2016 United States presidential election: Difference between revisions
m →References: fmt. |
|||
| Line 1,192: | Line 1,192: | ||
== References == |
== References == |
||
{{Reflist| |
{{Reflist|25em}} |
||
== External links == |
== External links == |
||
Revision as of 15:53, 24 September 2016
This article documents a current event. Information may change rapidly as the event progresses, and initial news reports may be unreliable. The latest updates to this article may not reflect the most current information. (September 2016) |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
538 members of the Electoral College 270 electoral votes needed to win | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Opinion polls | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
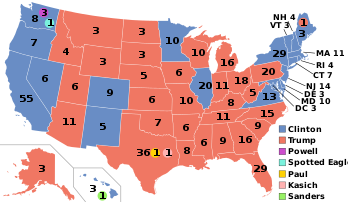 The electoral map for the 2016 election, based on apportionment following the 2010 census | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Republican Party | |
|---|---|
| Democratic Party | |
| Third parties | |
| Related races | |
| |
The United States presidential election of 2016, scheduled for Tuesday, November 8, 2016, will be the 58th quadrennial U.S. presidential election.
Voters will select presidential electors, who in turn will vote for a new president and vice president through the Electoral College. The term limit established in the Twenty-second Amendment to the United States Constitution prevents the incumbent president, Barack Obama of the Democratic Party, from being elected to a third term. The 2016 election will likely determine the 45th President and 48th Vice President of the United States.
The series of presidential primary elections and caucuses took place between February and June 2016, staggered among the 50 states, the District of Columbia and U.S. territories. This nominating process was also an indirect election, where voters cast ballots for a slate of delegates to a political party's nominating convention, who in turn elect their party's presidential nominee. Businessman and reality television personality Donald Trump became the Republican Party's presidential nominee on July 19, 2016, after defeating Texas Senator Ted Cruz, Ohio Governor John Kasich, Florida Senator Marco Rubio and other candidates in the Republican primary elections.[1] If elected, Trump would become the oldest president to take office.[2] Former Secretary of State and New York Senator Hillary Clinton became the Democratic Party's presidential nominee on July 26, 2016, after defeating Vermont Senator Bernie Sanders. Clinton is the first female presidential candidate nominated by a major political party.
Various third party and independent presidential candidates are also running in the election. Two are on the ballot in enough states to mathematically win the electoral college: Libertarian Party nominee and former Governor of New Mexico, Gary Johnson; and Green Party nominee, Jill Stein; both of whom have appeared in major national polls.[3][4] Johnson and Stein also ran as their parties' presidential nominees in the 2012 election.
Background

Article Two of the United States Constitution provides that the President and Vice President of the United States must be natural-born citizens of the United States at least 35 years old, and a resident of the United States for a period of at least 14 years. Candidates for the presidency typically seek the nomination of one of the political parties of the United States, in which case each party devises a method (such as a primary election) to choose the candidate the party deems best suited to run for the position. Traditionally, the primary elections are indirect elections where voters cast ballots for a slate of party delegates pledged to a particular candidate. The party's delegates then officially nominate a candidate to run on the party's behalf. The general election in November is also an indirect election, where voters cast ballots for a slate of members of the Electoral College; these electors in turn directly elect the President and Vice President.
Obama, a Democrat and former U.S. Senator from Illinois, is ineligible to seek reelection to a third term due to restrictions of the Twenty-second Amendment; in accordance with Section I of the Twentieth Amendment, his term expires at 12:00 noon EST on January 20, 2017.
2008 presidential election
In the 2008 election, Obama was elected president, defeating the Republican nominee, Senator John McCain of Arizona, with 53% of the popular vote and 68% of the electoral vote,[5][6] succeeding two-term Republican President George W. Bush, the former Governor of Texas. Since the end of 2009, Obama's first year in office, polling companies such as Gallup have found Obama's approval ratings to be between 40–50%.[7][8] Analysts such as Larry Sabato have noted that Obama's approval ratings could impact the 2016 campaign, having either a positive or negative effect on Clinton's campaign.[9][10]
2010 midterm elections
In the 2010 midterm elections, the Democratic Party suffered significant losses in Congress; the Republicans gained 63 seats in the House of Representatives – taking back control of the chamber in the process – and six seats in the Senate, though short of achieving a majority. As a result of the Republicans' recapture of the House after losing it to the Democrats in the 2006 midterm elections, John Boehner became the 53rd Speaker of the House of Representatives, making Obama the first President in 16 years to lose the House of Representatives in the first half of his first term in an election that was characterized by the economy's slow recovery, and the rise of the Tea Party movement.[11]
2012 presidential election
In the 2012 presidential election, Obama defeated former Governor of Massachusetts Mitt Romney with 51% of the popular vote and 62% of the electoral vote.[12] Meanwhile, despite minor losses, Republicans retained their majority of seats in the House of Representatives while Democrats increased their majority in the Senate.[6]
Speculation about the 2016 campaign began almost immediately following the 2012 campaign, with New York magazine declaring the race had begun in an article published on November 8, two days after the 2012 election.[13] On the same day, Politico released an article predicting the 2016 general election would be between Clinton and former Governor of Florida Jeb Bush, while a New York Times article named Governor of New Jersey Chris Christie and New Jersey Senator Cory Booker as potential candidates.[14][15]
2014 midterm elections
In the 2014 midterm elections, voter turnout was the lowest since 1942: 36% of eligible voters voted.[16] The Republicans retained control of the House of Representatives, increasing their majority to its largest since March 4, 1929,[17] and gained a majority in the Senate.[18]
Democratic Party
Primaries
| ||
|---|---|---|
|
First Lady of the United States
U.S. Senator from New York
U.S. Secretary of State
2008 presidential campaign 2016 presidential campaign Organizations
|
||
Former Secretary of State Hillary Clinton, who also served in the U.S. Senate and was the First Lady of the United States, became the first Democrat to formally launch a major candidacy for the presidency. Clinton made the announcement on April 12, 2015, via a video message.[19] While Nationwide opinion polls in 2015 indicated that Clinton was the front-runner for the 2016 Democratic presidential nomination, she faced challenges from Independent Vermont Senator Bernie Sanders,[20] who became the second major candidate when he formally announced on April 30, 2015, that he was running for the Democratic nomination.[21] September 2015 polling numbers indicated a narrowing gap between Clinton and Sanders.[20][22][23] On May 30, 2015, former Governor of Maryland Martin O'Malley was the third major candidate to enter the Democratic primary race.[24] On June 3, 2015, Lincoln Chafee, former Independent Governor and Republican Senator of Rhode Island, became the fourth major candidate to announce his candidacy for the Democratic nomination.[25][26] On July 2, 2015, former Virginia Senator Jim Webb became the fifth major Democratic candidate to announce his bid for the presidency.[27] On September 6, 2015, former Harvard law professor Lawrence Lessig became the sixth and final major Democratic candidate to enter the race.[28]
On October 20, 2015, Webb announced his withdrawal from the Democratic primaries, and explored a potential Independent run.[29] The next day Vice-President Joe Biden decided not to run, ending months of speculation, stating, "While I will not be a candidate, I will not be silent."[30][31] On October 23, Chafee withdrew, stating that he hoped for "an end to the endless wars and the beginning of a new era for the United States and humanity."[32] On November 2, after failing to qualify for the second DNC-sanctioned debate after adoption of a rule change negated polls which before might have necessitated his inclusion in the debate, Lessig withdrew as well, narrowing the field to Clinton, O'Malley, and Sanders.[33]
On February 1, 2016, in an extremely close contest, Clinton won the Iowa caucuses by a margin of 0.2% over Sanders. After winning no delegates in Iowa, O'Malley withdrew from the presidential race that day. On February 9, Sanders bounced back to win the New Hampshire primary with 60% of the vote. In the remaining two February contests, Clinton won the Nevada caucuses with 53% of the vote and scored a decisive victory in the South Carolina primary with 73% of the vote.[34][35] On March 1, 11 states participated in the first of four "Super Tuesday" primaries. Clinton won Alabama, Arkansas, Georgia, Massachusetts, Tennessee, Texas, and Virginia and 504 pledged delegates, while Sanders won Colorado, Minnesota, Oklahoma and his home state of Vermont and 340 delegates. The following weekend, Sanders won victories in Kansas, Nebraska and Maine with 15- to 30-point margins, while Clinton won the Louisiana primary with 71% of the vote. On March 8, despite never having a lead in the Michigan primary, Sanders won by a small margin of 1.5% and outperforming polls by over 19 points, while Clinton won 83% of the vote in Mississippi.[36] On March 15, the second of four "Super Tuesday" primaries, Clinton won in Florida, Illinois, Missouri, North Carolina and Ohio. Between March 22 and April 9, 2016, Sanders won six caucuses in Idaho, Utah, Alaska, Hawaii, Washington and Wyoming, as well as the Wisconsin primary, while Clinton won the Arizona primary. On April 19, Clinton won the New York primary with 58% of the vote. On April 26, in the third of four "Super Tuesday" primaries dubbed the "Acela primary," she won contests in Connecticut, Delaware, Maryland and Pennsylvania, while Sanders won in Rhode Island. Over the course of May, Sanders accomplished another surprise win in the Indiana primary[37] and also won in West Virginia and Oregon, while Clinton won the Guam caucus and Kentucky primary.
On June 4 and 5, Clinton won two victories in the Virgin Islands caucus and Puerto Rico primary. On June 6, 2016, the Associated Press and NBC News reported that Clinton had become the presumptive nominee after reaching the required number of delegates, including pledged delegates and superdelegates, to secure the nomination, becoming the first woman to ever clinch the presidential nomination of a major United States political party.[38] On June 7, Clinton secured a majority of pledged delegates after winning primaries in California, New Jersey, New Mexico and South Dakota, while Sanders only won in Montana and North Dakota. Clinton also won the final primary in Washington, D.C. on June 14. At the conclusion of the primary process, Clinton had won 2,204 pledged delegates (54% of the total) awarded by the primary elections and caucuses, while Sanders had won 1,847 (46%). Out of the 714 unpledged delegates or "superdelegates" who were set to vote in the convention in July, Clinton received endorsements from 560 (78%), while Sanders received 47 (7%).[39]
Although Sanders had not formally dropped out of the race, he announced on June 16, 2016, that his main goal in the coming months would be to work with Clinton to defeat Trump in the general election.[40] On July 8, appointees from the Clinton campaign, the Sanders campaign, and the Democratic National Committee negotiated a draft of the party's platform.[41] On July 12, Sanders formally endorsed Clinton at a rally in New Hampshire in which he appeared with Clinton.[42] On July 22, three days before the start of the Democratic National Convention, the Clinton campaign announced that Virginia Senator Tim Kaine had been selected as her running mate. Clinton is the first female presidential candidate nominated by a major political party.
Nominees
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hillary Clinton | Tim Kaine | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| for President | for Vice President | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 67th U.S. Secretary of State (2009–2013) |
U.S. Senator from Virginia (2013–present) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Campaign | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| [43][44][45] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Other major candidates
The following candidates were frequently interviewed by major broadcast networks and cable news channels, and were listed in publicly published national polls. Lessig was invited to one forum, but withdrew when rules were changed which prevented him from participating in officially sanctioned debates.
Clinton received 16,849,779 votes in the primary.
| Candidates in this section are sorted by date of withdrawal from the primaries | ||||||||
| Bernie Sanders | Martin O'Malley | Lawrence Lessig | Lincoln Chafee | Jim Webb | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 | ||||
Governor of Maryland (2007–2015) |
(2009–2016) |
Governor of Rhode Island (2011–2015) |
from Virginia (2007–2013) | |||||
13,167,848 primary votes and 1,846 delegates |
110,423 votes |
4 write-in votes in New Hampshire |
0 votes |
2 write-in votes in New Hampshire | ||||
Vice presidential selection
In April 2016, the Clinton campaign began to put together a list of 15 to 20 individuals to vet for the position of running mate, even though Sanders continued to challenge Clinton in the Democratic primaries.[51] In mid-June, the The Wall Street Journal reported that Clinton's shortlist included Representative Xavier Becerra of California, Senator Cory Booker of New Jersey, Senator Sherrod Brown of Ohio, Housing and Urban Development Secretary Julián Castro of Texas, Mayor of Los Angeles Eric Garcetti of California, Senator Tim Kaine of Virginia, Labor Secretary Tom Perez of Maryland, Representative Tim Ryan of Ohio, and Senator Elizabeth Warren of Massachusetts.[52] Subsequent reports stated that Clinton was also considering Secretary of Agriculture Tom Vilsack, retired Admiral James Stavridis, and Governor John Hickenlooper of Colorado.[53] In discussing her potential vice presidential choice, Clinton stated that the most important attribute she looked for was the ability and experience to immediately step into the role of president.[53]
On July 22, Clinton announced that she had chosen Senator Tim Kaine of Virginia as her running mate.[54] The delegates at the 2016 Democratic National Convention, which took place July 25–28, formally nominated the Democratic ticket.
Republican Party
Primaries
| ||
|---|---|---|
|
Business and personal 45th & 47th President of the United States Tenure
Impeachments Civil and criminal prosecutions  |
||
Seventeen major candidates entered the race starting March 23, 2015, when Senator Ted Cruz of Texas was the first to announce his candidacy: former Governor Jeb Bush of Florida, retired neurosurgeon Ben Carson of Maryland, Governor Chris Christie of New Jersey, businesswoman Carly Fiorina of California, former Governor Jim Gilmore of Virginia, Senator Lindsey Graham of South Carolina, former Governor Mike Huckabee of Arkansas, former Governor Bobby Jindal of Louisiana, Governor John Kasich of Ohio, former Governor George Pataki of New York, Senator Rand Paul of Kentucky, former Governor Rick Perry of Texas, Senator Marco Rubio of Florida, former Senator Rick Santorum of Pennsylvania, businessman Donald Trump of New York and Governor Scott Walker of Wisconsin. This was the largest presidential primary field for any political party in American history.[55]
Prior to the Iowa caucuses on February 1, 2016, Perry, Walker, Jindal, Graham and Pataki withdrew due to low polling numbers. Despite leading many polls in Iowa, Trump came in second to Cruz, after which Huckabee, Paul and Santorum withdrew due to poor performances at the ballot box. Following a sizable victory for Trump in the New Hampshire primary, Christie, Fiorina and Gilmore abandoned the race. Bush followed suit after scoring fourth place to Trump, Rubio and Cruz in South Carolina. On March 1, 2016, the first of four "Super Tuesday" primaries, Rubio won his first contest in Minnesota, Cruz won Alaska, Oklahoma and his home of Texas and Trump won the other seven states that voted. Failing to gain traction, Carson suspended his campaign a few days later.[56] On March 15, 2016, the second of four "Super Tuesday" primaries, Kasich won his only contest in his home state of Ohio and Trump won five primaries including Florida. Rubio suspended his campaign after losing his home state,[57] but retained a large share of his delegates for the national convention, which he released to Trump.[57]
Between March 16 and May 3, 2016, only three candidates remained in the race: Trump, Cruz and Kasich. Cruz won most delegates in four Western contests and in Wisconsin, keeping a credible path to denying Trump the nomination on first ballot with 1,237 delegates. Trump then augmented his lead by scoring landslide victories in New York and five Northeastern states in April and he grabbed all 57 delegates in the Indiana primary of May 3, 2016. Without any further chances of forcing a contested convention, both Cruz[58] and Kasich[59] suspended their campaigns. Trump remained the only active candidate and was declared the presumptive Republican nominee by Republican National Committee chairman Reince Priebus on the evening of May 3, 2016.[60]
It is the first election since 1944 in which both major party candidates were from the same home state. In both cases, the two candidates were from New York.
Nominees
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Donald Trump | Mike Pence | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| for President | for Vice President | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chairman of The Trump Organization (1971–present) |
50th Governor of Indiana (2013–present) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Campaign | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| [61][62][63] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Other major candidates
Major candidates were determined by the various media based on common consensus. The following were invited to sanctioned televised debates based on their poll ratings.
Trump received 14,010,177 total votes in the primary. He, Cruz, Rubio and Kasich each won at least one primary.
Vice presidential selection
Donald Trump turned his attention towards selecting a running mate after he became the presumptive nominee on May 4, 2016.[98] In mid-June, Eli Stokols and Burgess Everett of Politico reported that the Trump campaign was considering New Jersey Governor Chris Christie, former Speaker of the House Newt Gingrich of Georgia, Alabama Senator Jeff Sessions, and Oklahoma Governor Mary Fallin.[99] A June 30 Washington Post report also included Senators Bob Corker of Tennessee, Richard Burr of North Carolina, Tom Cotton of Arkansas, Joni Ernst of Iowa, and Indiana Governor Mike Pence as individuals still being considered for the ticket.[100] Trump also stated that he was considering two military generals for the position, including retired Lieutenant General Michael Flynn.[101]
In July 2016, it was reported that Trump had narrowed his list of possible running mates down to three: Christie, Gingrich, and Pence.[102]
On July 14, 2016, several major media outlets reported that Trump had selected Pence as his running mate. Trump confirmed these reports in a message on Twitter on July 15, 2016, and formally made the announcement the following day in New York.[103][104][105][106][107] On July 19, the second night of the 2016 Republican National Convention, Pence won the Republican vice presidential nomination by acclamation.[108]
Major third parties
Parties in this section have obtained ballot access or write-in access in enough states to theoretically obtain the minimum number of electoral votes (270 out of 538) needed to win the election. Individuals included in this section have received the presidential nomination of a third party, or are formally running as an independent candidate. Within each party, candidates are listed alphabetically by surname.
Libertarian Party
| ||
|---|---|---|
|
Governor of New Mexico
Presidential campaigns
|
||
Ballot access to all 538 electoral votes[109]
Nominees
Libertarian Party ticket, 2016 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gary Johnson | William Weld | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| for President | for Vice President | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 29th Governor of New Mexico (1995–2003) |
68th Governor of Massachusetts (1991–1997) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Campaign | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Green Party
| ||
|---|---|---|
|
Massachusetts campaigns
Presidential campaigns
Political party affiliations
|
||

Ballot access to 480 (522 with write-in) electoral votes[112][113]
- As write-in: Georgia, Indiana, North Carolina.[112][114]
- Ballot access lawsuit pending: Oklahoma[115]
- States with no ballot access: Nevada, South Dakota[112][116]
Nominees
| Jill Stein | Ajamu Baraka | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| for President | for Vice President | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physician from Lexington, Massachusetts |
Activist from Washington, D.C. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Campaign | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| [117][118] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Constitution Party
Ballot access to 207 (334 with write-in) electoral votes:[119][120]
- As write-in: Alabama, Delaware, Georgia, Indiana, Maine, Maryland, New Hampshire, Ohio, Oregon, Rhode Island, Texas, Vermont[119][121][122]
- Write-in anticipated: Arizona, California, Connecticut, Illinois, Kansas, Kentucky, Massachusetts, Montana, Nebraska, New York, North Carolina, Tennessee, Virginia[119]
- States with no ballot access: Oklahoma[119]
Nominees
| Darrell Castle | Scott Bradley | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| for President | for Vice President | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Attorney from Memphis, Tennessee |
Businessman from Utah | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Campaign | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| [123] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Evan McMullin's candidacy

Ballot access to 84 (303 with write-in) electoral votes:
- As write-in: Alabama, Alaska, Delaware, Georgia, Maine, Maryland, New Hampshire, New Jersey, Ohio, Oregon, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, Texas, Vermont, West Virginia, Wyoming[121][122][124][125][126][127][128][129]
- States with no ballot access: Arizona, California, Connectictut, District of Columbia, Florida, Hawaii, Illinois, Indiana, Kansas, Massachussetts, Michigan, Mississippi, Missouri, Montana, Nebraska, Nevada, New York, North Carolina, North Dakota, Oklahoma, South Dakota, Tennessee, Washington
| Independent ticket, 2016 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Evan McMullin | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| for President | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chief policy director for the House Republican Conference (2015-2016)[130] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Campaign | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| [131] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Other third parties and independents
Parties and candidates in this section have attained ballot access in one or more states but have not obtained access to the minimum number of electoral votes needed to theoretically win the election. Unless otherwise specified, individuals included in this section have either received the presidential nomination of a minor party, or are officially running as an independent presidential candidate.
| Party | Presidential nominee | Vice presidential nominee | Electors (write-in) |
States with ballot access (write-in) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Independent |
Rocky De La Fuente Businessman from San Diego, California |
Michael Steinberg Lawyer from Florida |
147 (181) |
Alaska, Colorado, Florida, Idaho, Iowa, Kentucky, Minnesota, Mississippi, Montana, Nevada, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New Mexico, North Dakota, Rhode Island, Tennessee, Utah, Vermont, Wisconsin, Wyoming[120][133][134][135][136][137][138] |
| Party for Socialism and Liberation |
Gloria La Riva Newspaper printer and activist from California |
Eugene Puryear Activist from Washington, D.C. |
112 (157) |
California, Colorado, Iowa, Louisiana, New Jersey, New Mexico, Vermont, Washington[142][143] (Alabama, Delaware, New Hampshire, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, West Virginia)[139][124][125] |
| Socialist Workers Party | Alyson Kennedy Mineworker and Labor Leader from Illinois |
Osborne Hart of Pennsylvania |
70 (124) |
Colorado, Louisiana, Minnesota, New Jersey, Tennessee, Utah, Washington[142] (Alabama, Iowa, New Hampshire, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, Vermont)[139] |
| Workers World Party | Monica Moorehead perennial candidate and political activist from Alabama[144] |
Lamont Lilly of North Carolina[145] |
30 (130) |
New Jersey, Utah, Wisconsin[142] (Alabama, Indiana, Iowa, New Hampshire, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, Texas, Vermont, West Virginia)[139][124][146][147] |
| Socialist Party USA |
Mimi Soltysik former National Co-Chair of the Socialist Party USA from California[149] Campaign |
Angela Walker of Wisconsin |
25 (140) |
Colorado, Michigan[142][143] (Alabama, Indiana, Iowa, New Hampshire, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, Texas, Utah, Vermont)[139][146][147][150] |
| America's Party | Tom Hoefling activist from Iowa[151] |
Steve Schulin of South Carolina |
23 (154) |
Arkansas, Colorado, Louisiana[142] (Alabama, Georgia, Indiana, Iowa, New Hampshire, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, Texas, Utah, Vermont)[121][139][146][147][150] |
| Prohibition Party | James Hedges former Tax Assessor for Thompson Township, Fulton County, Pennsylvania[152][153] |
Bill Bayes of Mississippi[152] |
21 (96) |
Arkansas, Colorado, Mississippi[142] (Alabama, Iowa, Maryland, New Hampshire, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, Vermont, West Virginia)[122][139][124] |
| Independent | Mike Smith Lawyer, Colorado |
Daniel White | 20 (110) |
Colorado, Tennessee[142] (Alabama, Alaska, Georgia, Iowa, New Hampshire, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, Utah, Vermont, West Virginia)[139][124][127][150] |
| Independent | Richard Duncan of Ohio |
Ricky Johnson | 18 (136) |
Ohio[154] (Alabama, Alaska, Delaware, Florida, Indiana, Iowa, Maryland, New Hampshire, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, Vermont, West Virginia)[122][139][124][143][125][127][146] |
| Independent | Laurence Kotlikoff Economics Professor at Boston University, Massachusetts |
Edward E. Leamer Economics Professor at UCLA, California |
17 (199) |
Colorado, Louisiana[142] (Alabama, Alaska, Florida, Georgia, Indiana, Iowa, Maine, Maryland, New Hampshire, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, Texas, Utah, Vermont, West Virginia)[122][139][124][143][127][146][147][150][155][156] |
| Veterans Party of America | Chris Keniston reliability engineer from Texas[157] |
Deacon Taylor of Nevada[158] |
17 (80) |
Colorado, Louisiana[142] (Alabama, Alaska, Iowa, New Hampshire, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, Vermont)[139][127] |
| Legal Marijuana Now Party | Dan Vacek of Minnesota |
Mark Elworth Jr. of Nebraska |
16 (70) |
Iowa, Minnesota[142] (Alabama, New Hampshire, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, Vermont)[139] |
| Independent | Lynn Kahn Doctor of Clinical Psychology from Maryland |
Kathleen Monahan of Florida |
12 (71) |
Arkansas, Iowa[134][142] (Alabama, New Hampshire, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, Vermont, West Virginia)[139][124] |
| American Solidarity Party | Mike Maturen sales professional and magician from Michigan |
Juan Muñoz of Texas |
9 (135) |
Colorado[159] (Alabama, Georgia, Iowa, Maryland, New Hampshire, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, Texas, Vermont)[121][122][139][147] |
| Independent | Joseph Allen Maldonado of Oklahoma |
Douglas K. Terranova | 9 (101) |
Colorado[159] (Alabama, Alaska, Delaware, Indiana, Iowa, Maryland, New Hampshire, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, Vermont, West Virginia)[122][139][124][125][127][146] |
| Independent | Ryan Alan Scott | Bruce Kendall Barnard | 9 (69) |
Colorado[159] (Alabama, Iowa, New Hampshire, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, Vermont)[139] |
| Approval Voting Party | Frank Atwood of Colorado |
Blake Huber of Colorado |
9 (69) |
Colorado[159] (Alabama, Iowa, New Hampshire, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, Vermont)[139] |
| Independent American Party | Kyle Kenle Kopitke of Michigan |
Narthan R. Sorenson | 9 (69) |
Colorado[159] (Alabama, Iowa, New Hampshire, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, Vermont)[139] |
| Nutrition Party | Rod Silva restaurateur from New Jersey[160][161] |
Richard Silva | 9 (69) |
Colorado[159] (Alabama, Iowa, New Hampshire, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, Vermont)[139] |
| United States Pacifist Party | Bradford Lyttle peace activist from Illinois |
Hannah Walsh | 9 (69) |
Colorado[159] (Alabama, Iowa, New Hampshire, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, Vermont)[139] |
| American Party (South Carolina) | Peter Skewes Animal Science Professor at Clemson University, South Carolina |
undeclared | 9 (69) |
South Carolina[162] (Alabama, Iowa, New Hampshire, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, Vermont)[139] |
| Independent | Princess Khadijah Jacob-Fambro of California |
Milton Fambro of California |
8 (68) |
Louisiana[163] (Alabama, Iowa, New Hampshire, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, Vermont)[139] |
| Socialist Equality Party | Jerry White peace activist from Michigan |
Niles Niemuth journalist from Wisconsin |
8 (68) |
Louisiana[163] (Alabama, Iowa, New Hampshire, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, Vermont)[139] |
| Independent American Party | Rocky Giordani from California |
Farley Anderson activist from Utah |
6 (66) |
Utah[150] (Alabama, Iowa, New Hampshire, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, Vermont)[139] |
| Constitution Party of Idaho | Scott Copeland of Texas |
J.R. Meyers | 4 (64) |
Idaho[164] (Alabama, Iowa, New Hampshire, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, Vermont)[139] |
Swing states

Presidential campaigns focus their resources on a relatively small number of competitive states, referred to as swing or battleground states.[165] Potential swing states are: Florida, Pennsylvania, Michigan, Ohio, North Carolina, Colorado, Virginia, Wisconsin, Nevada, Iowa and New Hampshire.[166][167] Florida is the largest swing state and has been won by the overall winner every election since 1992. Ohio is another large swing state and has a perfect bellwether record since 1960. The states regarded as competitive can fluctuate, as the polls fluctuate.
A pundit consensus came forth throughout the primary election season regarding swing states. Contributors included Larry Sabato's Crystal Ball and Nate Silver of FiveThirtyEight.[168] From the results of presidential elections from 2004 through to 2012, a general conclusion was reached that the Democratic and Republican parties start with a default electoral vote count of about 191 each.[169][170] The margins required to constitute a swing state are vague, however and local factors can come into play.[171][172] Left-leaning states in the Rust Belt could become more conservative, as Trump mostly appeals to blue-collar workers.[173] They represent a large portion of the American populace, and were a major factor in Trump's eventual nomination. Trump's primary campaign was propelled by victories in Democratic states, and his supporters often did not identify as Republican.
In Maine and Nebraska, two delegates are given to whoever has the most overall votes, and the winner of every congressional district receives one electoral vote.[174] Every other state awards all of its electoral votes to the candidate with the highest vote percentage.[175] Media reports indicate both candidates plan to concentrate on Florida, Pennsylvania, Wisconsin, Ohio and North Carolina.[176][177]
Among the Republican-leaning states, potential Democratic targets include Nebraska's second congressional district, Missouri, Indiana, Georgia, and Arizona.[178] Trump's relatively poor polling in some traditionally Republican states, such as Utah, has raised the possibility they could vote for Clinton, despite easy wins there by recent Republican nominees.[179] However, multiple analysts have asserted that Utah is not a viable Democratic destination.[180][181]
Sites and individuals publish electoral predictions. These generally rate the race by the probability either of the two main parties wins each state. "Tossup" is generally used to indicate that neither party has an advantage, "lean" to indicate a party has a slight edge, "likely" to indicate a party has a clear advantage, and "safe" to indicate a party is heavily favored. States ratings from the Cook Political Report, Sabato's Crystal Ball, or the Rothenberg-Gonzales Political Report are included in the table below. The state's Cook PVI and the latest swing for each state are also listed, as well as competitive congressional districts in Maine and Nebraska.
| State | Electoral votes |
2012 margin |
2014 Cook PVI |
Cook Sept. 22 2016[182] |
RCP Sept. 15 2016[183] |
Roth. Sept. 16 2016[184] |
Sabato Sept. 19 2016[185] |
Last swing[186] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arizona | 11 | 9.1 R | R+7 | Lean R | Tossup | Lean R | Lean R | 1996 |
| Colorado | 9 | 5.4 D | D+1 | Lean D | Tossup | Lean D | Lean D | 2004 |
| Florida | 29 | 0.9 D | R+2 | Tossup | Tossup | Tossup | Tossup | 2004 |
| Georgia | 16 | 7.8 R | R+6 | Lean R | Tossup | Lean R | Lean R | 1992 |
| Iowa | 6 | 5.8 D | D+1 | Lean R | Tossup | Tilt D | Lean R | 2004 |
| Maine CD-2 | 1 | 8.6 D | D+2 | Tossup | Tossup | No rating | Lean R | 1988 |
| Michigan | 16 | 9.5 D | D+4 | Lean D | Tossup | D Favored | Lean D | 1988 |
| Nebraska CD-2 | 1 | 7.2 R | R+4 | Tossup | Lean R | No rating | Tossup | 2008 |
| Nevada | 6 | 6.7 D | D+2 | Tossup | Tossup | Tilt D | Tossup | 2004 |
| New Hampshire | 4 | 5.6 D | D+1 | Lean D | Tossup | Lean D | Lean D | 2000 |
| North Carolina | 15 | 2.0 R | R+3 | Tossup | Tossup | Tossup | Tossup | 2008 |
| Ohio | 18 | 3.0 D | R+1 | Tossup | Tossup | Tossup | Lean R | 2004 |
| Pennsylvania | 20 | 5.4 D | D+1 | Lean D | Tossup | Lean D | Lean D | 1988 |
| Virginia | 13 | 3.9 D | Even | Likely D | Tossup | Lean D | Lean D | 2004 |
| Wisconsin | 10 | 6.9 D | D+2 | Lean D | Tossup | Tilt D | Lean D | 1984 |
Party conventions
- Constitution Party
- April 13–16, 2016: Constitution Party National Convention was held in Salt Lake City, Utah.[187]
- Libertarian Party
- Republican Party
- Democratic Party
- July 25–28, 2016: Democratic National Convention was held in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania.[192]
- Green Party
Campaign finance
This is an overview of the money used in the campaign as it is reported to Federal Election Commission (FEC) and released in September 2016. Outside groups are independent expenditure only committees—also called PACs and SuperPACs. The sources of the numbers are the FEC and Center for Responsive Politics.[195] Some spending totals are not available, due to withdrawals before the FEC deadline. As of September 2016, ten candidates with ballot access have filed financial reports with the FEC.
| Candidate | Campaign committee (as of August 31) | Outside groups (as of September 12) | Total spent | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Money raised | Money spent | Cash on hand | Debt | Money raised | Money spent | Cash on hand | ||
| Hillary Clinton[196][197] | $386,343,313 | $317,914,036 | $68,429,276 | $214,311 | $143,509,897 | $102,406,835 | $41,103,062 | $420,320,871 |
| Donald Trump[198][199] | $169,731,955 | $119,471,512 | $50,260,442 | $0 | $40,007,484 | $27,773,044 | $12,234,440 | $147,244,556 |
| Rocky De La Fuente[200] | $6,941,792 | $6,922,609 | $19,183 | $6,924,793 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $6,922,609 |
| Gary Johnson[201][202] | $7,937,914 | $5,445,399 | $2,493,150 | $1,538,118 | $530,100 | $5,000 | $525,100 | $5,450,399 |
| Jill Stein[203][204] | $2,762,007 | $2,608,275 | $153,732 | $40,000 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $2,608,275 |
| Evan McMullin[205] | $322,441 | $277,814 | $44,626 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $277,814 |
| Gloria La Riva[206] * | $25,234 | $10,092 | $15,140 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $10,092 |
| Darrell Castle[207] * | $10,289 | $7,313 | $2,976 | $2,500 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $7,313 |
| Monica Moorehead[208] * | $5,320 | $3,882 | $1,437 | $2,000 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $3,882 |
| Peter Skewes[209] * | $6,994 | $3,399 | $7,189 | $8,000 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $3,399 |
| * Last quarterly report filed June 30 | ||||||||
Debates
Primary election debates
General election debates
The Commission on Presidential Debates (CPD), a non-profit organization, plans to host debates between qualifying presidential and vice-presidential candidates. According to the commission's website, to be eligible to opt to participate in the anticipated debates, "... in addition to being Constitutionally eligible, candidates must appear on a sufficient number of state ballots to have a mathematical chance of winning a majority vote in the Electoral College, and have a level of support of at least 15 percent of the national electorate as determined by five selected national public opinion polling organizations, using the average of those organizations' most recently publicly-reported results at the time of the determination."[210]
The three locations chosen to host the presidential debates, and the one location selected to host the vice presidential debate, were announced on September 23, 2015. The site of the first debate was originally designated as Wright State University in Dayton, Ohio; however, due to rising costs and security concerns, the debate was moved to Hofstra University in Hempstead, New York.[211]
On August 19, Trump's campaign manager confirmed that he would participate in a series of three debates.[212][213][214][215] Trump had complained that two of the scheduled debates, one on September 26 and the other October 9, will have to compete for viewers with National Football League games, referencing the similar complaints made regarding the dates with low expected ratings during the Democratic Party presidential debates.[216]
The Free & Equal Elections Foundation plans to host an open debate among all presidential candidates who have ballot access sufficient to represent a majority of electoral votes.[217] It is to be held at the University of Colorado Boulder's Macky Auditorium on October 25, 2016.[218] As of May 2016[update], the nominees of the Democratic, Republican, Libertarian, and Green parties have been invited to participate.[218]
| No. | Date | Time | Host | City | Moderator(s) | Participants | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | September 26, 2016 | 9:00 ET | Hofstra University | Hempstead, New York | Lester Holt | Hillary Clinton Donald Trump | |||||||||||||||
| VP | October 4, 2016 | TBA | Longwood University | Farmville, Virginia | Elaine Quijano | Tim Kaine Mike Pence | |||||||||||||||
| P2 | October 9, 2016 | TBA | Washington University in St. Louis | St. Louis, Missouri | Anderson Cooper Martha Raddatz |
TBD | |||||||||||||||
| P3 | October 19, 2016 | TBA | University of Nevada, Las Vegas | Las Vegas, Nevada | Chris Wallace | TBD | |||||||||||||||
| P4 | October 25, 2016 | 4 pm MT | University of Colorado Boulder | Boulder, Colorado | TBA | TBD | |||||||||||||||
| = Sponsored by the CPD; = Sponsored by Free & Equal | |||||||||||||||||||||
Forecasting
There are many ways to try and predict the outcome of this (or any other) election. Since the advent of scientific polling in 1936, opinion polls have been a nearly universally accepted method to predict the outcome of elections throughout the world. More recently, prediction markets have been formed, starting in 1988 with Iowa Electronic Markets.
Academic scholars have constructed models of voting behavior to forecast the outcomes of elections. An early successful model which is still being used is The Keys to the White House by Allan Lichtman. Election forecasting in the United States was first brought to the attention of the wider public by Nate Silver and his FiveThirtyEight website in 2008. For the 2016 election, there are many competing models: FiveThirtyEight, The Upshot at the New York Times, Daily Kos, Princeton Election Consortium, Cook Political Report, Rothenberg and Gonzales.
Finally, PredictWise aggregates information from betting markets, opinion polls, and bookie data, and PollyVote takes a simple average of six types of inputs: prediction markets, index models, expert judgment, citizen forecasts, poll aggregators and econometric models. PollyVote's final predictions of the last three presidential elections were within 0.9% of the two-party popular vote. In 2016, it has shown a Democratic advantage of 4 to 7 percentage points since March.
All of these models have consistently shown a Democratic advantage (of varying sizes) ever since the nominees were confirmed.
- Nationwide opinion polling for the United States presidential election, 2016
- Statewide opinion polling for the United States presidential election, 2016
See also
- United States Senate elections, 2016
- United States House of Representatives elections, 2016
- United States gubernatorial elections, 2016
- United States presidential election, 2016 timeline
- Fundraising in the United States presidential election, 2016
- Social media in the United States presidential election, 2016
References
- ^ Collinson, Stephen; Kopan, Tal (July 19, 2016). "It's official: Trump is Republican nominee". CNN. Retrieved July 19, 2016.
- ^ Kurtzleben, Danielle (June 14, 2016). "It's Trump's Birthday. If He Wins, He'd Be The Oldest President Ever To Take Office". NPR. Retrieved September 23, 2016.
- ^ "Dr. Jill Stein secures Green Presidential nomination, rises to 5% in national poll". Jill2016.com. June 15, 2016. Retrieved June 15, 2016.
- ^ Stuart, Tessa (May 31, 2016). "Green Party's Jill Stein on Why Bernie Sanders Should Go Third-Party". Rolling Stone. Retrieved June 10, 2016.
- ^ "United States House of Representatives floor summary for Jan 8, 2009". Clerk.house.gov. Retrieved January 30, 2009.
- ^ a b "Federal elections 2008" (PDF). Federal Election Commission. Retrieved May 11, 2015.
- ^ "Presidential Approval Ratings – Barack Obama". Gallup. Retrieved January 19, 2016.
- ^ "Election Other – President Obama Job Approval". RealClearPolitics. Retrieved December 24, 2015.
- ^ Sabato, Larry J. (April 17, 2015). "Clinton's Real Opponent: Barack Obama". Politico. Retrieved May 11, 2015.
- ^ Cohn, Nate (January 16, 2015). "What a Rise in Obama's Approval Rating Means for 2016". The New York Times. Retrieved May 11, 2015.
- ^ "Mid-term Elections 2010: Democrats lose the House in Republican tsunami". Daily Mail.
- ^ "President Map". The New York Times. November 29, 2012. Retrieved May 11, 2015.
- ^ Amira, Dan (November 8, 2012). "Let the 2016 Campaign Season Begin!". New York. Retrieved July 5, 2015.
- ^ Martin, Johnathon; Haberman, Maggie (November 8, 2012). "2016 election: Hillary Clinton vs. Jeb Bush?". Politico. Retrieved July 5, 2015.
- ^ Barbaro, Micharl (November 8, 2012). "After Obama, Christie Wants a G.O.P. Hug". The New York Times. Retrieved July 5, 2015.
- ^ "2014 midterm election turnout lowest in 70 years | PBS NewsHour". PBS NewsHour. Retrieved December 5, 2015.
- ^ Sullivan, Sean (December 17, 2014). "McSally win gives GOP historic majority in House". The Washington Post. Retrieved April 1, 2016.
- ^ Collinson, Stephen (November 5, 2014). "Republicans seize Senate, gaining full control of Congress". CNN. Retrieved August 25, 2016.
- ^ Keith, Tamara; Montanar, Domenico (April 10, 2015). "Hillary Clinton Expected To Go Small With Big Announcement". NPR. Retrieved April 12, 2015.
- ^ a b "Second straight poll shows Bernie Sanders leading in New Hampshire". Boston Globe. Retrieved August 26, 2015.
- ^ Merica, Dan (April 30, 2015). "Bernie Sanders is running for president". CNN. Retrieved July 6, 2015.
- ^ "Bernie Sanders surpasses Hillary Clinton in New Hampshire polls". The Huffington Post. August 25, 2015. Retrieved August 25, 2015.
- ^ "Huffpost Pollster". The Huffington Post. October 1, 2015. Retrieved October 1, 2015.
- ^ Jackson, David; Cooper, Allen (May 30, 2015). "Martin O'Malley jumps into presidential race". USA Today. Retrieved May 30, 2015.
- ^ DelReal, Jose A. (June 3, 2015). "Lincoln Chafee announces long-shot presidential bid". The Washington Post. Retrieved June 3, 2015.
- ^ "Rhode Island's Chafee enters 2016 Democratic contest". Boston Herald. Associated Press. June 3, 2015. Retrieved June 3, 2015.
- ^ Catanese, David (July 2, 2015). "Jim Webb Announces For President". U.S. News & World Report. Retrieved July 2, 2015.
- ^ Meyer, Theodoric (September 6, 2015). "Lessig: I'm running for president". Slate. Retrieved September 7, 2015.
- ^ "Jim Webb to consider running as an independent". POLITICO. Retrieved October 25, 2015.
- ^ "Biden says he's not running in 2016". OnPolitics. Retrieved October 25, 2015.
- ^ "Joe Biden Not Running for President". ABC News. October 21, 2015. Retrieved October 25, 2015.
- ^ Wagner, John; Weigel, David (October 23, 2015). "Lincoln Chafee ends Democratic bid for president". The Washington Post. ISSN 0190-8286. Retrieved October 25, 2015.
- ^ a b Strauss, Daniel (November 2, 2015). "Lessig drops out of presidential race". Politico. Retrieved November 2, 2015.
- ^ "Nevada Caucus Results". The New York Times. Retrieved February 28, 2016.
- ^ "South Carolina Primary Results". The New York Times. Retrieved February 28, 2016.
- ^ "Why The Polls Missed Bernie Sanders's Michigan Upset". FiveThirtyEight. March 9, 2016. Retrieved May 1, 2016.
- ^ Roberts, Dan; Jacobs, Ben (May 4, 2016). "Bernie Sanders pulls off shock victory over Hillary Clinton in Indiana". The Guardian. Retrieved May 4, 2016.
- ^ Dann, Carrie (June 6, 2016). "Clinton hits 'magic number' of delegates to clinch nomination". NBC News. Retrieved June 7, 2016.
- ^ "Democratic Convention 2016". thegreenpapers.com. Retrieved May 14, 2016.
- ^ "Sanders vows to help Clinton beat Trump, but keeps campaign alive". Reuters. June 17, 2016. Retrieved June 20, 2016.
- ^ Sentinel, Orlando. "Sanders backers frustrated by defeats at Orlando platform meeting". Retrieved July 25, 2016.
- ^ Reily, Molly (July 12, 2016). "Bernie Sanders Endorses Hillary Clinton For President". Huffington Post. Retrieved July 13, 2016.
- ^ Chozick, Amy. "Hillary Clinton Announces 2016 Presidential Bid". The New York Times. Retrieved April 12, 2015.
- ^ Karni, Annie (April 12, 2015). "Hillary Clinton formally announces 2016 run". Politico. Retrieved April 18, 2015.
- ^ "Hillary Rodham Clinton FEC filing" (PDF). FEC. April 13, 2015. Retrieved April 13, 2015.
- ^ "Bernie Sanders endorses Hillary Clinton".
- ^ Yglesias, Matthew (February 1, 2016) "Iowa Results: Martin O'Malley drops out after third place finish", Vox.com. Retrieved February 1, 2016.
- ^ Fritze, John (June 9, 2016). "Martin O'Malley endorses Hillary Clinton". Baltimore Sun. Retrieved June 20, 2016.
- ^ Merica, Dan; LoBianco, Tom (October 23, 2015) "Lincoln Chafee drops out of Democratic primary race", CNN.com. Retrieved October 23, 2015
- ^ Walsh, Michael (October 20, 2015) "Jim Webb drops out of Democratic primary race", Yahoo! Politics. Retrieved October 23, 2015.
- ^ Healy, Patrick (April 23, 2016). "Hillary Clinton's Campaign, Cautious but Confident, Begins Considering Running Mates". New York Times. Retrieved April 23, 2016.
- ^ Matthews, Dylan (June 16, 2016). "Hillary Clinton's VP shortlist has leaked. Here are the pros and cons of each". Vox. Retrieved July 23, 2016.
- ^ a b Gearan, Anne (July 19, 2016). "Two names emerge from Clinton's VP deliberations: Kaine and Vilsack". Washington Post. Retrieved July 20, 2016.
- ^ Gearan, Anne; Wagner, John (July 22, 2016). "Sen. Timothy M. Kaine of Virginia chosen as Hillary Clinton's VP". The Washington Post. Retrieved July 23, 2016.
- ^ Linshi, Jack (July 7, 2015). "More People Are Running for Presidential Nomination Than Ever". Time. Retrieved February 14, 2016.
- ^ Rafferty, Andrew (March 4, 2016). "Ben Carson Suspends 2016 Campaign at CPAC". NBC News. Retrieved March 9, 2016.
- ^ a b Peters, Jeremy; Barbaro, Michael (March 16, 2016). "Marco Rubio Suspends His Presidential Campaign". The New York Times. Retrieved March 16, 2016.
- ^ Rosenfeld, Everett (May 3, 2016). "Ted Cruz suspends presidential campaign". CNBC . Retrieved May 4, 2016.
- ^ Kaplan, Thomas (May 4, 2016). "John Kasich Drops Out of Presidential Race". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved May 4, 2016.
- ^ @Reince (May 3, 2016). ".@realDonaldTrump will be presumptive @GOP nominee, we all need to unite and focus on defeating @HillaryClinton #NeverClinton" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- ^ "Donald Trump is running for president". Business Insider. June 16, 2015. Retrieved June 16, 2015.
- ^ "Donald Trump announces presidential bid". The Washington Post. June 16, 2015. Retrieved June 16, 2015.
- ^ "Donald Trump FEC filing" (PDF). FEC.gov. June 22, 2015. Retrieved June 24, 2015.
- ^ "John Kasich FEC Filing" (PDF). FEC.gov. July 23, 2015. Retrieved July 28, 2015.
- ^ Mascaro, Lisa; Lauter, David (March 22, 2015). "Texas Republican Sen. Ted Cruz Launches Presidential Bid". Los Angeles Times. Retrieved March 23, 2015.
- ^ Zezima, Katie (March 23, 2015). "Ted Cruz Announces He's Running for President". The Washington Post. Retrieved March 23, 2015.
- ^ "Ted Cruz FEC filing" (PDF). FEC.gov. March 23, 2015. Retrieved April 1, 2015.
- ^ Parker, Ashley (April 13, 2015). "Marco Rubio Announces 2016 Presidential Bid". The New York Times. Retrieved April 13, 2015.
- ^ Nelson, Rebecca (April 13, 2015). "Marco Rubio Makes His Pitch as the Fresh Face of the GOP in 2016". National Journal. Retrieved April 14, 2015.
- ^ "Marco Rubio FEC Filing" (PDF). FEC.gov. April 13, 2015. Retrieved May 7, 2015.
- ^ Terris, Ben (May 3, 2015). "Ben Carson announces presidential campaign". The Washington Post. Retrieved May 4, 2015.
- ^ Rafferty , Andrew (May 4, 2015). "Ben Carson Announces 2016 Run". NBCNews.com. Retrieved May 4, 2015.
- ^ "Ben Carson FEC Filing" (PDF). FEC.gov. May 4, 2015. Retrieved May 7, 2015.
- ^ Rafferty, Andrew (June 15, 2015). "Jeb Bush Makes 2016 Run Official". NBC News. Retrieved June 15, 2015.
- ^ "Jeb Bush FEC Filing" (PDF). FEC.gov. June 15, 2015. Retrieved June 16, 2015.
- ^ Allen, Cooper (July 30, 2015). "Jim Gilmore formally joins GOP presidential race". USA Today. Retrieved July 30, 2015.
- ^ "Jim Gilmore FEC Filing" (PDF). FEC.gov. July 29, 2015. Retrieved July 29, 2015.
- ^ Gass, Nick (May 4, 2015). "Carly Fiorina: 'Yes, I am running for president'". Politico. Retrieved May 4, 2015.
- ^ "Carly Fiorina FEC Filing" (PDF). FEC.gov. May 4, 2015. Retrieved May 7, 2015.
- ^ Barbaro, Michael (June 30, 2015). "Chris Christie Announces Run, Pledging 'Truth' About Nation's Woes". New York Times. Retrieved June 30, 2015.
- ^ "Christopher J. Christie FEC Filing" (PDF). FEC.gov. July 1, 2015. Retrieved July 6, 2015.
- ^ Lambert, Lisa (April 7, 2015). "Republican Rand Paul announces 2016 presidential run on website". Reuters. Retrieved April 7, 2015.
- ^ Killough, Ashley (April 7, 2015). "Rand Paul: 'I am running for president'". CNN. Retrieved April 7, 2015.
- ^ "Rand Paul FEC filing" (PDF). FEC.gov. April 8, 2015. Retrieved April 9, 2015.
- ^ Jackson, David (May 27, 2015). "Santorum officially begins 2016 presidential campaign". USA Today. Retrieved May 28, 2015.
- ^ "Rick Santorum FEC filing" (PDF). FEC.gov. May 27, 2015. Retrieved June 1, 2015.
- ^ Trip, Gabriel (May 5, 2015). "Mike Huckabee Joins Republican Presidential Race". New York Times. Retrieved May 5, 2015.
- ^ "Mike Huckabee FEC Filing" (PDF). FEC.gov. Retrieved May 10, 2015.
- ^ "George Pataki FEC filing" (PDF). FEC.gov. June 2, 2015. Retrieved June 4, 2015.
- ^ Jaffe, Alexandra (June 1, 2015) "Graham bets on foreign experience in White House bid announcement", CNN. Retrieved June 1, 2015.
- ^ "Lindsey Graham FEC Filing" (PDF). FEC.gov. June 1, 2015. Retrieved June 2, 2015.
- ^ Fahrenthold, David A.; Hohmann, James (June 24, 2015). "Bobby Jindal announces entry into 2016 presidential race". The Washington Post. Retrieved June 24, 2015.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "Bobby Jindal FEC Filing" (PDF). FEC.gov. June 29, 2015. Retrieved June 30, 2015.
- ^ Burlij, Terence; Lee, MJ; LoBianco, Tom (July 13, 2015). "Wisconsin Gov. Scott Walker officially enters 2016 presidential race". CNN. Retrieved July 13, 2015.
{{cite news}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "Scott Walker FEC filing". FEC. FEC.gov. Retrieved July 13, 2015.
- ^ Beckwith , Ryan Teague; Rhodan, Maya (June 4, 2015). "Rick Perry Announces Presidential Bid". Time. Retrieved June 4, 2015.
{{cite news}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "Rick Perry FEC filing" (PDF). FEC.gov. June 19, 2015. Retrieved June 22, 2015.
- ^ Keneally, Meghan (May 4, 2016). "Donald Trump Teases Possible VP Requirements". ABC News. Retrieved May 4, 2016.
- ^ Stokols, Eli; Everett, Burgess (June 17, 2016). "Trump's performance raises hard question: Who'd want to be his VP?". Politico. Retrieved June 21, 2016.
- ^ Costa, Robert (June 30, 2016). "Gingrich, Christie are the leading candidates to be Trump's running mate". Washington Post. Retrieved July 1, 2016.
- ^ Zurcher, Anthony (July 8, 2016). "US election: Who will Trump pick as his vice-president?". BBC. Retrieved July 8, 2016.
- ^ O'Donnell, Kelly (July 12, 2016). "Team Trump Plans Public Event Friday With VP Pick". NBC News. Retrieved July 12, 2016.
- ^ Bash, Dana; Acosta, Jim; Lee, MJ (July 14, 2016). "Donald Trump selects Mike Pence as VP". CNN. Retrieved July 14, 2016.
{{cite news}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Holland, Steve; Stephenson, Emily (July 14, 2016). "Trump expected to pick Indiana Governor Pence for running mate: sources". Reuters.com. Retrieved July 14, 2016.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Holly Bailey. "Donald Trump picks Indiana Gov. Mike Pence as VP [Video]". Yahoo.com. Retrieved July 16, 2016.
- ^ Levingston, Ivan (July 15, 2016). "Donald Trump officially names Mike Pence as his VP". CNBC. Retrieved July 16, 2016.
- ^ Geier, Ben (July 15, 2016). "Mike Pence Is Donald Trump's Vice President Pick". Fortune. Retrieved July 16, 2016.
- ^ Cook, Tony (July 19, 2016). "Gov. Mike Pence formally nominated as the Republican Party's vice presidential candidate". The Indianapolis Star. Retrieved July 20, 2016.
- ^ Stanek, Becca (September 14, 2016). "Gary Johnson becomes first third-party candidate in 20 years to qualify for the ballot in all 50 states". The Week. Retrieved September 15, 2016.
- ^ Collins, Eliza (January 6, 2016). "Libertarian Gary Johnson launches presidential bid". Politico. Retrieved January 6, 2016.
- ^ "Gary Johnson FEC filing", FEC.gov.
- ^ a b c "Ballot Access". gp.org. Retrieved June 19, 2016.
- ^ "New Hampshire Secretary of State Says Jill Stein Petition is Valid". ballot-access.org. Retrieved September 2, 2016.
- ^ "Jill Stein Qualifies for Write-in Status in North Carolina; No Other Write-in Presidential Candidate Does So | Ballot Access News". ballot-access.org. Retrieved August 20, 2016.
- ^ Winger, Richard (August 10, 2016). "Rocky De La Fuente and Jill Stein File Oklahoma Ballot Access Case". ballot-access.org. Ballot Access News. Retrieved September 10, 2016.
- ^ "Nevada Green Party Loses Ballot Access Lawsuit". ballot-access.org. Retrieved September 2, 2016.
- ^ "Exclusive: Green Party's Jill Stein Announces She Is Running for President on Democracy Now!". Democracy Now!. June 22, 2015. Retrieved May 18, 2016.
- ^ "Green Party candidate Jill Stein announces VP running mate". August 1, 2016. Retrieved August 1, 2016.
- ^ a b c d "Ballot access | The Constitution Party". www.constitutionparty.com. Retrieved May 28, 2016.
- ^ a b Winger, Richard (September 7, 2016). "North Dakota Says All Three Independent Presidential Petitions are Valid". Ballot Access News.
- ^ a b c d Kemp, Brian (September 12, 2016). "Qualifying Candidate Information". sos.ga.gov. Georgia Secretary of State. Retrieved September 13, 2016.
- ^ a b c d e f g "2016 Candidate Listing". elections.state.md.us. Maryland State Board of Elections. 2016. Retrieved September 21, 2016.
- ^ "Constitution Party Nominates Darrell Castle and Scott Bradley". April 16, 2016. Retrieved August 23, 2016.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j "Write-In Candidate Listing" (PDF). sos.wv.gov. West Virginia Secretary of State. 2016. Retrieved September 10, 2016.
- ^ a b c d "Declared Write-In Candidates, November 8, 2016 General Election" (PDF). elections.delaware.gov. Delaware Department of Elections. 2016. Retrieved September 21, 2016.
- ^ McMullin, Evan (September 6, 2016). "So far 19 states can vote for me (ballot & write-in): MN, CO, SC, LA, UT, AR, IA, ID, VA, WY, PA, NJ, AL, OR, NH, RI, VT, OH, GA. More soon!". twitter.com. Retrieved September 7, 2016.
- ^ a b c d e f "November 8, 2016 General Election Candidate List". elections.alaska.gov. State of Alaska Division of Elections. 2016. Retrieved September 22, 2016.
- ^ McMullin, Evan (September 15, 2016). "Great news! You can vote for me in Maine!". twitter.com. Retrieved September 15, 2016.
- ^ "Texas Certifies McMullin as Write-In Candidate for President". Texas Tribune. September 16, 2016. Retrieved September 16, 2016.
- ^ "Anti-Trump Republican Launching Independent Presidential Bid". BuzzFeed. Retrieved August 8, 2016.
- ^ "Anti-Trump Republican Launching Independent Presidential Bid". BuzzFeed. Retrieved August 8, 2016.
- ^ "Reform Party Nominates Rocky De La Fuente for President – Ballot Access News".
- ^ Winger, Richard (September 1, 2016). "September 2016 Ballot Access News Print Edition". ballot-access.org. p. 5. Retrieved September 15, 2016.
- ^ a b "Federal Nominations filed for the 2016 General Election". elections.ny.gov. New York State Board of Elections. August 11, 2016. Retrieved August 11, 2016.
- ^ "Wyoming Says Jill Stein and Rocky De La Fuente Have Enough Valid Signatures; Still Checking Evan McMullin | Ballot Access News". ballot-access.org. Retrieved September 8, 2016.
- ^ "New Hampshire Says Rocky De La Fuente Has Enough Valid Signatures | Ballot Acess News". ballot-access.org. Retrieved September 8, 2016.
- ^ "Rhode Island Secretary of State Says Three Independent Presidential Petitions Have Enough Valid Signatures | Ballot Access News". ballot-access.org. Retrieved September 9, 2016.
- ^ "Eight Presidential Candidates will be on Mississippi ballot". ballot-access.org. September 9, 2016.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y Winger, Richard (July 1, 2016). "Ballot Access News". ballot-access.org. p. 4. Retrieved September 10, 2016.
- ^ Winger, Richard (August 13, 2016). "Peace & Freedom Party Nominates Gloria LaRiva for President". ballot-access.org. Ballot Access News. Retrieved August 13, 2016.
- ^ Winger, Richard (May 15, 2016). "Liberty Union Party of Vermont Nominates Gloria La Riva for President". Ballot Access News. Retrieved May 16, 2016.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k Winger, Richard (September 1, 2016). "September 2016 Ballot Access News Print Edition". ballot-access.org. p. 6. Retrieved September 15, 2016.
- ^ a b c d "Candidate Listing". elections.myflorida.com. Florida Department of State, Division of Elections. 2016. Retrieved September 13, 2016.
- ^ "Workers World Party Nominates Monica Moorehead for President". November 9, 2015. Retrieved August 2, 2016.
- ^ Hudnall, David. "Durham's Lamont Lilly is Running for Vice President (of the United States)". Retrieved August 2, 2016.
- ^ a b c d e f "2016 Presidential Elector Candidates" (PDF). in.gov. Indiana Secretary of State. 2016. Retrieved September 13, 2016.
- ^ a b c d e "2016 Write-in Certificate with New Presidential Write-in" (PDF). sos.state.tx.us. Texas Secretary of State. 2016. Retrieved September 22, 2016.
- ^ "Natural Law Party of Michigan Nominates Socialist Party National Ticket | Ballot Access News". Ballot-access.org. Retrieved August 2, 2016.
- ^ Winger, Richard (October 17, 2015). "Socialist Party National Ticket Nominated". Ballot Access News. Retrieved October 17, 2015.
- ^ a b c d e "2016 Candidate Fillings". elections.utah.gov. Utah Lieutenant Governor. 2016. Retrieved September 10, 2016.
- ^ Ziggler, Jed (January 1, 2016). "Tom Hoefling Announces 2016 Presidential Campaign". Independent Political Report. Retrieved January 15, 2016.
- ^ a b "Prohibition Party Nominates National Ticket". Ballot Access News. July 31, 2015. Retrieved August 3, 2015.
- ^ "James Hedges FEC Filing" (PDF). Federal Election Commission. October 27, 2015. Retrieved October 30, 2015.
- ^ Husted, Jon (August 24, 2016). "Husted Announces Independent Candidates for President and Vice President". sos.state.oh.us. Ohio Secretary of State. Retrieved September 12, 2016.
- ^ Winger, Richard (September 19, 2016). "Georgia Secretary of State Now Says Laurence Kotlikoff May be a Declared Write-in Presidential Candidate". ballot-access.org. Ballot Access News. Retrieved September 21, 2016.
- ^ "List of Declared Write-in Candidates for the General Election". maine.gov. Maine Bureau of Corporations, Elections & Commissions. September 9, 2016. Retrieved September 22, 2016.
- ^ "Chris Keniston 2016". Chris Keniston 2016.
- ^ "Veterans Party of America". Veterans Party of America.
- ^ a b c d e f g Wayne Williams, ed. (August 31, 2016). "2016 General Election Candidate List". sos.state.co.us. Colorado Secretary of State. Retrieved September 10, 2016.
- ^ Silva, Rod (October 20, 2015). "FEC Form 2: Statement of Candidacy" (PDF). fec.gov. Retrieved December 22, 2015.
- ^ Silva, Rod. "My fellow Americans". Rod Silva for President 2016. Retrieved December 22, 2015.
- ^ Winger, Richard (June 1, 2016). "American Party of South Carolina Nominates Peter Skewes for President". Ballot Access News. Retrieved June 5, 2016.
- ^ a b Tom Schedler, ed. (2016). "Candidate Inquiry". sos.la.gov. Louisiana Department of State. Retrieved September 10, 2016.
- ^ "2016 November General Candidate List" (PDF). sos.idaho.gov. Idaho Secretary of State. September 1, 2016. Retrieved September 10, 2016.
- ^ Abramowitz, Alan (August 2, 2012). "Do Presidential Campaigns Matter? Evidence From the 2008 Election". Sabato's Crystal Ball. Retrieved November 8, 2014.
- ^ Silver, Nate (June 29, 2016). "2016 Election Forecast - FiveThirtyEight".
- ^ "Who Will Be President?". The New York Times. August 30, 2016.
- ^ "The 2016 Results We Can Already Predict". POLITICO Magazine. Retrieved June 11, 2016.
- ^ "2016 Presidential Election Interactive Map". 270toWin.com. Retrieved June 11, 2016.
- ^ "Larry J. Sabato's Crystal Ball » The Electoral College: The Only Thing That Matters". www.centerforpolitics.org. Retrieved June 11, 2016.
- ^ Levin, Sam (March 21, 2016). "Why Mormons in America's most conservative state could turn a Trump stronghold questionably Democratic". the Guardian. Retrieved June 11, 2016.
- ^ Roche, Lisa Riley (March 20, 2016). "Poll: Utah would vote for a Democrat for president over Trump". DeseretNews.com. Retrieved June 11, 2016.
- ^ Frum, David. "The Great Republican Revolt". Retrieved August 3, 2016.
- ^ Doherty, Brendan (July 31, 2012). "President Obama's Disproportionate Battleground State Focus Started Early, Echoed Predecessors' Actions". Monkey Cage. Retrieved November 4, 2014.
- ^ Yglesias, Matthew (November 8, 2014). "A totally legal, totally shady way that Republicans could ensure Hillary Clinton's defeat". Vox. Retrieved November 8, 2014.
- ^ Haberman, Maggie (July 30, 2016). "Electoral Map Gives Donald Trump Few Places to Go". The New York Times. Retrieved July 31, 2016.
- ^ Challan, David (July 20, 2016). "Road to 270: CNN's new electoral college map". CNN. Retrieved July 31, 2016.
- ^ Balz, Dan (January 18, 2014). "The Republican Party's uphill path to 270 electoral votes in 2016 elections". The Washington Post. Retrieved October 3, 2014.
- ^ Villa, Lissandra (July 10, 2016). "Why Utah Doesn't Like Donald Trump". Time. Retrieved July 18, 2016.
- ^ "Hillary Clinton's path to victory". Retrieved August 3, 2016.
- ^ Kondik, Kyle; Skelley, Geoffrey; Sabato, Larry (May 3, 2015). "The 2016 Results We Can Already Predict". Politico. Retrieved September 22, 2015.
- ^ "New August Electoral College Ratings". August 15, 2016. Retrieved September 23, 2016.
- ^ "2016 Battle for White House". Retrieved September 15, 2016.
- ^ "2016 Race Ratings". Rothenberg Political Report. Roll Call. Retrieved September 17, 2016.
- ^ "2016 President". University of Virginia Center for Politics. September 19, 2016.
- ^ The last election in which the party that did not win the state in 2012 carried the state.
- ^ Mills, Glen (April 14, 2016) "The Constitution Party hosts national convention in Salt Lake City", [Good4Utah]]. Retrieved September 14, 2016.
- ^ Winger, Richard (July 11, 2014). "Libertarian Party Moves into National Party Headquarters That it Owns". Ballot Access News. Retrieved July 11, 2014.
- ^ "Libertarian National Committee Minutes July 15–16, 2012" (PDF). Libertarian National Committee. p. 4. Retrieved July 11, 2014.
- ^ "RNC officially approves Cleveland as 2016 convention host". CBS News. August 8, 2014. Retrieved August 14, 2014.
- ^ Isenstadt, Alex (January 14, 2014). "GOP convention set for July 18–21 in 2016". Politico. Retrieved January 15, 2015.
- ^ Camia, Catalina; Moore, Martha A. (February 12, 2015). "Democrats pick Philadelphia for 2016 convention". USA Today. Retrieved February 12, 2015.
- ^ Winger, Richard (August 2, 2015) "Green Party Will Hold Presidential Convention in Houston", Ballot Access News. Retrieved August 5, 2015.
- ^ "Houston, We Have a Solution – Vote Green 2016". Green Party of the United States. April 4, 2016. Retrieved May 11, 2016.
- ^ "2016 Presidential Race". OpenSecrets.org. Center for Responsive Politics. Retrieved February 26, 2016.
- ^ "Summary data for Hillary Clinton, 2016 Cycle". opensecrets.org. 2016. Retrieved September 12, 2016.
- ^ "Details for Candidate ID: P00003392". fec.gov. Federal Election Commission. 2016. Retrieved September 23, 2016.
- ^ "Summary data for Donald Trump, 2016 Cycle". opensecrets.org. 2016. Retrieved September 12, 2016.
- ^ "Details for Candidate ID: P80001571". fec.gov. Federal Election Commission. 2016. Retrieved September 23, 2016.
- ^ "Details for Candidate ID: P60016342". fec.gov. Federal Election Commission. 2016. Retrieved August 23, 2016.
- ^ "Summary data for Gary Johnson, 2016 Cycle". opensecrets.org. 2016. Retrieved September 23, 2016.
- ^ "Details for Candidate ID: P20002671". fec.gov. Federal Election Commission. 2016. Retrieved September 23, 2016.
- ^ "Summary data for Jill Stein, 2016 Cycle". opensecrets.org. 2016. Retrieved September 23, 2016.
- ^ "Details for Committee ID: C00581199". fec.gov. Federal Election Commission. 2016. Retrieved September 23, 2016.
- ^ "Details for Candidate ID: P60022654". fec.gov. Federal Election Commission. 2016. Retrieved September 23, 2016.
- ^ "Details for Candidate ID: P80005572". fec.gov. Federal Election Commission. 2016. Retrieved September 23, 2016.
- ^ "Details for Candidate ID: P60021102". fec.gov. Federal Election Commission. 2016. Retrieved September 23, 2016.
- ^ "Details for Committee ID: C00607788". fec.gov. Federal Election Commission. 2016. Retrieved September 23, 2016.
- ^ "Details for Candidate ID: P60012960". fec.gov. Federal Election Commission. 2016. Retrieved September 23, 2016.
- ^ "The Commission on Presidential Debates: An Overview", Debates.org.
- ^ Hulsey, Lynn (July 19, 2016). "Hofstra University offers debate spots for WSU students". Dayton Daily News. Retrieved July 21, 2016.
- ^ Flores, Reena. "Campaign manager: Trump will attend all three presidential debates". CBS News. Retrieved August 19, 2016.
- ^ "CPD Announces 2016 Debate Host Applicants". Commission on Presidential Debates. Retrieved April 2, 2015.
- ^ Sanchez, Stephen M. "Three Texas Locations Vie For 2016 Presidential Debates". San Antonio Daily News. Archived from the original on April 3, 2015. Retrieved April 2, 2015.
- ^ "Commission on Presidential Debates announces sites and dates for 2016 general election debates". Commission on Presidential Debates. Retrieved September 23, 2015.
- ^ Lima, Cristiano (July 29, 2016). "Trump wants three presidential debates, accuses Clinton of rigging schedule". Politico. Retrieved July 30, 2016.
- ^ Winger, Richard (October 6, 2015). "Free and Equal Announces Date and Location for General Election Presidential Debate". Ballot Access News. Retrieved May 17, 2016.
- ^ a b "United We Stand Fest and Open Presidential Debate University Tour Program Outline". Free and Equal Foundation. 2016. Retrieved May 17, 2016.
External links































