central front in the War on Terror", and argued that if the United States pulled out of Iraq, "terrorists will follow us here".[363][364][365] While other proponents of the war regularly echoed this assertion, as the conflict dragged on, members of the US Congress, the US public, and even US troops questioned the connection between Iraq and the fight against anti-US terrorism. In particular, a consensus developed among intelligence experts that the Iraq War actually increased terrorism. Counterterrorism expert Rohan Gunaratna frequently referred to the invasion of Iraq as a "fatal mistake".[366]
London's International Institute for Strategic Studies concluded in 2004 that the occupation of Iraq had become "a potent global recruitment pretext" for Mujahideen and that the invasion "galvanised" al-Qaeda and "perversely inspired insurgent violence" there.[367] The US National Intelligence Council concluded in a January 2005 report that the war in Iraq had become a breeding ground for a new generation of terrorists; David Low, the national intelligence officer for transnational threats, indicated that the report concluded that the war in Iraq provided terrorists with "a training ground, a recruitment ground, the opportunity for enhancing technical skills ... There is even, under the best scenario, over time, the likelihood that some of the jihadists who are not killed there will, in a sense, go home, wherever home is, and will, therefore, disperse to various other countries." The council's chairman Robert Hutchings said, "At the moment, Iraq is a magnet for international terrorist activity."[368] And the 2006 National Intelligence Estimate, which outlined the considered judgment of all 16 US intelligence agencies, held that "The Iraq conflict has become the 'cause célèbre' for jihadists, breeding a deep resentment of US involvement in the Muslim world and cultivating supporters for the global jihadist movement."[369]
A report by the Council on Foreign Relations, released on the 20th anniversary of the invasion analyzed the rationale to go to war and the subsequent decisions during the occupation. The report states that the "justification for going to war was based on scanty and deeply flawed intelligence" and that the invasion was an "error compounded by the absence of an agreed exit strategy and the decision to embark on a massive, open-ended nation-building project". The same report also ascertained that "the occupation authority's first acts were to disband the Iraqi army and the Ba'athist governing party, igniting what would become a lethal, long-running insurgency and eventually a multinational terrorist organization that took over most of the country".[370][56]
Geopolitical tensions
From a geopolitical perspective, the war in Iraq has been interpreted as weakening the West's moral high ground and hampering its ability to effectively counter Russia and China. With regard to the Russo-Ukrainian War, Russian foreign minister Sergey Lavrov said in March 2022 that the U.S. exerted similar pressures on Iraq in 2003, which the US invaded later for no reason other than "a vial of unidentified chemicals".[371] In March 2023, Tony Blair, former British prime minister rejected comparisons between Russia's war in Ukraine and the US-led invasion of Iraq, claiming that the Iraq War cannot be used as a justification by Russia to annex Russian-speaking zones in eastern Ukraine.[372]
Criticism


The Bush administration's rationale for the Iraq War has faced heavy criticism from an array of popular and official sources both inside and outside the United States,[374][375][308] with many US citizens finding many parallels with the Vietnam War.[376] For example, a former CIA officer described the Office of Special Plans as a group of ideologues who were dangerous to US national security and a threat to world peace, and stated that the group lied and manipulated intelligence to further its agenda of removing Saddam.[377] The Center for Public Integrity stated that the Bush administration made a total of 935 false statements between 2001 and 2003 about Iraq's alleged threat to the United States.[378]
Both proponents and opponents of the invasion have also criticized the prosecution of the war effort along with a number of other lines. Most significantly, critics have assailed the United States and its allies for not devoting enough troops to the mission, not adequately planning for post-invasion Iraq, and for permitting and perpetrating human rights abuses. As the war has progressed, critics have also railed against the high human and financial costs. In 2016, the United Kingdom published the Iraq Inquiry, a public inquiry which was broadly critical of the actions of the British government and military in making the case for the war, in tactics and in planning for the aftermath of the war.[379][380][381]
Criticisms include:
- Legality of the invasion[382][383][384][385][386]
- Human casualties[387][388][389][390]
- Human rights violations such as the Iraq prison abuse scandals
- Insufficient post-invasion plans, in particular inadequate troop levels (A RAND Corporation study stated that 500,000 troops would be required for success.)[391]
- Financial costs with approximately $612 billion spent as of 4/09 the CBO has estimated the total cost of the war in Iraq to the United States will be around $1.9 trillion.[392]
- Adverse effect on US-led global "war on terror"[393][394]
- Damage to US' traditional alliances and influence in the region.[395][396]
- Endangerment and ethnic cleansing of religious and ethnic minorities by insurgents[188][397][398][399][400]
- Disruption of Iraqi oil production and related energy security concerns (the price of oil quadrupled between 2002 and 2008).[401][402]
War crimes
Throughout the war, many human rights abuses and war crimes were committed.
By Coalition forces and private contractors

- Deaths of civilians as a result of bombing and missile strikes that fail to take feasible precautions with regards to civilians casualties.[403]
- Abu Ghraib torture and prisoner abuse by US Army personnel,[404] involving the detention of thousands of Iraqi people. Torture at Abu Ghraib included rape, sodomy and extensive sexual abuse, waterboarding, pouring phosphoric acid on detainees, sleep deprivation and physical beatings.
- Haditha massacre of 24 civilians by US soldiers.
- Widespread use of the incendiary munition white phosphorus such as during the battle of Fallujah. The documentary Fallujah, The Hidden Massacre, claimed that Iraqi civilians, including women and children, had died of burns caused by white phosphorus during the battle, however, US Department of Defense spokesman Lieutenant Colonel Barry Venable denied that this was true but confirmed to the BBC that US forces had used white phosphorus as an incendiary weapon there against enemy combatants.[405][406][407] The use of white phosphorus against civilian populations is banned by international legislation.[408]
- Mahmudiyah rape and killings, where US soldiers raped and killed 14-year old Abeer Qasim Humza. They also killed 3 of her relatives.[409][410]
- The torture and killing of prisoner of war, Iraqi Air Force commander, Abed Hamed Mowhoush.
- The killing of Baha Mousa while in British Army custody.
- Mukaradeeb wedding party massacre, where 42 civilians were allegedly killed by coalition airstrikes.[411]
- Planting weapons on noncombatant, unarmed Iraqis by three US Marines after killing them.[412][413] According to a report by The Nation, other similar acts have been witnessed by US soldiers.[414]
- Nisour Square massacre by Blackwater Security Consulting personnel.
- Allegations of beatings, electrocution, mock executions, and sexual assault by British troops were presented to the International Criminal Court (ICC) by Public Interest Lawyers (PIL) and the European Center for Constitutional and Human Rights (ECCHR) on 12 January 2014.[415]
By insurgent groups

- Killing over 12,000 Iraqis from January 2005 to June 2006, according to Iraqi Interior Minister Bayan Jabr, giving the first official count for the victims of bombings, ambushes and other deadly attacks.[416] The insurgents have also conducted numerous suicide attacks on the Iraqi civilian population, mostly targeting the majority Shia community.[417][418] An October 2005 report from Human Rights Watch examines the range of civilian attacks and their purported justification.[419]
- Attacks against civilians by sectarian death squads primarily during the Iraqi Civil War. Iraq Body Count project data shows that 33% of civilian deaths during the Iraq War resulted from execution after abduction or capture. These were overwhelmingly carried out by unknown actors including insurgents, sectarian militias and criminals.[420]
- Attacks on diplomats and diplomatic facilities including; the bombing of the UN headquarters in Baghdad in August 2003 killing the top UN representative in Iraq and 21 other UN staff members;[421] beheading several diplomats: two Algerian diplomatic envoys Ali Belaroussi and Azzedine Belkadi,[422] Egyptian diplomatic envoy al-Sherif,[423] and four Russian diplomats[424]
- The February 2006 bombing of the al-Askari Mosque, destroying one of the holiest Shiite shrines, killing over 165 worshipers and igniting sectarian strife and reprisal killings[425]
- The publicised killing of several contractors; Eugene Armstrong, Jack Hensley, Kenneth Bigley, Ivaylo Kepov and Georgi Lazov (Bulgarian truck drivers.)[426] Other non-military personnel murdered include: translator Kim Sun-il, Shosei Koda, Fabrizio Quattrocchi (Italian), charity worker Margaret Hassan, reconstruction engineer Nick Berg, photographer Salvatore Santoro (Italian)[427] and supply worker Seif Adnan Kanaan (Iraqi.) Four private armed contractors, Scott Helvenston, Jerko Zovko, Wesley Batalona and Michael Teague, were killed with grenades and small arms fire, their bodies dragged from their vehicles, beaten and set ablaze. Their burned corpses were then dragged through the streets before being hung over a bridge crossing the Euphrates.[428]
- Torture or killing of members of the New Iraqi Army,[429] and assassination of civilians associated with the Coalition Provisional Authority, such as Fern Holland, or the Iraqi Governing Council, such as Aqila al-Hashimi and Ezzedine Salim, or other foreign civilians, such as those from Kenya[430]
By Post-invasion Iraqi Government
The post-invasion Iraqi government used torture against detainees, including children. Some techniques of torture used included beatings, electric shocks, prolonged hanging by the wrists, food and water deprivation, and blindfolding for multiple days.[431] Iraqi police from the Interior Ministry were accused of forming Death Squads and committing numerous massacres of Sunni Arabs.[432] Many of these human rights abuses were carried out by Iraqi government-sponsored Shi'ite militias.[433]
Public opinion on the war
International opinion

In a March 2003 Gallup poll, the day after the invasion, 76% of Americans had approved of military action against Iraq.[434] In a March 2003 YouGov poll, 54% of Britons supported the military action against Iraq.[435] A remarkable aspect was the support for invasion expressed by many left-wing intellectuals such as Christopher Hitchens, Paul Berman, Michael Walzer and Jean Bethke Elshtain.[436][437] In a February 2003 poll by the national public research institute CIS, 91% of Spaniards opposed any military intervention in Iraq.[438]
According to a January 2007 BBC World Service poll of more than 26,000 people in 25 countries, 73% of the global population disapproved of US handling of the Iraq War.[439] A September 2007 poll conducted by the BBC found that two-thirds of the world's population believed the US should withdraw its forces from Iraq.[440]
In 2006 it was found that majorities in the UK and Canada believed that the war in Iraq was "unjustified" and – in the UK – were critical of their government's support of US policies in Iraq.[441]
According to polls conducted by the Arab American Institute, four years after the invasion of Iraq, 83% of Egyptians had a negative view of the US role in Iraq; 68% of Saudi Arabians had a negative view; 96% of the Jordanian population had a negative view; 70% of the population of the United Arab Emirates and 76% of the Lebanese population also described their view as negative.[442] The Pew Global Attitudes Project reports that in 2006 majorities in the Netherlands, Germany, Jordan, France, Lebanon, Russia, China, Canada, Poland, Pakistan, Spain, Indonesia, Turkey, and Morocco believed the world was safer before the Iraq War and the toppling of Saddam, while pluralities in the United States and India believe the world is safer without Saddam Hussein.[443]
Iraqi opinion

Directly after the invasion, an NDTV poll of Baghdad residents reported a slight majority of respondents supported the US invasion.[444] Polls conducted between 2005 and 2007 showed 31–37% of Iraqis wanted US and other Coalition forces to withdraw once security was restored and that 26–35% wanted immediate withdrawal instead.[445][446][447] In 2006, a poll conducted on the Iraqi public revealed that 52% of the ones polled said Iraq was going in the right direction and 61% claimed it was worth ousting Saddam Hussein.[445] In a March 2007 BBC poll, 82% of Iraqis expressed a lack of confidence in coalition forces based in Iraq.[448] According to a 2009 poll conducted by the University of Maryland, 7 out of 10 Iraqis wanted US troops to withdraw within one year and also 78% felt that US military presence was "provoking more conflict than it is preventing".[449] Despite a majority having previously been opposed to the US presence, according to a poll conducted by the Asharq Research Centre, a private Iraqi company, 60% of Iraqis had believed it was "the wrong time" for a major withdrawal of American troops prior to the withdrawal in 2011, with 51% saying withdrawal would have a negative effect.[450][451]
Foreign involvement
Suicide bombers
According to studies, most of the suicide bombers in Iraq were foreigners, especially Saudis.[452][453][454]
Role of Iran
According to two unnamed US officials, the Pentagon is examining the possibility that the Karbala provincial headquarters raid, in which insurgents managed to infiltrate an American base, kill five US soldiers, wound three, and destroy three humvees before fleeing, was supported by Iranians. In a speech on 31 January 2007, Iraqi Prime Minister Nouri al-Maliki stated that Iran was supporting attacks against Coalition forces in Iraq[455] and some Iraqis suspect that the raid may have been perpetrated by the Quds Force in retaliation for the detention of five Iranian officials by US forces in the northern Iraqi city of Irbil on 11 January.[456][457] In 2014, the legacy of Iran's presence in Iraq after the invasion had been mixed with regard to the fight against regional terrorist groups. The U.S. occupation and subsequent regional instability had spawned the creation of the PMF (Popular Mobilization Forces), an Iranian militia that effectively fought the influence of emerging caliphates in the region.[458]
Later, a 1,300-page US Army Iraq War study, released in January 2019, concluded that "At the time of this project's completion in 2018, an emboldened and expansionist Iran appears to be the only victor" and that the outcome of the war triggered a "deep skepticism about foreign interventions" among America's public opinion.[386]
Role of Israel
Israel did not officially support or take part in the Iraq War. According to former State Department official Lawrence Wilkerson and former CIA agent and Iran expert Robert Baer, Israeli officials warned the Bush administration against invading Iraq, saying that it would destabilize the region and empower the much more dangerous regime in Iran.[459][460][461][462] However it was reported in the Washington Post that "Israel is urging United States' officials not to delay a military strike against Iraq's Saddam Hussein".[463] It was also reported in 2002 that Israeli intelligence provided Washington with alarming reports about Iraq's alleged program to develop weapons of mass destruction.[464]
According to former US undersecretary of defense Douglas Feith, Israeli officials did not push their American counterparts to initiate the war in Iraq. In an interview with Ynet, Feith stated that "what you heard from the Israelis was not any kind of advocacy of war with Iraq" and that "[w]hat you heard from Israeli officials in private discussions was that they were not really focused on Iraq... [t]hey were much more focused on Iran."[465]
At Washington's behest, Israel did not provide vocal support for the war, as the US government was concerned that Israeli support for or participation in the war would potentially alienate the Arab world. In January 2007, the Forward reported that sometime before March 2003, Israeli Prime Minister Ariel Sharon told Bush that Israel "would not push one way or the other" for or against an Iraq war. Sharon said that he believed that Iraq was a genuine threat to the Middle East and that Saddam had weapons of mass destruction, but explicitly warned Bush that if the US did go to war with Iraq that he should make sure to formulate a viable exit strategy, prepare a counterinsurgency strategy, and should not attempt to implant democracy in the Arab world. One of the sources who provided this information was Israeli Ambassador to the US Daniel Ayalon.[466]
Israel has also assisted the US military by sharing its expertise on counterinsurgency methods, such as utilizing drones and operating checkpoints.[467]
In 2003 the Israeli news magazine, the Ha'aretz, in its published story "White Man's Burden" reported that belief in the war against Iraq was disseminated by "a small group of 25 or 30 neoconservatives, almost all of them Jewish".[468]Role of Russia
The invasion of Iraq prompted a widespread wave of criticism from several world leaders, including Russian President Vladimir Putin.[469] Before and during the invasion of Iraq, the Russian government provided intelligence to Saddam Hussein about the location of US forces and their plans.[470]
See also
- Foreign interventions by the United States
- United States involvement in regime change
- Criticism of United States foreign policy
- Iran–Saudi Arabia proxy conflict
- Iraq–United States relations
- The Iraq War: A Historiography of Wikipedia Changelogs
- List of wars by death toll
- National Network to End the War Against Iraq
- United States military casualties of war
- Joint Special Operations Command Task Force in the Iraq War
Footnotes
- ^ disbanded in 2003
References
- ^ Graham, Bradley (7 April 2003). "U.S. Airlifts Iraqi Exile Force For Duties Near Nasiriyah". The Washington Post. Archived from the original on 8 August 2007. Retrieved 13 September 2009.
- ^ "A Timeline of Iraq War, Troop Levels". The Huffington Post.
- ^ https://sgp.fas.org/crs/mideast/RL31763.pdf [bare URL PDF]
- ^ "Deputy Assistant Secretary for International Programs Charlene Lamb's Remarks on Private Contractors in Iraq". US Department of State. 17 July 2009. Retrieved 23 October 2010.
- ^ International Institute for Strategic Studies (3 February 2010). Hackett, James (ed.). The Military Balance 2010. London: Routledge. ISBN 978-1-85743-557-3.
- ^ Rubin, Alissa J.; Nordland, Rod (29 March 2009). "Troops Arrest an Awakening Council Leader in Iraq, Setting Off Fighting". The New York Times. Retrieved 30 March 2010.
- ^ "The Kurdish peshmerga forces will not be integrated into the Iraqi army: Mahmoud Sangawi – Interview". Ekurd.net. 22 January 2010. Archived from the original on 2 April 2019. Retrieved 23 October 2010.
- ^ The Brookings Institution Iraq Index: Tracking Variables of Reconstruction & Security in Post-Saddam Iraq Archived 2 October 2007 at the Wayback Machine 1 October 2007
- ^ Pincus, Walter. "Violence in Iraq Called Increasingly Complex". The Washington Post, 17 November 2006.
- ^ 260 killed in 2003,[1] 15,196 killed from 2004 through 2009 (with the exceptions of May 2004 and March 2009),[2] 67 killed in March 2009,[3] 1,100 killed in 2010,[4] and 1,067 killed in 2011,[5] thus giving a total of 17,690 dead
- ^ "Iraq War" (PDF). US Department of State. Retrieved 18 November 2012.
- ^ The US DoD and the DMDC list 4,505 US fatalities during the Iraq War.[6][7] In addition to these, two service members were also previously confirmed by the DoD to have died while supporting operations in Iraq,[8][9] but have been excluded from the DoD and DMDC list. This brings the total of US fatalities in the Iraq War to 4,507.
- ^ "Fact Sheets | Operations Factsheets | Operations in Iraq: British Fatalities". Ministry of Defence of the United Kingdom. Archived from the original on 11 October 2009. Retrieved 17 October 2009.
- ^ "Operation Iraqi Freedom". iCasualties. Archived from the original on 21 March 2011. Retrieved 24 August 2010.
- ^ "POW and MIA in Iraq and Afghanistan Fast Facts". CNN. Retrieved 5 June 2014.; As of July 2012, seven American private contractors remain unaccounted for. Their names are: Jeffrey Ake, Aban Elias, Abbas Kareem Naama, Neenus Khoshaba, Bob Hamze, Dean Sadek and Hussain al-Zurufi. Healy, Jack, "With Withdrawal Looming, Trails Grow Cold For Americans Missing In Iraq", The New York Times, 22 May 2011, p. 6.
- ^ "Casualty" (PDF). Retrieved 29 June 2016.
- ^ 33 Ukrainians,[10] 31+ Italians,[11][12] 30 Bulgarians,[13][14] 20 Salvadorans,[15] 19 Georgians,[16] Archived 13 May 2011 at the Wayback Machine 18 Estonians,[citation needed] 14+ Poles,[17][18][19] 15 Spaniards,[20][21] Archived 2 April 2019 at the Wayback Machine [22][23] 10 Romanians,[24] 6 Australians,[25] 5 Albanians, 4 Kazakhs,[26] 3 Filipinos,[27] and 2 Thais,[28][29] for a total of 210+ wounded
- ^ a b Many official US tables at "Military Casualty Information" Archived 3 March 2011 at the Wayback Machine. See latest totals for injury, disease/other medical Archived 2 June 2011 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Casualties in Iraq".
- ^ a b iCasualties.org (was lunaville.org). Benicia, California. Patricia Kneisler, et al., "Iraq Coalition Casualties" Archived 21 March 2011 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ a b "Defence Internet Fact Sheets Operations in Iraq: British Casualties" Archived 14 November 2006 at the Wayback Machine. UK Ministry of Defense. Latest combined casualty and fatality tables Archived 4 October 2012 at the Wayback Machine.
- ^ "Global War on Terrorism – Operation Iraqi Freedom March 19, 2003 Through May 31, 2011 By Casualty Category Within Service" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2 June 2011. Retrieved 7 February 2016.
- ^ "Human Costs of U.S. Post-9/11 Wars: Direct War Deaths in Major War Zones | Figures | Costs of War".
- ^ a b "Office of Workers' Compensation Programs (OWCP) – Defense Base Act Case Summary by Nation". US Department of Labor. Retrieved 15 December 2011.
- ^ a b T. Christian Miller (23 September 2009). "US Government Private Contract Worker Deaths and Injuries". Projects.propublica.org. Archived from the original on 27 July 2011. Retrieved 23 October 2010.
- ^ 185 in Diyala from June 2007 to December 2007,[30] 4 in assassination of Abu Risha, 25 on 12 November 2007,[31] Archived 14 May 2013 at the Wayback Machine 528 in 2008,[32] Archived 10 December 2016 at the Wayback Machine 27 on 2 January 2009,[33] 13 on 16 November 2009,"Thirteen anti-Qaeda tribe members killed in Iraq – France 24". Archived from the original on 29 April 2011. Retrieved 14 February 2011. 15 in December 2009,[34] 100+ from April to June 2010,[35] [36] 52 on 18 July 2010,[37] [38] total of 1,002+ dead Archived 18 April 2009 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Moore, Solomon; Oppel, Richard A. (24 January 2008). "Attacks Imperil U.S.-Backed Militias in Iraq". The New York Times.
- ^ Greg Bruno. "Finding a Place for the 'Sons of Iraq'". Council on Foreign Relations. Archived from the original on 10 December 2016. Retrieved 26 December 2011.
- ^ Conetta, Carl (23 October 2003). "The Wages of War: Iraqi Combatant and Noncombatant Fatalities in the 2003 Conflict – Project on Defense Alternative Research Monograph #8". Project on Defense Alternatives (via Commonwealth Institute). Retrieved 2 September 2010.
- ^ "Jonathan Steele: Body counts". TheGuardian.com. 28 May 2003.
- ^ 597 killed in 2003,[39], 23,984 killed from 2004 through 2009 (with the exceptions of May 2004 and March 2009),[40] 652 killed in May 2004,[41] 45 killed in March 2009,[42] Archived 3 September 2009 at the Wayback Machine 676 killed in 2010,[43] and 590 killed in 2011,[44] thus giving a total of 26,544 dead
- ^ "4,000 fighters killed, 'al-Qaida in Iraq' tape says." The Guardian. 28 September 2006.
- ^ "Amnesty: Iraq holds up to 30,000 detainees without trial". CNN. 13 September 2010. Archived from the original on 23 October 2010. Retrieved 6 January 2011.
- ^ "Insurgent body count documents released." Archived 27 July 2020 at the Wayback Machine Stars and Stripes. 1 October 2007. Number of convictions not specified.
- ^ "Iraq Body Count". Retrieved 27 April 2014.
- ^ "Iraq War Logs: What the numbers reveal". Iraq Body Count. Retrieved 3 December 2010.
- ^ Kim Gamel (23 April 2009). "AP Impact: Secret tally has 87,215 Iraqis dead". Fox News. Retrieved 26 April 2014.
- ^ "Mortality after the 2003 invasion of Iraq: a cross-sectional cluster sample survey" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 7 September 2015. (242 KB). By Gilbert Burnham, Riyadh Lafta, Shannon Doocy, and Les Roberts. The Lancet, 11 October 2006
- ^ "The Human Cost of the War in Iraq: A Mortality Study, 2002–2006" (PDF). (603 KB). By Gilbert Burnham, Shannon Doocy, Elizabeth Dzeng, Riyadh Lafta, and Les Roberts. A supplement to the October 2006 Lancet study. It is also found here: "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 28 November 2007. Retrieved 9 May 2012.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) [45] - ^ "Iraq Family Health Survey" New England Journal of Medicine 31 January 2008
- ^ "Greenspan admits Iraq was about oil, as deaths put at 1.2m". the Guardian. 16 September 2007. Retrieved 12 July 2020.
- ^ a b Hagopian, Amy; Flaxman, Abraham D.; Takaro, Tim K.; Esa Al Shatari, Sahar A.; Rajaratnam, Julie; Becker, Stan; Levin-Rector, Alison; Galway, Lindsay; Hadi Al-Yasseri, Berq J.; Weiss, William M.; Murray, Christopher J.; Burnham, Gilbert; Mills, Edward J. (15 October 2013). "Mortality in Iraq Associated with the 2003–2011 War and Occupation: Findings from a National Cluster Sample Survey by the University Collaborative Iraq Mortality Study". PLOS Medicine. 10 (10): e1001533. doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.1001533. PMC 3797136. PMID 24143140.
- ^ Lewis, Paul; Times, Special To the New York (3 August 1990). "The Iraqi Invasion; U.N. Condemns the Invasion With Threat to Punish Iraq". The New York Times.
- ^ a b Zilinskas, Raymond A., "UNSCOM and the UNSCOM Experience in Iraq", Politics and the Life Sciences, Vol. 14, No. 2 (Aug. 1995), 230.
- ^ Robert Fisk (2007). The Great War for Civilisation: The Conquest of the Middle East. Knopf Doubleday Publishing Group. ISBN 978-0-307-42871-4. Digital copy, does not include page numbers.
- ^ Barton Gellman (2 March 1999). "U.S. Spied on Iraq Via U.N." Washington Post. Retrieved 9 November 2017.
- ^ "Iraq Liberation Act of 1998 (Enrolled as Agreed to or Passed by Both House and Senate)". Library of Congress. 31 October 1998. Archived from the original on 11 July 2008. Retrieved 25 May 2006.
- ^ "Resolution 687 (1991)". 8 April 1991. Archived from the original on 23 May 2006. Retrieved 25 May 2006.
- ^ William, Arkin (17 January 1999). "The Difference Was in the Details". The Washington Post. p. B1. Archived from the original on 9 September 2006. Retrieved 23 April 2007.
- ^ "Republican Platform 2000". CNN. Archived from the original on 21 April 2006. Retrieved 25 May 2006.
- ^ Bob Woodward (2004). Plan of Attack. Simon and Schuster. pp. 9–23. ISBN 978-0-7432-6287-3.
- ^ Julian Borger (12 January 2004). "Bush decided to remove Saddam 'on day one'". The Guardian. Retrieved 12 November 2020.
- ^ a b "'Building momentum for regime change': Rumsfeld's secret memos". MSNBC. 16 February 2013. Retrieved 19 January 2014.
- ^ "Plans For Iraq Attack Began on 9/11". CBS News. 4 September 2002. Archived from the original on 25 May 2006. Retrieved 26 May 2006.
- ^ Woodward 2004, 1–3.
- ^ a b c Schlosser, Nicholas J. (2023). "The IRAQ WAR TWENTY Years Later". Army History (126): 6–25. ISSN 1546-5330. JSTOR 48725101.
- ^ Michael Isikoff (16 February 2013). "'Building momentum for regime change': Rumsfeld's secret memos". MSNBC. Retrieved 31 March 2013.
- ^ Smith, Jeffrey R. "Hussein's Prewar Ties To Al-Qaeda Discounted". The Washington Post, Friday, 6 April 2007; p. A01. Retrieved on 23 April 2007.
- ^ "Iraq War". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 27 October 2012.
- ^ "Cheney on torture report: Saddam Hussein 'had a 10-year relationship with al-Qaida'". @politifact. Retrieved 28 May 2019.
- ^ "The Iraq War and WMDs: An intelligence failure or White House spin?". The Washington Post. 2019.
- ^ Jervis, Robert (February 2006). "Reports, Politics, and Intelligence Failures: The Case of Iraq". Journal of Strategic Studies. 29 (1): 3–52. doi:10.1080/01402390600566282. S2CID 216088620.
- ^ L, Jonathan S.; Newspapers, ay-McClatchy. "Pentagon office produced 'alternative' intelligence on Iraq". mcclatchydc. Retrieved 21 April 2019.
- ^ "President Delivers State of the Union Address". georgewbush-whitehouse.archives.gov. Archived from the original on 2 May 2009.
- ^ Vox, 9 July 2016, "No, Really, George W. Bush Lied about WMDs"
- ^ "Saddam's al Qaeda Connection". The Weekly Standard. Archived from the original on 23 December 2014. Retrieved 3 November 2007.
- ^ Center for American Progress (29 January 2004) "In Their Own Words: Iraq's 'Imminent' Threat" Archived 15 January 2016 at the Wayback Machine americanprogress.org
- ^ Senator Bill Nelson (28 January 2004) "New Information on Iraq's Possession of Weapons of Mass Destruction", Archived 20 April 2016 at the Wayback Machine Congressional Record
- ^ "Raw Data: Text of Resolution on Iraq". Fox News. Associated Press. 25 March 2015.
- ^ George W. Bush, "President's Remarks at the United Nations General Assembly: Remarks by the President in Address to the United Nations General Assembly, New York City", official transcript, press release, The White House, 12 September 2002. Retrieved 24 May 2007.
- ^ IBT Staff Reporter (8 February 2011). "Little evidence for Iraq WMDs ahead of 2003 war: U.S. declassified report". International Business Times. Retrieved 30 December 2018.
- ^ Shaffer, Glen (5 September 2002). "Iraq: Status of WMD Programs". Politico. Archived from the original on 24 April 2016. Retrieved 30 December 2018.
- ^ The Independent, 15 December 2006 "Diplomat's Suppressed Document Lays Bare the Lies behind Iraq War"
- ^ "France threatens rival UN Iraq draft". BBC News, 26 October 2002. Retrieved on 23 April 2007
- ^ "U.S. Wants Peaceful Disarmament of Iraq, Says Negroponte". Embassy of the United States in Manila. 8 November 2002. Archived from the original on 3 January 2006. Retrieved 26 May 2006.
- ^ "Statements of the Director General". IAEA. 6 March 2003. Archived from the original on 3 September 2006. Retrieved 7 September 2006.
- ^ Blix, H. (7 March 2003) "Transcript of Blix's U.N. presentation" Archived 9 November 2016 at the Wayback Machine CNN
- ^ Collins, Dan (3 October 2002). "Congress Says Yes To Iraq Resolution". CBS News. Archived from the original on 23 August 2019. Retrieved 12 March 2019.
- ^ "Poll: Talk First, Fight Later". CBS.com, 24 January 2003. Retrieved on 23 April 2007.
- ^ Ferran, Lee (15 February 2011). "Iraqi Defector 'Curveball' Admits WMD Lies, Is Proud of Tricking U.S." ABC News.
- ^ Powell, Secretary Colin L. (5 February 2003). "Remarks to the United Nations Security Council". New York City: US Department of State. Archived from the original on 5 February 2009. Retrieved 21 October 2021.
- ^ "US, Britain and Spain Abandon Resolution". Associated Press. 17 March 2003. Retrieved 6 August 2006.
- ^ "Bush: Iraq is playing 'willful charade'". CNN. 7 March 2003. Retrieved 6 August 2006.
- ^ "President Says Saddam Hussein Must Leave Iraq Within 48 Hours" (Press release). White House Office of the Press Secretary. 17 March 2003. Retrieved 28 July 2010.
- ^ "Division No. 117 (Iraq)". Hansard. 401 (365). Parliament of the United Kingdom. 18 March 2003. Retrieved 29 October 2011.
- ^ "CNN Inside Politics". CNN. Retrieved 23 October 2010.
- ^ Grice, Andrew (3 October 2002). "Clinton urges caution over Iraq as Bush is granted war powers". The Independent. London. Archived from the original on 13 May 2011. Retrieved 23 October 2010.
- ^ Knight, Danielle. "Winning Over the Senate With Frank Words and a Keen Mind". U.S. News & World Report. Retrieved 26 July 2015.
- ^ LaRepubblica, [46] (it]
- ^ "Anti-war protests underway". BBC News. 31 October 2002. Retrieved 26 July 2015.
- ^ "Press conference of Foreign Affairs Minister Dominique de Villepin (excerpts)". Embassy of France in the U.S. 20 January 2003. Archived from the original on 27 September 2006. Retrieved 13 February 2007.
- ^ Anti-war protests do make a difference Archived 21 March 2006 at the Wayback Machine, Alex Callinicos, Socialist Worker, 19 March 2005.
- ^ Jarrett Murphy (30 January 2003). "Mandela Slams Bush on Iraq". CBS News. Retrieved 19 January 2014.
- ^ "Army chief: Force to occupy Iraq massive". USA Today. 25 February 2003. Retrieved 23 October 2010.
- ^ "Administration fends off demands for war estimates – Mar. 3, 2003". CNN. 26 February 2003. Retrieved 23 October 2010.
- ^ Connolly, Kate (10 February 2003). "I am not convinced, Fischer tells Rumsfeld". Daily Telegraph. ISSN 0307-1235.
- ^ Ricks, Thomas E. (2007). Fiasco: The American Military Adventure in Iraq, 2003 to 2005 (Illustrated ed.). Penguin Books. pp. 94–95. ISBN 978-0-14-303891-7.
- ^ "Iraq war illegal, says Annan". BBC News. 16 September 2004. Retrieved 26 November 2016.
- ^ a b Operation Hotel California, The Clandestine War inside Iraq, Mike Tucker and Charles Faddis, 2008.
- ^ a b c Bob Woodward (2004). Plan of Attack: The Definitive Account of the Decision to Invade Iraq. Simon & Schuster. ISBN 978-0743255486.[page needed]
- ^ Chivers, C. J. (24 March 2003). "A Nation at War: Second Front; Allied Troops Are Flown Into Airfields In North Iraq". The New York Times. Retrieved 8 July 2021.
- ^ Chivers, C. J. (30 March 2003). "A Nation at War: in the Field the Northern Front; Militants Gone, Caves in North Lie Abandoned". The New York Times.
- ^ "Iraq War | 2003–2011". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 31 January 2017.
- ^ "Keeping 4th ID in the Mediterranean created element of surprise. Iraq did not expect attack to begin until 4th ID arrived in Kuwait." Rumsfeld, D., Franks, T.: Summary of Lessons Learned Archived 31 January 2012 at the Wayback Machine. Prepared testimony for the Senate Armed Services Committee, 9 July 2003.
- ^ Friedman, G.: What Happened To The American Declaration Of War? Archived 29 July 2017 at the Wayback Machine, Forbes, 30 March 2011.
- ^ Patrick E. Tyler (21 March 2003). "A nation at war: The attack; U.S. and British troops push into Iraq as missiles strike Baghdad compound". The New York Times. p. B8.
- ^ Australian Department of Defence (2004). The War in Iraq. ADF Operations in the Middle East in 2003 Archived 9 October 2016 at the Wayback Machine. Page 11.
- ^ MAJ Isaac J. Peltier. "Surrogate Warfare: The Role of U.S. Army Special Forces". US Army. p. 29. Archived from the original on 11 February 2009. Retrieved 13 September 2009.
- ^ Sale, Michelle; Khan, Javid (11 April 2003). "Missions Accomplished?". The Learning Network.
- ^ Keegan, John (2005). The Iraq War. Vintage Books. p. 169. ISBN 978-1-4000-7920-9.
- ^ Carney, Stephen A. (2011). Allied Participation in Operation Iraqi Freedom (PDF). United States Army Center of Military History. pp. 10, 98.
- ^ Keegan, 145.
- ^ Keegan, 148–153.
- ^ Gordon, Michael R.; Trainor, Bernard E. (2006). Cobra II: The Inside Story of the Invasion and Occupation of Iraq. Pantheon. p. 205. ISBN 978-0-375-42262-1.
- ^ Keegan, 154–155.
- ^ West, Bing; General Ray L. Smith (2003). The March Up: Taking Baghdad with the 1st Marine Division. New York: Bantam Books. ISBN 978-0-553-80376-1.[page needed]
- ^ a b Zucchino, David (3 July 2004). "Army Stage-Managed Fall of Saddam Statue". Los Angeles Times. Retrieved 23 October 2010.
- ^ The Rachel Maddow Show. 18 August 2010, MSNBC
- ^ Collier, R. (9 April 2003) "Baghdad closer to collapse" Archived 16 May 2012 at the Wayback Machine San Francisco Chronicle
- ^ "Stuff Happens". Defenselink.mil. Retrieved 23 October 2010.
- ^ Conetta, Carl (20 October 2003). "Research Monograph no. 8: The Wages of War: Iraqi Combatant and Noncombatant Fatalities in the 2003 Conflict". Project on Defense Alternatives. Archived from the original on 31 August 2009.
- ^ "A Look at U.S. Deaths in the Iraq War". The Washington Post. Reuters. 25 October 2005. Retrieved 11 November 2013.
- ^ "Operation Iraqi Freedom | Iraq | Fatalities By Nationality". iCasualties. 28 May 2010. Archived from the original on 1 February 2014. Retrieved 23 April 2014.
- ^ "iCasualties: Iraq Coalition Casualty Count – Deaths by Province Year/Month". Icasualties.org. Archived from the original on 8 July 2008. Retrieved 27 October 2008.
- ^ Karouny, Mariam (23 July 2006). "Gloom descends on Iraqi leaders as civil war looms". Turkish Daily News. Reuters. Archived from the original on 30 September 2007.
- ^ "US Blunders in Iraq" Archived 29 November 2016 at the Wayback Machine Intelligence and National Security Vol. 25, No. 1, 76–85, February 2010.
- ^ Sanchez, Wiser in Battle, p.185.
- ^ "Reintegration of Regular [IRAQ] Army", DDR Tasks – The Army, 3 July 2003 10:03 AM
- ^ America vs. Iraq, 26 August 2013, National Geographic, Television Production, Documentary
- ^ "Comprehensive Report of the Special Advisor to the DCI on Iraq's WMD – Central Intelligence Agency". Archived from the original on 2 October 2013. Retrieved 14 January 2016.
- ^ Anderson, Curt (9 January 2017). "FBI agent who interrogated Saddam Hussein leads airport case". Associated Press. Retrieved 8 January 2020.
- ^ Luke Harding (6 July 2016). "Chilcot delivers crushing verdict on Blair and the Iraq war". The Guardian. Archived from the original on 7 July 2016. Retrieved 6 July 2016.
- ^ Leon Watson (6 July 2016). "Chilcot report: 2003 Iraq war was 'unnecessary', invasion was not 'last resort' and Saddam Hussein was 'no imminent threat'". The Telegraph. Archived from the original on 6 July 2016. Retrieved 6 July 2016.
- ^ Philippe Sands, A Grand and Disastrous Deceit, Archived 5 August 2016 at the Wayback Machine London Review of Books Vol. 38 No. 15, 28 July 2016 pp. 9–11.
- ^ "Iraq war illegal, says Annan". BBC News. 16 September 2004. Archived from the original on 10 August 2022. Retrieved 26 August 2022.
- ^ "Pentagon: Saddam is POW". CNN. 10 January 2004.
- ^ "Saddam 'caught like a rat' in a hole". CNN. 15 December 2003.
- ^ "Why the U.S. Is Running Scared of Elections in Iraq". The Guardian. London. 19 January 2004. Retrieved 21 November 2006.
- ^ "Twenty years after the US invasion, where are Iraq's antiquities?" AlJazeera-The Iraq War: 20 years on] aljazeera. Accessed 9 April 2023.
- ^ United States Files Civil Action To Forfeit Thousands Of Ancient Iraqi Artifacts Imported By Hobby Lobby DOJ USAO Eastern District of New York. justice.gov. Accessed 9 April 2023.
- ^ Gordon, Michael R.; Trainor, Bernard E. (2012). The Endgame: The Inside Story of the Struggle for Iraq, from George W. Bush to Barack Obama. Pantheon Books. p. 59. ISBN 978-0-307-37722-7.
- ^ "frontline: private warriors: contractors: the high-risk contracting business". PBS. Retrieved 23 October 2010.
- ^ Flower, Kevin; Gray, Melissa; Kroll, Sue; Paulsen, Vivian; Sadik, Auday (31 March 2004). "U.S. expects more attacks in Iraq: Residents hang slain Americans' bodies from bridge". CNN. Archived from the original on 6 April 2004. Retrieved 6 April 2004.
- ^ ScanEagle Proves Worth in Fallujah Fight Archived 15 January 2016 at the Wayback Machine, DefenseLINK News
- ^ Thomas Ricks (2006) Fiasco: 398–405
- ^ Hersh, S. (10 May 2004) "Torture at Abu Ghraib" Archived 1 July 2014 at the Wayback Machine The New Yorker
- ^ Thomas E. Ricks (2006) Fiasco, The American Military Adventure in Iraq. Penguin
- ^ "U.S. to pull out 15,000 from Iraq". BBC News. 4 February 2005. Retrieved 5 January 2010.
- ^ "Insurgents attack Abu Ghraib prison". CNN. 3 April 2005. Archived from the original on 3 December 2017. Retrieved 26 March 2014.
- ^ a b Thomas Ricks (2006) Fiasco: 413
- ^ Thomas Ricks (2006) Fiasco: 414
- ^ "Decrying violence in Iraq, UN envoy urges national dialogue, international support". UN News Centre. 25 November 2006.
- ^ A Soldier's Shame Archived 23 August 2013 at the Wayback Machine 9 July 2006
- ^ Killings shattered dreams of rural Iraqi families NBC News
- ^ Barrouquere, Brett (29 May 2009). "Iraqi family's relatives confront killer". The Sydney Morning Herald.
- ^ "Attacks in Iraq at All-Time High, Pentagon Report Says". Newshour. PBS. 19 December 2006. Archived from the original on 15 January 2014. Retrieved 27 August 2017.
- ^ Watkins, Thomas (22 December 2006). "Marine Officers Charged in Haditha Case". The Washington Post.
- ^ "Saddam Hussein executed in Iraq". BBC News. 30 December 2006. Retrieved 5 January 2010.
- ^ "President's Address to the Nation". The White House. 10 January 2007.
- ^ Holusha, John (23 January 2007). "Petraeus Calls Iraq Situation Dire". The New York Times.
- ^ Gordon, Michael (5 January 2007). "Bush to Name a New General to Oversee Iraq". The New York Times.
- ^ Iraq Bill Demands U.S. Troop Withdraw Archived 14 May 2013 at the Wayback Machine Associated Press, Fox News, 10 May 2007
- ^ "Iraqi parliament wants say in extension of US-led forces". The Jerusalem Post. 5 June 2007. Archived from the original on 29 April 2011.
- ^ BBC News 21 February 2007, Blair announces Iraq troops cut Archived 5 December 2016 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Al-Jazeera English, 21 February 2007, Blair announces Iraq troop pullout Archived 5 December 2016 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "No re-opening of Iraq war commission: Danish government". The Local Denmark. 2 October 2019.
- ^ Flaherty, A. (10 September 2007) "Petraeus Talks of Troop Withdrawal" Associated Press
- ^ "Bush pledges Iraq troop reduction". BBC News. 14 September 2007. Retrieved 14 September 2007.
- ^ "Pentagon: Violence down in Iraq since 'surge'". CNN. 23 June 2008.
- ^ U.S. surge has failed – Iraqi poll Archived 12 October 2016 at the Wayback Machine BBC 10 September 2007
- ^ Few See Security Gains Archived 15 December 2016 at the Wayback Machine ABC 10 September 2007
- ^ Damien Cave (15 March 2007). "Baghdad violence decrease debatable". Telegram & Gazette. Worcester, Mass. The New York Times. Archived from the original on 13 June 2020. Retrieved 18 March 2007.
- ^ Rubin, Alissa J.; Wong, Edward (9 April 2007). "Patterns of War Shift in Iraq Amid U.S. Buildup". The New York Times. Retrieved 30 March 2010.
- ^ "icasualties.org". Archived from the original on 10 April 2008.
- ^ "Search goes on as Iraq death toll tops 250" The Guardian 15 August.
- ^ Auer, Doug (17 August 2007). "Iraq toll could hit 500". Herald Sun. Melbourne. Archived from the original on 4 September 2012. Retrieved 23 October 2010.
- ^ "They won't stop until we are all wiped out" The Guardian 18 August 2007
- ^ Cave, Damien; Glanz, James (22 August 2007). "Toll in Iraq Bombings Is Raised to More Than 500". The New York Times. Retrieved 15 January 2011.
- ^ "Iraqi insurgents kill key U.S. ally". BBC News. 13 September 2007. Retrieved 14 September 2007.
- ^ Compton, Ann; Terry McCarthy; Martha Raddatz (13 September 2007). "Top Sunni Sheik Killed in IED Attack". ABC News.
- ^ Rising, David (14 September 2007). "Mourners Vow Revenge at Sheik's Funeral". The Washington Post. Retrieved 10 September 2008.
- ^ U.S. General Says Iraq Violence Down Archived 19 August 2016 at the Wayback Machine Associated Press, 17 December 2007
- ^ Iraq – the best story of the year Archived 19 September 2011 at the Wayback Machine The Times, 17 December 2007
- ^ Surge hasn't curbed violence in Iraq Archived 12 October 2008 at the Wayback Machine The Australian, 5 September 2007
- ^ "Measuring Stability and Security in Iraq" Archived 26 August 2009 at the Wayback Machine December 2007 Report to Congress, sec. 1.3-Security Environment, p. 18-Overall trends in violence
- ^ Nancy A. Youssef (18 December 2007). "Despite drop in violence, Pentagon finds little long-term progress in Iraq". McClatchy. Archived from the original on 17 September 2008. Retrieved 10 September 2008.
- ^ Peter Beaumont (4 March 2007). "Sects slice up Iraq as U.S. troops 'surge' misfires". The Guardian. London. Retrieved 23 October 2010.
- ^ a b Cockburn, Patrick (20 May 2006). "Iraq is disintegrating as ethnic cleansing takes hold". The Independent. London. Archived from the original on 2 February 2010. Retrieved 23 October 2010.
- ^ "There is ethnic cleansing". Al-Ahram Weekly Online. 8 March 2006. Archived from the original on 12 October 2010. Retrieved 23 October 2010.
- ^ BBC News, 5 September 2008, "U.S. 'Spying' on Iraqi Leadership" Archived 13 April 2016 at the Wayback Machine citing the book The War Within: A Secret White House History, 2006–2008 by Bob Woodward
- ^ "AFP: Iraq takes control of Basra from British army". AFP via Google. 15 December 2007. Archived from the original on 27 May 2013. Retrieved 10 September 2008.
- ^ Abdul-Zahra, Q. (10 May 2007) "Iraqi Bill on Troop Pullout Discussed" Archived 15 November 2016 at the Wayback Machine The Washington Post, Retrieved 10 May 2007
- ^ Saad, L. (9 May 2007) "Americans Favor Iraq Timetable, Don't Foresee Increased Terrorism" Archived 17 August 2016 at the Wayback Machine USA Today/Gallup poll. Retrieved 10 May 2007
- ^ "US uses Sunnis to patrol streets". The New York Times. Melbourne. 20 August 2007.
- ^ Collins, Chris; Yaseen Taha (23 August 2007). "Iranians attack Kurdish rebels in Iraq". McClatchy Washington Bureau. Archived from the original on 3 July 2009.
- ^ "US general says Iran helping stop Iraq bloodshed". Agence France-Presse. 21 November 2007. Archived from the original on 27 May 2013.
- ^ HACAOGLU, SELCAN (10 October 2007). "Turkey Bombs Suspected Kurdish Rebels" – via washingtonpost.com.
- ^ Robertson, Nic; Ingrid Formanek; Talia Kayali (14 October 2007). "Attacks cross Iraq-Turkey border". CNN.
- ^ Meixler, Louis (23 October 2007). "Turkey May Attack Kurds Using Airstrikes, Troops". Bloomberg L.P. Archived from the original on 13 June 2010.
- ^ Barazanji, Yahya (13 November 2007). "Turkish Helicopters Strike Inside Iraq". The Huffington Post. Archived from the original on 16 February 2008.
- ^ Tavernise, Sabrina (16 December 2007). "Turkey Bombs Kurdish Militant Targets in Iraq". The New York Times.
- ^ Cloud, David S.; Eric Schmitt (30 August 2007). "U.S. Weapons, Given to Iraqis, Move to Turkey". The New York Times.
- ^ Glanz, James; Sabrina Tavernise (28 September 2007). "Blackwater Shooting Scene Was Chaotic". The New York Times.
- ^ a b c "U.S. Deaths in Iraq Decrease in 2008". Defenselink.mil. Retrieved 23 October 2010.
- ^ "Iraq Index: Tracking Variables of Reconstruction and Security in Post-Saddam Iraq" Archived 4 March 2016 at the Wayback Machine, Brookings Institution
- ^ "DoD News Briefing with Maj. Gen. Salmon from Iraq" Archived 30 November 2009 at the Wayback Machine, US Department of Defense news transcript
- ^ Tran, Mark (12 December 2008). "U.S. credits Iran for drop in Iraq roadside bombs". The Guardian. London. Retrieved 5 May 2010.
- ^ Sykes, Hugh (1 October 2008). "Awakening fears for Iraq's future". BBC News.
- ^ Steele, Jonathan (15 September 2008). "Iraq: Al-Qaida intensifies its stranglehold in the world's most dangerous city". The Guardian. London. Retrieved 5 May 2010.
- ^ "Operation Mother of Two Springs". Institute for the Study of War. 29 May 2008. Archived from the original on 1 April 2010.
- ^ "EU terror list" (PDF). Retrieved 23 October 2010.
- ^ "U.S. terror list". Archived from the original on 20 February 2008.
- ^ "NATO chief declares PKK terrorist group". Xinhua News Agency. 20 December 2005.
- ^ Bentley, Mark (22 February 2008). "Turkish Army Begins Ground Assault on PKK in Iraq". Bloomberg L.P. Archived from the original on 13 June 2010.
- ^ "Gov't gives no timetable for return". Turkish Daily News. 26 February 2008. Archived from the original on 16 January 2013.
- ^ Kamber, Michael (27 February 2008). "Iraq Cabinet Demands Turks Leave Kurdish Area in North". The New York Times.
- ^ Gordon and Trainor 2012, p. 461.
- ^ Dagher, Sam (26 March 2008). "Across Iraq, battles erupt with Mahdi Army". The Christian Science Monitor. p. 2.
- ^ a b Stephen Farrell and Ahmar Karim (12 May 2008). "Drive in Basra by Iraqi Army Makes Gains". The New York Times. Retrieved 12 May 2008.
- ^ Gordon and Trainor 2012, pp. 481–482.
- ^ Zremski, J. (9 April 2008). "Petraeus urges withdrawal delay". Buffalo News. Archived from the original on 15 April 2008.
- ^ Smith, S.A. (9 April 2008). "Senators grill Petraeus". Journal-Gazette. Archived from the original on 22 February 2014.
- ^ Ambinder, M. (9 April 2002), "Biden's Audition?" The Atlantic. Archived 12 October 2009 at the Wayback Machine.
- ^ Michaels, Jim (22 May 2008). "Iraqi forces load up on U.S. arms". USA Today. Archived from the original on 28 April 2011. Retrieved 23 October 2010.
- ^ Berrigan, Frida (24 September 2008). "Business as usual for U.S. arms sales". Asia Times. Archived from the original on 24 July 2009. Retrieved 23 October 2010.
{{cite news}}: CS1 maint: unfit URL (link) - ^ Cole, August; Dreazen, Yochi J. (5 September 2008). "Iraq Seeks F-16 Fighters". Wall St. Journal. Archived from the original on 13 May 2013.
- ^ Re-Arming Iraq Archived 9 June 2016 at the Wayback Machine (Center for American Progress)
- ^ "Center for Arms Control and Non-Proliferation: U.S. Surges $11 Billion in Arms Sales to Iraq". Armscontrolcenter.org. 6 August 2008. Archived from the original on 13 July 2010. Retrieved 23 October 2010.
- ^ a b "Iraq presidential council endorses U.S. security pact". Zawya.com. Archived from the original on 11 May 2011. Retrieved 23 October 2010.
- ^ BBC News (27 November 2008) "Iraqi parliament backs U.S. pullout" Archived 6 December 2016 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "White House: Iraq Status of Forces Agreement" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 27 May 2010.
- ^ "Status of Forces Agreement". McClatchyDC. Archived from the original on 1 August 2009. Retrieved 23 October 2010.
- ^ "On the other hand, Iraq has primary legal jurisdiction over off-duty soldiers and civilians who commit "major and premeditated crimes" outside of US installations. These major crimes were to be defined by a joint committee and the United States was to retain the right to determine whether or not its personnel were on- or off-duty. Iraq also maintains primary legal jurisdiction over contractors (and their employees) that have contracts with the United States. Arms Control Center: How Comfortable is the U.S.-Iraq SOFA? Archived 28 January 2015 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Committees assigned to deal with US-led combat operations and jurisdiction over US military personnel are among those that have not met even as Iraq moves toward sovereignty, US Army General Ray Odierno told reporters." Los Angeles Times: In Iraq, transfer-of-power committees have yet to take shape Archived 23 February 2009 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Status of Forces Agreement (Unofficial Translation)". McClatchyDC. Archived from the original on 1 August 2009. Retrieved 23 October 2010.
- ^ Rubin, A. (27 November 2008) "Iraqi Parliament approves security pact" International Herald Tribune
- ^ "U.S. staying silent on its view of Iraq pact until after vote". McClatchyDC. 25 November 2008. Archived from the original on 31 December 2008. Retrieved 23 October 2010.
- ^ a b Raghavan, Sudarsan; Sarhan, Saad (29 November 2008). "Top Shiite Cleric in Iraq Raises Concerns About Security Pact". The Washington Post. Retrieved 23 October 2010.
- ^ Bumiller, Elisabeth (22 December 2008). "Trying to Redefine Role of U.S. Military in Iraq". The New York Times. Retrieved 15 January 2011.
- ^ "Iraq: Cleric al-Sadr calls for peaceful protests" (Associated Press) Archived 1 December 2008 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "SOFA not sitting well in Iraq". Asia Times. 2 December 2008. Archived from the original on 2 December 2008. Retrieved 23 October 2010.
{{cite news}}: CS1 maint: unfit URL (link) - ^ "Iraqi refugees in Syria protest against military pact with U.S". Daily Star. 3 December 2008. Archived from the original on 7 January 2009. Retrieved 23 October 2010.
- ^ a b "Iraqi people will judge on U.S. pact". Al Jazeera. Retrieved 23 October 2010.[dead link]
- ^ Robertson, Campbell (28 October 2008). "Feelings are mixed as Iraqis ponder U.S. security agreement". International Herald Tribune. Archived from the original on 28 November 2008. Retrieved 26 December 2011.
- ^ "Iraqis hold anti‑U.S. rally in Baghdad". Al Jazeera. Archived from the original on 28 April 2011. Retrieved 23 October 2010.
- ^ "Iraqi civilian deaths down in January". CNN. 31 January 2009. Retrieved 23 October 2010.
- ^ Steven Lee Myers (8 February 2009). "America's Scorecard in Iraq". The New York Times.
- ^ Dagher, Sam (21 January 2009). "A Top Sunni Survives an Attack in Iraq". The New York Times. Retrieved 26 December 2011.
- ^ "Gunmen kill Iraqi soldier south of Baghdad". News.trend.az. Archived from the original on 12 July 2012. Retrieved 23 October 2010.
- ^ Sarhan, Saad (17 January 2009). "Province Candidate Killed in Iraq". The Washington Post. Retrieved 23 October 2010.
- ^ Dagher, Sam (12 February 2009). "Violence Across Iraq Kills 13, Including a Sunni Politician". The New York Times. Retrieved 26 December 2011.
- ^ a b Centre Daily: Low turnout in Iraq's election reflects a disillusioned nation Archived 12 February 2009 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Morin, Monte (2 February 2009). "Iraq vote turnout fails to meet expectations". Los Angeles Times. Retrieved 23 October 2010.
- ^ Nabil Al-jurani (4 February 2009). "Iraq: Sunni tribal leader says he can prove fraud". NBC News. Associated Press. Retrieved 23 October 2010.
- ^ "Iraq's Sadrists complain of vote fraud". Middle-east-online.com. 7 February 2009. Archived from the original on 10 October 2017. Retrieved 23 October 2010.
- ^ Lee, Steven (10 February 2009). "Election results spur threats and infighting in Iraq". International Herald Tribune. Archived from the original on 14 February 2009. Retrieved 26 December 2011.
- ^ "Obama's Speech at Camp Lejeune, N.C." The New York Times. 27 February 2009.
- ^ Bel Aiba, Ines (26 February 2009). "Iraq not fazed by pending US pullout: Maliki". AFP. Retrieved 13 February 2021.
- ^ "Six years on, huge protest marks Baghdad's fall". The Star. Archived from the original on 1 May 2011. Retrieved 23 October 2010.
- ^ Miami Herald: Tens of thousands of Iraqis rally against U.S.[dead link]
- ^ "UK combat operations end in Iraq". BBC News. 30 April 2009. Retrieved 23 October 2010.
- ^ Christie, Michael (30 November 2009). "Iraqi civilian deaths drop to lowest level of war". Reuters. Retrieved 30 November 2009.
- ^ "Oil firms awarded Iraq contracts". Al Jazeera. 11 December 2009. Retrieved 23 October 2010.
- ^ "BP group wins Iraq oil contract". Al Jazeera. 30 June 2009. Retrieved 23 October 2010.
- ^ "US report: Iraq of leading oil producers 2040". 18 February 2014. Retrieved 26 February 2014.
- ^ "Exclusive: War in Iraq to Be Given New Name". ABC News. 18 February 2010. Archived from the original on 20 February 2010.
- ^ "2 Most Wanted Al Qaeda Leaders in Iraq Killed by U.S., Iraqi Forces" Archived 1 July 2015 at the Wayback Machine Fox News, 19 April 2010
- ^ "US : Al-Qaida in Iraq warlord slain" MSNBC, 20 April 2010
- ^ "Iraqi al-Qaeda leaders 'killed'". BBC News. 19 April 2010.
- ^ Ali, Khalid D.; Williams, Timothy (20 June 2010). "Car Bombs Hit Crowds Outside Bank in Baghdad". The New York Times.
- ^ Shadid, Anthony (25 August 2010). "Insurgents Assert Their Strength With Wave of Bombings Across Iraq". The New York Times.
- ^ "U.S. ending combat operations in Iraq". NBC News. 18 August 2010. Retrieved 18 August 2010.
- ^ "U.S. ends combat operations in Iraq". Al Jazeera English. 18 August 2010. Retrieved 18 August 2010.
- ^ Londoño, Ernesto (18 August 2010). "Final U.S. combat brigade pulls out of Iraq". The Washington Post. Retrieved 19 August 2010.
- ^ Linkins, Jason (3 September 2010). "AP Issues Standards Memo: 'Combat In Iraq Is Not Over'". The Huffington Post. Retrieved 23 October 2010.
- ^ "Last US combat brigade exits Iraq". BBC News. 19 August 2010. Retrieved 19 December 2011.
- ^ "President Obama's Address on Iraq". The New York Times. 31 August 2010.
- ^ Gordon, Michael (1 September 2010). "U.S. Formally Begins a New Era in Iraq". The New York Times.
- ^ "G.I. Deaths Are First for U.S. After Combat Mission's End". The New York Times. 7 September 2010.
- ^ "First U.S. Advise and Assist Brigade arrives under New Dawn". US Army. 8 September 2010. Retrieved 22 September 2012.
- ^ Williams, Timothy; Adnan, Duraid (16 October 2010). "Sunnis in Iraq Allied With U.S. Rejoin Rebels". The New York Times.
- ^ "The WikiLeaks Iraq War Logs: Greatest Data Leak in U.S. Military History". Der Spiegel. 22 October 2010. Retrieved 23 October 2010.
- ^ Davies, Nick; Steele, Jonathan; Leigh, David (22 October 2010). "Iraq war logs: secret files show how U.S. ignored torture". The Guardian. London. Retrieved 23 October 2010.
- ^ Carlstrom, Gregg (22 October 2010). "WikiLeaks releases secret Iraq file". Al Jazeera English. Retrieved 23 October 2010.
- ^ Martin Chulov in Baghdad (1 November 2010). "Baghdad church siege survivors speak of taunts, killings and explosions | World news". The Guardian. London. Retrieved 15 January 2011.
- ^ Parker, Ned; Zeki, Jaber (3 November 2010). "Iraq bombings: 113 killed in bombings in Baghdad". Los Angeles Times. Retrieved 15 January 2011.
- ^ Michaels, Jim (1 September 2010). "Iraq to spend $13B on U.S. arms, equipment". USA Today.
- ^ a b "U.S. plans $4.2 billion arms sale to Iraq". UPI. 1 October 2010. Retrieved 15 January 2011.
- ^ "Iraqi Army receives last shipment of Abrams tanks" Archived 28 September 2013 at the Wayback Machine. Army.mil, 6 September 2011.
- ^ Martin Matishak (13 July 2015). "US delivers first F-16 fighters to Iraq". The Hill. Retrieved 7 November 2017.
- ^ "US Navy Delivers Final Coastal Patrol Boat to Iraq". US Navy. 11 July 2013. Archived from the original on 13 June 2020. Retrieved 7 November 2017.
- ^ Anthony H. Cordesman; Sam Khazai (2014). Iraq in Crisis. Center for Strategic & International Studies. p. 255. ISBN 978-1-4422-2856-6.
- ^ "UN Security Council Lifts Some Restrictions on Iraq". Voice of America. 15 December 2010. Archived from the original on 17 December 2010. Retrieved 15 January 2011.
- ^ Shadid, Anthony; Leland, John (5 January 2011). "Moktada al-Sadr Returns to Iraq". The New York Times.
- ^ Lara Jakes. "3 American Soldiers Killed in Iraq". Aolnews.com. Archived from the original on 10 January 2012. Retrieved 26 December 2011.
- ^ "Five US troops killed in Iraq attack". Al Jazeera. Retrieved 26 December 2011.
- ^ "DOD Identifies Army Casualty". US Department of Defense. 12 March 2009. Retrieved 26 December 2011.
- ^ "Two U.S. soldiers die in IED attack". KUT. 16 June 2011. Retrieved 14 January 2017.
- ^ "Falmouth soldier killed in Iraq". Falmouth Patch. 1 July 2011. Retrieved 14 January 2017.
- ^ "Soldiers to serve prison time for role in Matthew Gallagher's death". The Enterprise. 30 March 2012. Archived from the original on 16 January 2017. Retrieved 14 January 2017.
- ^ "Three U.S. soldiers killed in southern Iraq". BBC News. 30 June 2011.
- ^ "June bloodiest month for U.S. in Iraq in 2 years". CBS News. 30 June 2011. Archived from the original on 14 May 2013. Retrieved 26 December 2011.
- ^ "2 Idaho National Guard soldiers killed, 1 severely wounded in Iraq". Idaho State Journal. 9 July 2011. Retrieved 5 October 2018.
- ^ "Iraq to buy US warplanes worth around $3 billion". NBC News.
- ^ "Barack Obama: All U.S. troops to leave Iraq in 2011". BBC News. 21 October 2011. Retrieved 21 October 2011.
- ^ Feller, Ben (27 February 2009). "Obama sets firm withdrawal timetable for Iraq". Yahoo! News. Associated Press. Archived from the original on 2 March 2009.
- ^ "Unofficial Translation of U.S.–Iraq Troop Agreement from the Arabic Text". mcclatchydc. Retrieved 7 January 2019.
- ^ a b "Why U.S. forces remain in Iraq 20 years after 'shock and awe'". PBS NewsHour. 15 March 2023. Retrieved 1 August 2023.
- ^ Hanson, Victor Davis (December 2011). "Iraq and Afghanistan: A tale of two surges". CBS News. Retrieved 14 March 2019.
- ^ "Timeline: Invasion, surge, withdrawal; U.S. forces in Iraq". Reuters. 18 December 2011.
- ^ Johnson, Craig (16 December 2011). "N.C. soldier reportedly last to die in Iraq war". CNN. Archived from the original on 3 December 2017. Retrieved 16 December 2011.
- ^ Antle, W. James. "Senate Tackles Iraq War Powers, Indefinite Detention". The Spectacle Blog. The American Spectator. Archived from the original on 23 May 2013. Retrieved 23 February 2015.
- ^ "US lowers flag to end Iraq war". independent.co.uk. 15 December 2011.
- ^ "The office of security cooperation maintaining a presence in Iraq once soldiers go home". army.mil. 30 November 2011.
- ^ Denselow, James (25 October 2011). "The US departure from Iraq is an illusion". The Guardian. London. Retrieved 10 February 2014.
- ^ Jaffe, Greg (18 December 2011). "Last U.S. troops cross Iraqi border into Kuwait". The Washington Post. Retrieved 19 December 2011.
- ^ "Arrest warrant for Iraq Vice-President Tariq al-Hashemi". BBC News. 12 January 2012. Retrieved 12 January 2012.
- ^ "110,000 fewer Iraqis displaced: Red Crescent". Reuters. 5 December 2007.
- ^ Keith Wagstaff (27 May 2013). "Is Iraq heading toward civil war?". The Week. Retrieved 28 May 2013.
- ^ Sinan Salaheddin (20 May 2013). "Attacks Kill 95 in Iraq, Hint of Syrian Spillover". Associated Press. Archived from the original on 28 January 2015. Retrieved 28 May 2013.
- ^ "Iraq: hundreds escape from Abu Ghraib jail". The Guardian. London. Associated Press. 22 July 2013. Retrieved 19 January 2014.
- ^ Michael R. Gordon; Duraid Adnan (24 July 2013). "Brazen Attacks at Prisons Raise Worries of Al Qaeda's Strength in Iraq". The New York Times.
- ^ Karouny, Mariam (4 September 2014). "How ISIS Is Filling A Government Vacuum In Syria With An 'Islamic State'". Huffington Post.
- ^ "Iraq crisis: Isis gains strength near Baghdad as Kurdish forces seize Kirkuk". The Guardian. Retrieved 12 June 2014.
- ^ "Obama: U.S. underestimated rise of ISIS in Iraq and Syria". CBS News. 28 September 2014. Retrieved 30 May 2019.
- ^ "Obama Authorizes Air Strikes in Iraq". The New York Times. 8 August 2014. Retrieved 22 August 2014.
- ^ Schmitt, Eric (20 May 2017). "Mattis Says Escalation Against ISIS Doesn't Imperil More Civilians". The New York Times.
- ^ Timm, Jane. "Fact check: Trump's right, ISIS did lose almost all its territory in Iraq and Syria". NBC News. Retrieved 17 May 2019.
- ^ Mostafa, Nehal (9 December 2017). "Iraq announces end of war against IS, liberation of borders with Syria: Abadi". Iraqi News. Retrieved 9 December 2017.
- ^ "Violence in Iraq at Lowest Level in 10 years". Chicago Daily Observer. 4 June 2018. Archived from the original on 22 August 2018. Retrieved 9 September 2018.
- ^ "Iraqi parliament votes to expel US troops – awaits government approval". DW.COM. 5 January 2020. Retrieved 15 May 2020.
- ^ "Iraqi PM supports indefinite U.S. troop presence, Wall Street Journal reports". Reuters. 15 January 2023. Retrieved 30 May 2023.
- ^ The Wall Street Journal 15 March 2013
- ^ Trotta, Daniel (2 March 2008). "Iraq war hits U.S. economy: Nobel winner". Reuters. Archived from the original on 12 October 2017. Retrieved 16 January 2018.
- ^ Trotta, Daniel (14 March 2013). "Iraq war costs US more than $2 trillion: study". Reuters. Archived from the original on 19 September 2017. Retrieved 16 January 2018.
- ^ Bilmes, Linda (26 March 2013). "The Financial Legacy of Iraq and Afghanistan: How Wartime Spending Decisions Will Constrain Future National Security Budgets". Harvard Kennedy School. doi:10.2139/ssrn.2281275. S2CID 152971939. SSRN 2281275.. HKS Working Paper No. RWP13-006.
- ^ Stiglitz, Joseph E.; Bilmes, Linda J. (5 September 2010). "The true cost of the Iraq war: $3 trillion and beyond". Washington Post. Retrieved 6 December 2017.
- ^ "Audit: U.S. lost track of $9 billion in Iraq funds". CNN. 30 January 2005. Retrieved 18 June 2023.
- ^ "Report: $6B missing in Iraq may have been stolen". CBS News. 14 June 2011. Retrieved 19 January 2014.
- ^ "US reparations for Iraq are long overdue". america.aljazeera.com. Retrieved 12 November 2021.
- ^ Hawa, Kaleem (1 September 2021). "Reparations for Iraq". Intelligencer. Retrieved 12 November 2021.
- ^ Arraf J. (Jan. 4, 2021). "Iraq, Struggling to Pay Debts and Salaries, Plunges Into Economic Crisis" NYT. Accessed 9 April 2023.
- ^ "Hunger, disease spread in Iraq – Oxfam report". Reuters. 30 July 2007. Retrieved 14 July 2014.
- ^ "Iraq: Traumatised Iraqi children suffer psychological damage". Alertnet.org. 16 July 2007. Retrieved 14 July 2014.
- ^ Cockburn, Patrick (31 August 2007). "Cholera spreads in Iraq as health services collapse". The Independent. London. Archived from the original on 15 October 2007. Retrieved 14 July 2014.
- ^ Laurance, Jeremy (20 October 2006). "Medics beg for help as Iraqis die needlessly". The Independent. London. Archived from the original on 13 October 2008. Retrieved 14 July 2014.
- ^ UNHCR. "Global Trends: Forced Displacement in 2015". Retrieved 18 July 2016.
- ^ Griswold, Eliza (22 July 2015). "Is This the End of Christianity in the Middle East?". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved 18 July 2016.
- ^ "Global Views: Iraq's refugees", by R. Nolan, Foreign Policy Association Features, Resource Library, 12 June 2007.
- ^ Rosen, Nir (13 May 2007). "The Flight From Iraq". The New York Times. Retrieved 23 March 2014.
- ^ "Iraqi Refugee Processing Fact Sheet". US Citizenship and Immigration Services. Archived from the original on 14 March 2014. Retrieved 23 March 2014.
- ^ a b c "The Environmental Consequences of the War on Iraq". www.greenparty.org.uk. Retrieved 24 July 2022.
- ^ Al-Bayati, Russell M.; Al-Salihi, Ali M. (22 August 2019). "Monitoring carbon dioxide from (AIRS) over Iraq during 2003–2016". AIP Conference Proceedings. 2144 (1): 030007. Bibcode:2019AIPC.2144c0007A. doi:10.1063/1.5123077. ISSN 0094-243X. S2CID 202177040.
- ^ a b c d Al-Shammari, Ahmed Majeed (1 June 2016). "Environmental pollutions associated to conflicts in Iraq and related health problems". Reviews on Environmental Health. 31 (2): 245–250. doi:10.1515/reveh-2015-0024. ISSN 2191-0308. PMID 26512425. S2CID 41359706.
- ^ Edwards, Rob (19 June 2014). "US fired depleted uranium at civilian areas in 2003 Iraq war, report finds". The Guardian (US ed.). eISSN 1756-3224. ISSN 0261-3077. OCLC 60623878. Archived from the original on 8 August 2022. Retrieved 26 August 2022.
- ^ a b c d Fathi, Riyad Abdullah; Matti, Lilyan Yaqup; Al-Salih, Hana Said; Godbold, Douglas (1 March 2013). "Environmental pollution by depleted uranium in Iraq with special reference to Mosul and possible effects on cancer and birth defect rates". Medicine, Conflict and Survival. 29 (1): 7–25. doi:10.1080/13623699.2013.765173. ISSN 1362-3699. PMID 23729095. S2CID 45404607.
- ^ Burkle, Frederick; Garfield, Richard (16 March 2013). "Civilian mortality after the 2003 invasion of Iraq". The Lancet. 381 (9870): 877–879. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(12)62196-5. PMID 23499026. S2CID 20887504.
- ^ Jamail, Dahr (16 March 2013). "Iraq's wars, a legacy of cancer". Al Jazeera. Retrieved 29 November 2018.
- ^ "New Research Shows Gulf War Illness Not Caused by Depleted Uranium From Munitions". SciTechDaily. 18 February 2021. Retrieved 19 February 2021.
- ^ Al-Hadithi, Tariq S.; Saleh, Abubakir M.; Al-Diwan, Jawad K.; Shabila, Nazar P. (2012). "Birth defects in Iraq and the plausibility of environmental exposure: A review". Conflict and Health. 6 (3): 245–250. doi:10.1186/1752-1505-6-3. PMC 3492088. PMID 22839108.
- ^ Bonds, Eric (3 May 2016). "Legitimating the environmental injustices of war: toxic exposures and media silence in Iraq and Afghanistan". Environmental Politics. 25 (3): 395–413. Bibcode:2016EnvPo..25..395B. doi:10.1080/09644016.2015.1090369. ISSN 0964-4016. S2CID 154998558.
- ^ Office of the Federal Register; et al. (2010). Administration of George W. Bush, 2006: Book II, July 1 to December 31, 2006. Public Papers of the Presidents. Washington, DC: United States Government Printing Office. p. 1542.
- ^ Bush, George W. (9 September 2003). "A Central Front in the War on Terror". The White House.
- ^ Garamone, Jim (19 September 2002). "Iraq Part of Global War on Terrorism, Rumsfeld Says". American Forces Press Service. Archived from the original on 29 September 2007.
- ^ Bush, George W. (21 August 2006). "Press Conference by the President". Peace in the Middle East. The White House.
- ^ Gunaratna, Rohan (Summer 2004). "The Post-Madrid Face of Al Qaeda". Washington Quarterly. 27 (3): 98. doi:10.1162/016366004323090278. S2CID 154500987.
- ^ Sengupta, Kim (26 May 2004). "Occupation Made World Less Safe, Pro-War Institute Says". The Independent. Archived from the original on 20 September 2006.
- ^ Priest, Dana (14 January 2005). "Iraq New Terror Breeding Ground". The Washington Post.
- ^ "Declassified Key Judgments of the National Intelligence Estimate "Trends in Global Terrorism: Implications for the United States"" (PDF) (Press release). Office of the Director of National Intelligence. April 2006. Archived from the original (PDF) on 30 September 2006.
- ^ Robinson L. (March 20, 2023) "The Long Shadow of the Iraq War: Lessons and Legacies Twenty Years Later" cfr.org. Accessed 9 April 2023.
- ^ "Interview des Außenministers der Russischen Föderation, Sergej Lawrow, für den TV-Sender Al Jazeera, Moskau, 2. März 2022" Archived 11 March 2022 at the Wayback Machine (in German) mid.ru/de/foreign_policy/news. Retrieved 6 March 2022.
- ^ "Tony Blair: Putin can't use Iraq to justify Ukraine invasion" DW. Accessed 9 April 2023.
- ^ "Iraq". Forces: U.S. & Coalition/Casualties. CNN. May 2008. Archived from the original on 1 July 2008.
- ^ "Regrets and disappointments? Bush had a few". Reuters. 12 January 2009. Retrieved 24 October 2022.
- ^ Marquis, Christopher (4 June 2003). "After the War: Opinion; World's View of U.S. Sours After Iraq War, Poll Finds". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved 1 August 2023.
- ^ Vietnam war-eyewitness booksW.; Iraq and Vietnam: Differences, Similarities and Insights, (2004: Strategic Studies Institute)
- ^ "Revealed: The Secret Cabal Which Spun for Blair", Sunday Herald, Neil Mackay, 8 June 2003
- ^ "Group: 'Orchestrated Deception' by Bush on Iraq". NPR. Retrieved 23 October 2010.
- ^ Luke Harding (6 July 2016). "Chilcot delivers crushing verdict on Blair and the Iraq war". The Guardian. Retrieved 6 July 2016.
- ^ Leon Watson (6 July 2016). "Chilcot report: 2003 Iraq war was 'unnecessary', invasion was not 'last resort' and Saddam Hussein was 'no imminent threat'". The Telegraph. Retrieved 6 July 2016.
- ^ "Chilcot report: Findings at a glance". BBC News. 6 July 2016. Retrieved 6 July 2016.
- ^ War critics astonished as U.S. hawk admits invasion was illegal, The Guardian, 20 November 2003
- ^ Top judge: US and UK acted as 'vigilantes' in Iraq invasion, The Guardian, 18 November 2008
- ^ Seshardri, Aparnaa (7 September 2006). "Tony Blair to Resign in a Year". ABC News. Retrieved 24 October 2022.
- ^ "The World Today – Blair to quit within 12 months". www.abc.net.au. Retrieved 24 October 2022.
- ^ a b South, Todd (4 February 2019). "Army's long-awaited Iraq war study finds Iran was the only winner in a conflict that holds many lessons for future wars". Army Times. Retrieved 6 February 2019.
- ^ "Germany Assists UN Migration Agency's Humanitarian Operations in Iraq as Winter Advances". www.uniraq.org.
- ^ "Displacement in Iraq Exceeds 3.3 Million: IOM". International Organization for Migration. 23 February 2016.
- ^ [47] 2,780,406 displaced and 2,844,618 returnees. Retrieved 2 January 2018.
- ^ "How Sri Lanka Won the War".
- ^ "RAND Review | Summer 2003 – Burden of Victory". Rand.org. Archived from the original on 27 September 2008. Retrieved 10 September 2008.
- ^ "U.S. CBO estimates $2.4 trillion long-term war costs". Reuters. 24 October 2007. Retrieved 10 September 2008.
- ^ Norton-Taylor, Richard (28 September 2006). "Iraq war was terrorism 'recruiting sergeant'". The Guardian.
- ^ Spy Agencies Say Iraq War Hurting U.S. Terror Fight, The Washington Post, 23 September 2006
- ^ Tarabay, Jamie (18 March 2013). "Global Opportunity Costs: How the Iraq War Undermined U.S. Influence". The Atlantic. Retrieved 18 April 2021.
- ^ Cordesman, Anthony H. (2 January 2020). "America's Failed Strategy in the Middle East: Losing Iraq and the Gulf". www.csis.org. Retrieved 18 April 2021.
- ^ Crawford, Angus (4 March 2007). "Iraq's Mandaeans 'face extinction'". BBC News. Retrieved 23 October 2010.
- ^ "Iraq's Yazidis fear annihilation". NBC News. 16 August 2007. Retrieved 23 October 2010.
- ^ Sabah, Zaid (23 March 2007). "Christians, targeted and suffering, flee Iraq". USA Today. Retrieved 23 October 2010.
- ^ "Assyrians Face Escalating Abuses in "New Iraq"". IPS News. 3 May 2006. Archived from the original on 28 May 2010. Retrieved 23 October 2010.
- ^ "Light Crude Oil (CL, NYMEX): Monthly Price Chart". Futures.tradingcharts.com. Retrieved 10 September 2008.
- ^ "Iraq to revive oil deal with China". International Herald Tribune. 29 March 2009. Archived from the original on 19 September 2008. Retrieved 23 October 2010.
- ^ "Off Target: The Conduct of the War and Civilian Casualties in Iraq". Human Rights Watch. Retrieved 21 October 2015.
- ^ Hersh, Seymour M. (17 May 2004). "Chain of Command". The New Yorker. Retrieved 13 September 2011.
NBC News later quoted U.S. military officials as saying that the unreleased photographs showed American soldiers "severely beating an Iraqi prisoner nearly to death, having sex with a female Iraqi prisoner, and 'acting inappropriately with a dead body.' The officials said there also was a videotape, apparently shot by U.S. personnel, showing Iraqi guards raping young boys."
- ^ "US forces used 'chemical weapon' in Iraq". The Independent. 16 November 2005. Retrieved 26 December 2020.
- ^ Wilson, Jamie (16 November 2005). "US admits using white phosphorus in Falluja". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Retrieved 23 April 2020.
- ^ "White phosphorus use by US-led coalition forces in Iraq condemned by humanitarian groups". The Independent. 14 June 2017. Retrieved 23 April 2020.
- ^ Haddad, Tareq (4 November 2019). "White phosphorus melts children's flesh but no government wants to investigate – and the U.S. keeps using it, too". Newsweek. Retrieved 23 April 2020.
- ^ Amnesty International Report 2007, the state of the world's human rights. New York: Amnesty International USA. 2007. p. 143. ISBN 978-1-887204-46-0.
- ^ "Iraq rape soldier jailed for life". BBC News. 16 November 2006. Retrieved 10 September 2008.
- ^ Mackay, Neil (14 March 2004). "Iraq: The Wedding Party Massacre". Sunday Herald. Archived from the original on 7 January 2009.
- ^ "2 GIs charged with murder of Iraqis". International Herald Tribune. Archived from the original on 18 September 2008. Retrieved 10 September 2008.
- ^ "Multi-National Force – Iraq – Additional Soldier charged with murder". Mnf-iraq.com. Archived from the original on 16 August 2007. Retrieved 10 September 2008.
- ^ Chris Hedges. "The Other War: Iraq Vets Bear Witness". The Nation. Retrieved 10 September 2008.
- ^ Owen, Jonathan (12 January 2014). "Exclusive: Devastating dossier on 'abuse' by UK forces in Iraq goes to International Criminal Court". The Independent. London.
- ^ Ellen Knickmeyer (3 June 2005). "Iraq Puts Civilian Toll at 12,000". The Washington Post.
- ^ Paul McGeough (2 February 2005). "Handicapped boy who was made into a bomb". The Sydney Morning Herald.
- ^ Iraq bombing toll rises. The Age 2 July 2006
- ^ A Face and a Name. Civilian Victims of Insurgent Groups in Iraq Archived 2 September 2020 at the Wayback Machine. Human Rights Watch October 2005.
- ^ The Weapons That Kill Civilians – Deaths of Children and Noncombatants in Iraq, 2003–2008 by Madelyn Hsiao-Rei Hicks, M.D., M.R.C.Psych., Hamit Dardagan, Gabriela Guerrero Serdán, M.A., Peter M. Bagnall, M.Res., John A. Sloboda, PhD, F.B.A., and Michael Spagat, PhD, The New England Journal of Medicine.
- ^ "Who are the Iraq Insurgents?". NewsHour with Jim Lehrer. PBS. 12 June 2006. Archived from the original on 15 June 2006.
- ^ "Kidnappers Kill Algerian Diplomats". Free Internet Press. 27 July 2005. Archived from the original on 27 September 2007.
- ^ "Captors kill Egypt envoy to Iraq". BBC News. 8 July 2005. Retrieved 5 January 2010.
- ^ "Russian diplomat deaths confirmed". BBC News. 26 June 2006. Retrieved 5 January 2010.
- ^ Alex Rodriguez, Iraqi shrine blast suspect caught Archived 2 April 2013 at the Wayback Machine (paid archive), The Chicago Tribune 29 June 2006.
- ^ "Insurgents kill Bulgarian hostage: Al-Jazeera". CBC News. 14 July 2004.
- ^ "Foreign hostages in Iraq". CBC News. 22 June 2006. Archived from the original on 7 August 2006.
- ^ "4 Contractors murdered by al Qaeda". The Washington Post. 31 March 2004. Retrieved 23 October 2010.
- ^ Sabrina Tavernise (19 June 2005). "Iraqis Found in Torture House Tell of Brutality of Insurgents". The New York Times.
- ^ "Iraq kidnappings stun Kenya press". BBC News. 23 July 2004. Retrieved 5 January 2010.
- ^ "Iraq: Torture Continues at Hands of New Government". Human Rights News. 25 January 2005.
- ^ Dexter Filkins (29 November 2005). "Sunnis Accuse Iraqi Military of Kidnappings and Slayings". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 19 June 2015. Retrieved 10 June 2021.
- ^ "Torture by Iraqi militias: the report Washington did not want you to see". Reuters. 14 December 2015.
- ^ "Seventy-Two Percent of Americans Support War Against Iraq". Gallup. 24 March 2003.
- ^ "Surveys reveal how we remember opposing the Iraq war – but at the time we supported it". The Independent. 5 June 2015.
- ^ Stephen Eric Bronner, Kurt Jacobsen (Fall 2004). "Dubya's Fellow Travellers: Left Intellectuals and Mr. Bush's War".
- ^ Judt, Tony (September 2006). "Bush's Useful Idiots". London Review of Books. 28 (18).
- ^ "Un 91% de los españoles son contrarios a la intervención en Irak | Noticias de actualidad" [91% of Spaniards are against the intervention in Iraq]. El País (in European Spanish). 27 March 2003. Retrieved 13 June 2023.
- ^ "World View of U.S. Role Goes from Bad to Worse" (PDF). BBC World Service. 23 January 2007. Retrieved 23 May 2007.
- ^ "Most people 'want Iraq pull-out'". BBC News. 7 September 2007. Retrieved 5 January 2010.
- ^ "Guardian July Poll" (PDF). ICM Research. July 2006. Archived from the original (PDF) on 27 May 2008.
- ^ Zogby, James (March 2007). "Four Years Later: Arab Opinion Troubled by Consequences of Iraq War" (PDF). Arab American Institute. Archived from the original (PDF) on 28 January 2015.
- ^ "India: Pro-America, Pro-Bush". Pew Global Attitudes Project. Pew Research Center. 28 February 2006.
- ^ Most Iraqis in Baghdad welcome US: NDTV poll The Indian Express
- ^ a b "The Iraqi Public on the U.S. Presence and the Future of Iraq" (PDF). World Public Opinion. 27 September 2006. Archived from the original (PDF) on 24 August 2016. Retrieved 23 November 2008.
- ^ Iraq Poll conducted by D3 Systems for the BBC, ABC News, ARD German TV and USA Today. More than 2,000 people were questioned in more than 450 neighbourhoods and villages across all 18 provinces of Iraq between 25 February and 5 March 2007. The margin of error is + or – 2.5%.
- ^ Iraqis Oppose Oil Development Plans, Poll Finds (6 August 2007) (Oil Change International, Institute for Policy Studies, War on Want, Platform and Global Policy Forum)
- ^ "Iraq poll March 2007: In graphics". BBC. 19 March 2007.
- ^ "Poll: Most Iraqis Want US Troops to Leave Within a Year". VOA. 31 October 2009. Retrieved 2 February 2023.
- ^ Most Iraqis in Baghdad welcome US: NDTV poll The Indian Express Archived 22 December 2011 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ US under 50,000 – Iraqis 'down' on drawdown Arab Times Archived 21 February 2015 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ a b Bernstein-Wax, Jessica (8 August 2007). "Studies: Suicide bombers in Iraq are mostly foreigners". McClatchy Newspapers. Archived from the original on 16 May 2015. Retrieved 24 September 2012.
- ^ Glasser, Susan B. (15 May 2005). "'Martyrs' In Iraq Mostly Saudis". The Washington Post.
- ^ See also: Hafez, Mohammed M. Suicide Bomber in Iraq. United States Institute of Peace Press. ISBN 1601270046.
- ^ "Al-Maliki: Iraq won't be battleground for U.S., Iran". CNN. 31 January 2007. Archived from the original on 2 February 2007. Retrieved 31 January 2007.
- ^ "Iran involvement suspected in Karbala compound attack". CNN. 31 January 2007. Retrieved 31 January 2007.
- ^ Baer, Robert (30 January 2007). "Are the Iranians Out for Revenge?". Time. Archived from the original on 2 February 2007. Retrieved 31 January 2007.
- ^ "This Iran-backed militia helped save Iraq from ISIS. Now Washington wants them to disband". pbs.org. Accessed 9 April 2023.
- ^ "POLITICS: Israel Warned US Not to Invade Iraq after 9/11 – Inter Press Service". www.ipsnews.net. 28 August 2007. Archived from the original on 24 September 2015. Retrieved 31 August 2015.
- ^ "terror and tehran". www.pbs.org. 2 May 2002. Archived from the original on 4 June 2017. Retrieved 29 August 2017.
- ^ "Interview" (PDF). fletcher.tufts.edu. Archived from the original (PDF) on 25 January 2015.
- ^ Rosenberg, MJ. "CIA veteran: Israel to attack Iran in fall". www.aljazeera.com. Archived from the original on 19 September 2015. Retrieved 31 August 2015.
- ^ Kayer, J (16 August 2002). "Israel urges U.S. to attack". The Washington Post.
- ^ Alon, Gideon (13 August 2002). "Sharon Panel: Iraq is our biggest danger". Haaretz.
- ^ "Doug Feith: Israel didn't push for Iraq War". Ynetnews. 13 May 2008. Archived from the original on 30 September 2014. Retrieved 12 March 2015.
- ^ "Sharon Warned Bush". 13 January 2007. Archived from the original on 25 May 2009. Retrieved 18 June 2009.
- ^ "MSN – Outlook, Office, Skype, Bing, Breaking News, and Latest Videos". NBC News. 13 December 2003. Retrieved 18 June 2009.
- ^ Shavit, Ari (3 April 2003). "White Man's Burden". Haaretz. Retrieved 11 May 2019.
- ^ "Putin warns on Iraq war". CNN. 28 March 2003.
- ^ "Russia 'gave Saddam intelligence on invasion'". The Independent. 25 March 2006. Retrieved 19 September 2020.
Sources
- Bishku, Michael B. (2018), Israel and the Kurds: A Pragmatic Relationship in Middle Eastern Politics, vol. 41, Journal of South Asian and Middle Eastern Studies
Further reading
- Bellavia, David (2007). House to House: An Epic Memoir of War. Simon & Schuster. ISBN 978-1416574712.
- A Bitter Legacy: Lessons of Debaathification in Iraq (Report). International Center for Transitional Justice.
- Butt, Ahsan. 2019. "Why did the United States Invade Iraq in 2003?" Security Studies
- Dexter Filkins (17 December 2012). "General Principles: How good was David Petraeus?". The New Yorker. pp. 76–81.
- Gates, Robert M. (2014). Duty: Memoirs of a Secretary at War. New York: Alfred A. Knopf. ISBN 978-0307959478. 318 pages
- Gordon, Michael R. (2006). Cobra II: The Inside Story of the Invasion and Occupation of Iraq. Pantheon. ISBN 978-1557782328.
michael gordon cobra II.
- Larson, Luke S. (2008). Senator's Son: An Iraq War Novel. Phoenix, Arizona: Key Edition Incorporated. ISBN 978-1449969868.
- MacDonald, Michael. 2014. Overreach: Delusions of Regime Change in Iraq. Harvard University Press.
- Mikulaschek, Christoph and Jacob Shapiro. (2018). Lessons on Political Violence from America's Post-9/11 Wars. Journal of Conflict Resolution 62(1): 174–202.
- North, Richard (2009). Ministry of Defeat: The British War in Iraq 2003–2009. Continuum Publishing Corporation. ISBN 978-1441169976.
- Payne, Andrew. 2019/2020. "Presidents, Politics, and Military Strategy: Electoral Constraints during the Iraq War." International Security 44(3):163–203
- Bruce R. Pirnie; Edward O'Connell (2008). Counterinsurgency in Iraq (2003–2006). Santa Monica, CA: Rand Corporation. ISBN 978-0-8330-4297-2.
- Thomas E. Ricks (2006). Fiasco: The American Military Adventure in Iraq. Penguin. ISBN 978-1594201035.
- Robben, Antonius C.G.M., ed. (2010). Iraq at a Distance: What Anthropologists Can Teach Us About the War. Philadelphia: University of Pennsylvania Press. ISBN 978-0-8122-4203-4.
- Siracusa, Joseph M., and Laurens J. Visser, "George W. Bush, Diplomacy, and Going to War with Iraq, 2001–2003." The Journal of Diplomatic Research/Diplomasi Araştırmaları Dergisi (2019) 1#1: 1–29 online
- Wertheim, Stephen, "Iraq and the Pathologies of Primacy: The Flawed Logic That Produced the War Is Alive and Well", Foreign Affairs, vol. 102, no. 3 (May/June 2023), pp. 136–140, 142–152. "Washington is still in thrall to primacy and caught in a doom loop, lurching from self-inflicted problems to even bigger self-inflicted problems, holding up the latter while covering up the former. In this sense, the Iraq war remains unfinished business for the United States." (p. 152.)
External links
- International Center for Transitional Justice, Iraq
- Dollar cost of war: total US cost of the Iraq War
- "Bleak Pentagon study admits 'civil war' in Iraq", by Rupert Cornwell, The Independent, March 2007
- High resolution maps of Iraq, GulfWarrior.org
- Presidential address by George W. Bush on the evening of 19 March 2003, announcing war against Iraq.
- Bibliography: The Second US–Iraq War (2003– )
- 1st Major Survey of Iraq. Zogby International, 10 September 2003.
- Iraq at Polling Report.com. Chronological polls of Americans 18 and older
- Just War in Iraq 2003 (PDF) – Legal dissertation by Thomas Dyhr from University of Copenhagen.
- Iraq war stories, a Guardian and Observer archive in words and pictures documenting the human and political cost, The Guardian, April 2009.
- Iraq: The War Card Archived 3 September 2018 at the Wayback Machine. Center for Public Integrity.
- Jargin SV. "Health care in Iraq: 2013 vs. 2003". CMAJ. 17 September 2013.
- Mather-Cosgrove, Bootie (17 March 2005). "The War with Iraq: Changing Views". CBS News.
- Iraq War
- 2000s conflicts
- 2000s in Iraq
- 2000s in Iraqi Kurdistan
- 2010s conflicts
- 2010s in Iraq
- 2010s in Iraqi Kurdistan
- Presidency of George W. Bush
- George W. Bush administration controversies
- Presidency of Barack Obama
- Imperialism
- Iraq–United States relations
- History of Iraqi Kurdistan
- Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant in Iraq
- Modern history of Iraq
- Proxy wars
- United States involvement in regime change
- War on terror
- Wars involving Albania
- Wars involving Armenia
- Wars involving Australia
- Wars involving Azerbaijan
- Wars involving Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Wars involving Bulgaria
- Wars involving Denmark
- Wars involving El Salvador
- Wars involving Estonia
- Wars involving Georgia (country)
- Wars involving Honduras
- Wars involving Iceland
- Wars involving Iraq
- Wars involving Italy
- Wars involving Japan
- Wars involving Kazakhstan
- Wars involving Latvia
- Wars involving Lithuania
- Wars involving Moldova
- Wars involving Mongolia
- Wars involving New Zealand
- Wars involving Nicaragua
- Wars involving North Macedonia
- Wars involving Norway
- Wars involving Poland
- Wars involving Portugal
- Wars involving Romania
- Wars involving Singapore
- Wars involving Slovakia
- Wars involving South Korea
- Wars involving Spain
- Wars involving Thailand
- Wars involving Turkey
- Wars involving the Czech Republic
- Wars involving the Dominican Republic
- Wars involving the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant
- Wars involving the Netherlands
- Wars involving the Philippines
- Wars involving the United Kingdom
- Wars involving the United States
- Wars involving Tonga
- Wars involving Ukraine
