Strategy pattern
In computer programming, the strategy pattern (also known as the policy pattern) is a behavioral software design pattern that enables selecting an algorithm at runtime. Instead of implementing a single algorithm directly, code receives run-time instructions as to which in a family of algorithms to use.[1]
Strategy lets the algorithm vary independently from clients that use it.[2] Strategy is one of the patterns included in the influential book Design Patterns by Gamma et al.[3] that popularized the concept of using design patterns to describe how to design flexible and reusable object-oriented software. Deferring the decision about which algorithm to use until runtime allows the calling code to be more flexible and reusable.
For instance, a class that performs validation on incoming data may use the strategy pattern to select a validation algorithm depending on the type of data, the source of the data, user choice, or other discriminating factors. These factors are not known until run-time and may require radically different validation to be performed. The validation algorithms (strategies), encapsulated separately from the validating object, may be used by other validating objects in different areas of the system (or even different systems) without code duplication.
Typically, the strategy pattern stores a reference to some code in a data structure and retrieves it. This can be achieved by mechanisms such as the native function pointer, the first-class function, classes or class instances in object-oriented programming languages, or accessing the language implementation's internal storage of code via reflection.
Structure
UML class and sequence diagram

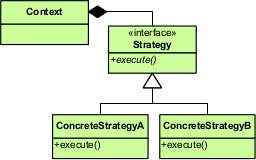
In the above UML class diagram, the Context class doesn't implement an algorithm directly.
Instead, Context refers to the Strategy interface for performing an algorithm (strategy.algorithm()), which makes Context independent of how an algorithm is implemented.
The Strategy1 and Strategy2 classes implement the Strategy interface, that is, implement (encapsulate) an algorithm.
The UML sequence diagram
shows the run-time interactions: The Context object delegates an algorithm to different Strategy objects. First, Context calls algorithm() on a Strategy1 object,
which performs the algorithm and returns the result to Context.
Thereafter, Context changes its strategy and calls algorithm() on a Strategy2 object,
which performs the algorithm and returns the result to Context.
Class diagram

Example
C#
The following example is in C#.
public class StrategyPatternWiki
{
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// Prepare strategies
var normalStrategy = new NormalStrategy();
var happyHourStrategy = new HappyHourStrategy();
var firstCustomer = new CustomerBill(normalStrategy);
// Normal billing
firstCustomer.Add(1.0, 1);
// Start Happy Hour
firstCustomer.Strategy = happyHourStrategy;
firstCustomer.Add(1.0, 2);
// New Customer
var secondCustomer = new CustomerBill(happyHourStrategy);
secondCustomer.Add(0.8, 1);
// The Customer pays
firstCustomer.Print();
// End Happy Hour
secondCustomer.Strategy = normalStrategy;
secondCustomer.Add(1.3, 2);
secondCustomer.Add(2.5, 1);
secondCustomer.Print();
}
}
// CustomerBill as class name since it narrowly pertains to a customer's bill
class CustomerBill
{
private IList<double> drinks;
// Get/Set Strategy
public IBillingStrategy Strategy { get; set; }
public CustomerBill(IBillingStrategy strategy)
{
this.drinks = new List<double>();
this.Strategy = strategy;
}
public void Add(double price, int quantity)
{
this.drinks.Add(this.Strategy.GetActPrice(price * quantity));
}
// Payment of bill
public void Print()
{
double sum = 0;
foreach (var drinkCost in this.drinks)
{
sum += drinkCost;
}
Console.WriteLine($"Total due: {sum}.");
this.drinks.Clear();
}
}
interface IBillingStrategy
{
double GetActPrice(double rawPrice);
}
// Normal billing strategy (unchanged price)
class NormalStrategy : IBillingStrategy
{
public double GetActPrice(double rawPrice) => rawPrice;
}
// Strategy for Happy hour (50% discount)
class HappyHourStrategy : IBillingStrategy
{
public double GetActPrice(double rawPrice) => rawPrice * 0.5;
}
Java
The following example is in Java.
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
interface BillingStrategy {
// Use a price in cents to avoid floating point round-off error
int getActPrice(int rawPrice);
// Normal billing strategy (unchanged price)
static BillingStrategy normalStrategy() {
return rawPrice -> rawPrice;
}
// Strategy for Happy hour (50% discount)
static BillingStrategy happyHourStrategy() {
return rawPrice -> rawPrice / 2;
}
}
class CustomerBill {
private final List<Integer> drinks = new ArrayList<>();
private BillingStrategy strategy;
public CustomerBill(BillingStrategy strategy) {
this.strategy = strategy;
}
public void add(int price, int quantity) {
this.drinks.add(this.strategy.getActPrice(price*quantity));
}
// Payment of bill
public void print() {
int sum = this.drinks.stream().mapToInt(v -> v).sum();
System.out.println("Total due: " + sum);
this.drinks.clear();
}
// Set Strategy
public void setStrategy(BillingStrategy strategy) {
this.strategy = strategy;
}
}
public class StrategyPattern {
public static void main(String[] arguments) {
// Prepare strategies
BillingStrategy normalStrategy = BillingStrategy.normalStrategy();
BillingStrategy happyHourStrategy = BillingStrategy.happyHourStrategy();
CustomerBill firstCustomer = new CustomerBill(normalStrategy);
// Normal billing
firstCustomer.add(100, 1);
// Start Happy Hour
firstCustomer.setStrategy(happyHourStrategy);
firstCustomer.add(100, 2);
// New Customer
CustomerBill secondCustomer = new CustomerBill(happyHourStrategy);
secondCustomer.add(80, 1);
// The Customer pays
firstCustomer.print();
// End Happy Hour
secondCustomer.setStrategy(normalStrategy);
secondCustomer.add(130, 2);
secondCustomer.add(250, 1);
secondCustomer.print();
}
}
Strategy and open/closed principle

According to the strategy pattern, the behaviors of a class should not be inherited. Instead, they should be encapsulated using interfaces. This is compatible with the open/closed principle (OCP), which proposes that classes should be open for extension but closed for modification.
As an example, consider a car class. Two possible functionalities for car are brake and accelerate. Since accelerate and brake behaviors change frequently between models, a common approach is to implement these behaviors in subclasses. This approach has significant drawbacks: accelerate and brake behaviors must be declared in each new Car model. The work of managing these behaviors increases greatly as the number of models increases, and requires code to be duplicated across models. Additionally, it is not easy to determine the exact nature of the behavior for each model without investigating the code in each.
The strategy pattern uses composition instead of inheritance. In the strategy pattern, behaviors are defined as separate interfaces and specific classes that implement these interfaces. This allows better decoupling between the behavior and the class that uses the behavior. The behavior can be changed without breaking the classes that use it, and the classes can switch between behaviors by changing the specific implementation used without requiring any significant code changes. Behaviors can also be changed at run-time as well as at design-time. For instance, a car object's brake behavior can be changed from BrakeWithABS() to Brake() by changing the brakeBehavior member to:
brakeBehavior = new Brake();
/* Encapsulated family of Algorithms
* Interface and its implementations
*/
public interface IBrakeBehavior {
public void brake();
}
public class BrakeWithABS implements IBrakeBehavior {
public void brake() {
System.out.println("Brake with ABS applied");
}
}
public class Brake implements IBrakeBehavior {
public void brake() {
System.out.println("Simple Brake applied");
}
}
/* Client that can use the algorithms above interchangeably */
public abstract class Car {
private IBrakeBehavior brakeBehavior;
public Car(IBrakeBehavior brakeBehavior) {
this.brakeBehavior = brakeBehavior;
}
public void applyBrake() {
brakeBehavior.brake();
}
public void setBrakeBehavior(IBrakeBehavior brakeType) {
this.brakeBehavior = brakeType;
}
}
/* Client 1 uses one algorithm (Brake) in the constructor */
public class Sedan extends Car {
public Sedan() {
super(new Brake());
}
}
/* Client 2 uses another algorithm (BrakeWithABS) in the constructor */
public class SUV extends Car {
public SUV() {
super(new BrakeWithABS());
}
}
/* Using the Car example */
public class CarExample {
public static void main(final String[] arguments) {
Car sedanCar = new Sedan();
sedanCar.applyBrake(); // This will invoke class "Brake"
Car suvCar = new SUV();
suvCar.applyBrake(); // This will invoke class "BrakeWithABS"
// set brake behavior dynamically
suvCar.setBrakeBehavior( new Brake() );
suvCar.applyBrake(); // This will invoke class "Brake"
}
}
See also
- Dependency injection
- Higher-order function
- List of object-oriented programming terms
- Mixin
- Policy-based design
- Type class
- Entity–component–system
- Composition over inheritance
References
- ^ "The Strategy design pattern - Problem, Solution, and Applicability". w3sDesign.com. Retrieved 2017-08-12.
- ^ Eric Freeman, Elisabeth Freeman, Kathy Sierra and Bert Bates, Head First Design Patterns, First Edition, Chapter 1, Page 24, O'Reilly Media, Inc, 2004. ISBN 978-0-596-00712-6
- ^ Erich Gamma, Richard Helm, Ralph Johnson, John Vlissides (1994). Design Patterns: Elements of Reusable Object-Oriented Software. Addison Wesley. pp. 315ff. ISBN 0-201-63361-2.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "The Strategy design pattern - Structure and Collaboration". w3sDesign.com. Retrieved 2017-08-12.
- ^ http://www.mcdonaldland.info/2007/11/28/40/
External links
- Strategy Pattern in UML (in Spanish)
- Geary, David (April 26, 2002). "Strategy for success". Java Design Patterns. JavaWorld. Retrieved 2020-07-20.
- Strategy Pattern for C article
- Refactoring: Replace Type Code with State/Strategy
- The Strategy Design Pattern at the Wayback Machine (archived 2017-04-15) Implementation of the Strategy pattern in JavaScript
