Czech Republic: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
Revert to revision 54556260 using popups |
||
| Line 95: | Line 95: | ||
{| class="wikitable" style="font-size: 90%; float: right; margin: 0 0 1em 1em;" |
{| class="wikitable" style="font-size: 90%; float: right; margin: 0 0 1em 1em;" |
||
! colspan="6" | Population of the Czech lands <small> (CSU, Prague) </small> |
! colspan="6" | Population of the Czech lands <small> (CSU, Prague) </small> |
||
|- |
|||
|-nick was here |
|||
! Year !! Total !! Change |
! Year !! Total !! Change |
||
! Year !! Total !! Change |
! Year !! Total !! Change |
||
| Line 153: | Line 153: | ||
<!--Please add new information into relevant articles of the series--> |
<!--Please add new information into relevant articles of the series--> |
||
{{more|country=the Czech Republic}} |
{{more|country=the Czech Republic}} |
||
Politics of the [[Czech Republic]] takes place in a framework of a [[parliamentary system|parliamentary]] [[representative democracy|representative democratic]] [[republic]], whereby the [[List of Prime Ministers of the Czech Republic|Prime Minister]] is the [[head of government]], and of |
Politics of the [[Czech Republic]] takes place in a framework of a [[parliamentary system|parliamentary]] [[representative democracy|representative democratic]] [[republic]], whereby the [[List of Prime Ministers of the Czech Republic|Prime Minister]] is the [[head of government]], and of a pluriform multi-party system. [[Executive power]] is exercised by the government. [[Legislative power]] is vested in both the [[government]] and the two chambers of parliament, the [[Chamber of Deputies of the Czech Republic|Chamber of Deputies]] (''Poslanecká sněmovna'') and the [[Senate of the Czech Republic|Senate]]. |
||
=== Military === |
|||
{{main|Military of the Czech Republic}} |
|||
The Czech Armed Forces ([[Czech Language|Czech]]: ''Armáda České republiky'') consists of Land and [[Czech Air Force|Air Forces]] and of specialized support units. The country has been a member of [[NATO]] since [[1999]]. Military spending is around 1.8% of GDP (2005). |
|||
=== Regions === |
|||
{{main|Regions of the Czech Republic}} |
|||
The Czech Republic consists of 13 regions (''kraje'', singular - ''kraj'') and one capital city (''hlavní město''), marked by a *: |
|||
[[Image:Czech-regions.png|right|Map of the Czech Republic with colored regions]] |
|||
{| class="wikitable" |
|||
|- |
|||
!width="25"| |
|||
!Region!!Capital |
|||
|- |
|||
|bgcolor="#FFFFFF"| |
|||
|[[Prague]]* (Praha)|| |
|||
|- |
|||
|bgcolor="#0000CC"| |
|||
|[[Central Bohemian Region]] (Středočeský kraj)||its offices are located in [[Prague]] (Praha) |
|||
|- |
|||
|bgcolor="#00CC00"| |
|||
|[[South Bohemian Region]] (Jihočeský kraj)||[[České Budějovice]] |
|||
|- |
|||
|bgcolor="#CC00CC"| |
|||
|[[Plzeň Region]] (Plzeňský kraj)||[[Plzeň]] |
|||
|- |
|||
|bgcolor="#CCCCCC"| |
|||
|[[Carlsbad Region]] (Karlovarský kraj)||[[Karlovy Vary]] (Carlsbad) |
|||
|- |
|||
|bgcolor="#CC9900"| |
|||
|[[Ústí nad Labem Region]] (Ústecký kraj)||[[Ústí nad Labem]] |
|||
|- |
|||
|bgcolor="#666666"| |
|||
|[[Liberec Region]] (Liberecký kraj)||[[Liberec]] |
|||
|- |
|||
|bgcolor="#00FFCC"| |
|||
|[[Hradec Králové Region]] (Královéhradecký kraj)||[[Hradec Králové]] |
|||
|- |
|||
|bgcolor="#FFFF99"| |
|||
|[[Pardubice Region]] (Pardubický kraj)||[[Pardubice]] |
|||
|- |
|||
|bgcolor="#660066"| |
|||
|[[Olomouc Region]] (Olomoucký kraj)||[[Olomouc]] |
|||
|- |
|||
|bgcolor="#009900"| |
|||
|[[Moravian-Silesian Region]] (Moravskoslezský kraj)||[[Ostrava]] |
|||
|- |
|||
|bgcolor="#ff8800"| |
|||
|[[South Moravian Region]] (Jihomoravský kraj)||[[Brno]] |
|||
|- |
|||
|bgcolor="#00CCFF"| |
|||
|[[Zlín Region]] (Zlínský kraj)||[[Zlín]] |
|||
|- |
|||
|bgcolor="#CC0000"| |
|||
|[[Vysočina Region]] (Vysočina)||[[Jihlava]] |
|||
|} |
|||
== Economy == |
|||
{{main|Economy of the Czech Republic}} |
|||
One of the most stable and prosperous of the post-Communist states, the Czech Republic has been recovering from recession since mid-1999. Growth in [[2000]]-[[2001]] was led by exports to the [[European Union]], especially [[Germany]], and foreign investment, while domestic demand is reviving. |
|||
The rate of corruption remains one of the highest among [[OECD]] countries. |
|||
Uncomfortably high fiscal and current account deficits could be future problems. |
|||
Moves to complete [[banking]], [[telecommunication]]s, and energy [[privatisation]] will add to foreign investment, while intensified restructuring among large enterprises and banks and improvements in the financial sector should strengthen output growth. |
|||
The Czech government has expressed a desire to adopt the [[euro]] currency in 2010, but the introduction of the currency is currently only in the early planning stages. |
|||
== Tourism == |
|||
The Czech economy gets a substantial amount of its income from tourism, and there are several centres of tourist activity. |
|||
The historic city of Prague is the primary tourist attraction, and the city is also the most common point of entry for tourists visitng other parts of the country. Most other cities in the country attract significant numbers of tourists, but the spa towns such as [[Karlovy Vary]] and [[Mariánské Lázně]] are particularly popular holiday destinations. Other popular tourist sites are the many castles and chateaux, such as those at [[Karlštejn]], [[Pernštejn]] and [[Český Krumlov]]. Away from the towns, areas such [[Český Ráj]], [[Šumava]] and the [[Krkonoše]] mountains attract visitors seeking outdoor pursuits. |
|||
The significance of the tourism industry on the country's economy cannot be underestimated; figures from 2001 revealed that the total earnings from tourism reached 118.13 billion [[Czech koruna|CZK]], making up 5.5 % of GNP and 9.3% of overall export earnings. The industry employs more than 110,000 persons - over 2% of the population. [http://www.Czechtourism.com/index.php?show=001006&lang=3] |
|||
== Culture == |
|||
* [[Cinema of the Czech Republic]] |
|||
* [[Famous Czech People]] |
|||
* [[Literature of the Czech Republic]] |
|||
* [[Music of the Czech Republic]] |
|||
* [[National Theatre (Prague)]] |
|||
* [[List of Czech language television channels]] |
|||
* [[Czech cuisine]] |
|||
=== Religion === |
|||
Major religions in the Czech Republic are ([[2001]] census): [[Roman Catholic]] (26.7%), [[Evangelical Church of Czech Brethren]] (1.1%), [[Czechoslovak Hussite Church]] (1.0%), [[Jehovah's Witnesses]] (0.22%), [[Czech and Slovak Orthodox Church]] (0.22%), other (2.8%). 58.9% is nonreligious, 8.8% gave no answer. |
|||
== International rankings == |
|||
* [[Human Development Index]] 2003: Rank 31st out of 177 countries. |
|||
* [[Index of Economic Freedom]] 2005: Rank 33rd out of 155 countries. |
|||
* [[Reporters Without Borders]] world-wide press freedom index 2005: Rank 9th out of 167 countries. |
|||
== Miscellaneous topics == |
|||
{{sisterlinks|Czech Republic}} |
|||
* [[Communications in the Czech Republic]] |
|||
* [[Foreign relations of the Czech Republic]] |
|||
* [[Economy of the Czech Republic]] |
|||
* [[Junák]] |
|||
* [[List of cities in the Czech Republic]] |
|||
* [[List of postal codes in the Czech Republic]] |
|||
* [[List of Czech Republic-related topics]] |
|||
* [[Military of the Czech Republic]] |
|||
* [[Public holidays in the Czech Republic]] |
|||
* [[Tourism in the Czech Republic]] |
|||
* [[Transportation in the Czech Republic]] |
|||
* [[Spa towns in the Czech Republic]] |
|||
==Reference== |
|||
<div class="references-small"> |
|||
*''Much of the material in these articles comes from the [[CIA World Factbook]] 2000 and the 2003 U.S. Department of State website.'' |
|||
</div> |
|||
== External links == |
|||
* [http://www.psp.cz/cgi-bin/eng Chamber of Deputies website], in English |
|||
* [http://www.ceskenoviny.cz/news/ Czech Press Agency news in English] |
|||
* [http://www.Czechtourism.com/index.php?lang=3 CzechTourism] - governmental agency aimed at promoting tourism in the Czech Republic |
|||
* [http://www.canadiancontent.net/profiles/Czech-Republic.html#travelling Travel advisories for Czech Republic] - Updated section on travel dangers |
|||
* [http://wtd.vlada.cz/eng/aktuality.htm Government website], in English |
|||
* [http://www.Czech.cz/ Official Czech portal] |
|||
* [http://portal.gov.cz/wps/portal/_s.155/5906?lng=en Portal of the Public Administration of Czech Republic] |
|||
* [http://www.slackertravel.com/pictures/Czech_Republic/Czechrepublic.html Pictures of the Czech Republic] - from slackertravel.com |
|||
* [http://www.praguemonitor.com/ Prague Daily Monitor] - Czech news in English |
|||
* [http://www.praguepost.com/ Prague Post] - English-language newsweekly |
|||
* [http://www.hrad.cz/en/ Presidential website], click for a pop-up overview of English-language content |
|||
* [http://radio.cz/en/ Radio Prague] - website of the English service of Czech Radio |
|||
* [http://www.senat.cz/index-eng.php Senate website], in English |
|||
* [http://www.Czechforum.net Czech Forum], about all the different aspects of the Czech Republic |
|||
* [[Wikitravel:Czech Republic|Czech Republic at Wikitravel]] - share your tourist experience. |
|||
* [http://www.worldwide-tax.com/Czech/indexCzech.asp Czech R. economy and business indicators] Czech Republic key Data on Taxes and Income Tax. |
|||
* [http://www.myCzechrepublic.com/ Message Boards, advices, destination guides and more about info or your trip to Czechia.] |
|||
{{EU countries}} |
|||
{{Europe}} |
|||
{{Visegrád group}} |
|||
[[Category:Czech Republic| ]] |
|||
[[Category:European Union member states]] |
|||
[[Category:Landlocked countries]] |
|||
{{Link FA|cs}} |
|||
{{Link FA|eo}} |
|||
[[af:Tsjeggië]] |
|||
[[ang:Cecland]] |
|||
[[ar:تشيك]] |
|||
[[an:Republica Checa]] |
|||
[[ast:República Checa]] |
|||
[[az:Çex Respublikası]] |
|||
[[id:Ceko]] |
|||
[[bg:Чехия]] |
|||
[[zh-min-nan:Česko]] |
|||
[[be:Чэхія]] |
|||
[[bn:চেক প্রজাতন্ত্র]] |
|||
[[bs:Češka]] |
|||
[[ca:República Txeca]] |
|||
[[cs:Česko]] |
|||
[[csb:Czeskô Repùblika]] |
|||
[[cy:Gweriniaeth Tsiec]] |
|||
[[da:Tjekkiet]] |
|||
[[de:Tschechien]] |
|||
[[et:Tšehhi]] |
|||
[[el:Τσεχία]] |
|||
[[es:República Checa]] |
|||
[[eo:Ĉeĥio]] |
|||
[[fa:جمهوری چک]] |
|||
[[fr:République tchèque]] |
|||
[[fy:Tsjechje]] |
|||
[[fur:Republiche Ceche]] |
|||
[[ga:An tSeic]] |
|||
[[gl:Chequia - Česko]] |
|||
[[hy:Չեխիայի Հանրապետություն]] |
|||
[[ko:체코]] |
|||
[[hr:Češka]] |
|||
[[io:Chekia]] |
|||
[[ia:Republica Chec]] |
|||
[[is:Tékkland]] |
|||
[[it:Repubblica Ceca]] |
|||
[[he:צ'כיה]] |
|||
[[ka:ჩეხეთი]] |
|||
[[la:Tzekia]] |
|||
[[lv:Čehija]] |
|||
[[lb:Tschechesch Republik]] |
|||
[[lt:Čekija]] |
|||
[[li:Tsjechië]] |
|||
[[hu:Csehország]] |
|||
[[mk:Чешка]] |
|||
[[ms:Republik Czech]] |
|||
[[na:Republik Czechia]] |
|||
[[nl:Tsjechië]] |
|||
[[nds:Tschechien]] |
|||
[[nrm:Républyique Tchèque]] |
|||
[[ja:チェコ]] |
|||
[[no:Tsjekkia]] |
|||
[[nn:Tsjekkia]] |
|||
[[oc:Republica Chèca]] |
|||
[[os:Чехи]] |
|||
[[pl:Czechy]] |
|||
[[pt:República Checa]] |
|||
[[ro:Republica Cehă]] |
|||
[[rmy:Chexiya]] |
|||
[[ru:Чехия]] |
|||
[[scn:Ripùbblica Ceca]] |
|||
[[se:Čeahkka]] |
|||
[[sq:Republika Çeke]] |
|||
[[simple:Czech Republic]] |
|||
[[sk:Česko]] |
|||
[[sl:Češka]] |
|||
[[sr:Чешка Република]] |
|||
[[fi:Tšekki]] |
|||
[[sv:Tjeckien]] |
|||
[[th:สาธารณรัฐเช็ก]] |
|||
[[tl:Czechia]] |
|||
[[vi:Cộng hòa Séc]] |
|||
[[tr:Çek Cumhuriyeti]] |
|||
[[uk:Чехія]] |
|||
[[fiu-vro:Tsehhi]] |
|||
[[yi:טשעכיע]] |
|||
[[zh:捷克]] |
|||
Revision as of 17:51, 22 May 2006
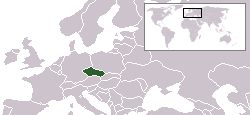
Czech Republic Česká republika | |
|---|---|
| Motto: Czech: Pravda vítězí (English: "Truth prevails") | |
| Anthem: Kde domov můj | |
 | |
| Capital and largest city | Prague |
| Official languages | Czech |
| Religion | Catholicism, atheism |
| Government | Republic |
| Formation Independence | |
• Water (%) | 2.0% |
| Population | |
• 2005 estimate | 10,241,138 (79th) |
• 2001 census | 10,230,060 |
| GDP (PPP) | 2005 estimate |
• Total | $198,976 million (41st) |
• Per capita | $19,488 (39th) |
| HDI (2003) | 0.874 very high (31st) |
| Currency | Czech koruna (CZK) |
| Time zone | UTC+1 (CET) |
• Summer (DST) | UTC+2 (CEST) |
| Calling code | 4201 |
| ISO 3166 code | CZ |
| Internet TLD | .cz |
The Czech Republic (Czech: Česká republika or Česko) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. The country has borders with Poland to the north, Germany to the northwest and west, Austria to the south, and Slovakia to the east. Historic Prague (Czech: Praha), a major tourist attraction, is its capital and largest city. Other major cities include Brno, Ostrava, Zlín, Plzeň, Pardubice, Hradec Králové, České Budějovice, Liberec, Olomouc, and Ústí nad Labem.
The country is composed of two entire historic regions, Bohemia and Moravia, parts of Silesia and small sections of historic Lower Austria. The Czech Republic has been a member state of the European Union since May 1 2004.
Name
The Czech Ministry of Foreign Affairs in 1993 announced that the name Czechia is recommended to be used in all situations other than formal official documents and the full names of government institutions [1], [2], but this has not caught on in English usage. Its Czech equivalent Česko is disputed by many Czech people but often used by others. See Names of the Czech Republic and Czech lands.
History
Archaeologists have found evidence of prehistoric human settlement in the area dating back to the Neolithic era. In the classical era, from the 3rd century BC Celtic migrations, the Boii (see Bohemia) and later in the 1st century Germanic tribes of Marcomanni and Quadi settled there. During the Migration Period of ca. the 5th century, many Germanic tribes moved westward and southward out of Central Europe. In an equally significant migration, Slavic people from the Black Sea and Carpathian regions settled in the area (a movement that was also stimulated by the onslaught of peoples from Siberia and Eastern Europe: Huns, Avars, Bulgars and Magyars). Following in the Germans' wake, they moved southward into Bohemia, Moravia, and some of present day Austria.
During the 7th century the Frankish merchant Samo, supporting the Slavs fighting their Avar rulers, became the ruler of the first known Slav state in Central Europe. The Moravian principality arose in the 8th century (see under Great Moravia).
The Bohemian or Czech state emerged in the late 9th century when it was unified by the Přemyslids. The kingdom of Bohemia was a significant local power during the Middle Ages. It was part of the Holy Roman Empire during the entire existence of this confederation.
Religious conflicts such as the 15th century Hussite Wars and the 17th century Thirty Years' War had a devastating effect on the local population. Bohemia later came under Habsburg influence and became part of Austria-Hungary.
Following the collapse of this empire after World War I, the independent republic of Czechoslovakia was created in 1918. This new country contained large German, Hungarian and Polish minorities. Although Czechoslovakia was a democratic and liberal state guaranteeing and also implementing cultural and language rights to its minorities (schools in German language areas were entirely German), the centralistic state did not grant its minorities territorial political autonomy, which resulted in discontent and strong support among the minorities to break away from Czechoslovakia. Hitler used the opportunity and, supported by Konrad Henlein's Sudeten German Party, gained the majority German speaking Sudetenland through the Munich Agreement. Poland occupied majority Polish speaking areas around Cesky Tesin, while Slovakia gained greater autonomy, with the state being renamed to "Czecho-Slovakia". Eventually Slovakia broke away further in 1939 and the remaining Czech territory was occupied by Hitler who installed the so-called Protectorate of Bohemia and Moravia, which was proclaimed part of the Reich and where the Protectorate President and Prime Minister were subordinate to the Nazi Reichsprotektor ('imperial protector'). Approximately 125,000 citizens, including 83,000 Jews, were killed, and hundreds of thousand of others were sent to prisons and concentration camps or forced labour. The Czechoslovak government-in-exile and its army fighting against Nazis were acknowledged by Allies.
From 1945 to 1948 the Sudetenland was cleansed of ethnic Germans (under the so-called Beneš decrees and the Treaty of Potsdam). About 3 million Germans, almost the entire German minority of pre-War Czechoslovakia, were expelled to Germany and Austria. As a consequence, hundreds of thousand of Germans were sent to prisons and concentration camps or forced labour. Official Czech figures state 15,000–30,000 deaths, the homeland registry of the Roman Catholic church put the number of deaths at 295,000 whereas the German Ministry for Expulsion Affairs claims 267,000. Only a few Germans who had been active in the resistance or were required for economic reasons were allowed to stay, though many of them emigrated later due to the anti-German sentiment prevalent in post-war Czechoslovakia.
In 1948, a reconstituted Czechoslovakia fell within the Soviet sphere of influence. In 1968, an invasion by Warsaw Pact troops ended the efforts of the country's leaders to liberalize party rule and create "socialism with a human face" during the Prague Spring. In 1989, Czechoslovakia regained its political independence through a peaceful "Velvet Revolution". On January 1, 1993, the country peacefully split in two, creating the independent Czech and Slovak republics.
The Czech Republic joined NATO in 1999 and the European Union on May 1, 2004.
Geography

The Czech landscape is quite varied; Bohemia to the west consists of a basin, drained by the Elbe (Czech: Labe) and Vltava rivers, surrounded by mostly low mountains such as the Sudeten with its part Krkonoše, where one also finds the highest point in the country, the Sněžka at 1,602 metres (5,256 ft). Moravia, the eastern part, is also quite hilly and is drained predominantly by the Morava river, but also contains the source of the Oder (Czech: Odra) river. Water from the landlocked Czech Republic flows to three different seas: the North Sea, Baltic Sea and Black Sea.
The local climate is temperate with warm summers and cold, cloudy, humid winters, typified by a mixture of maritime and continental influences.
Demographics
| Population of the Czech lands (CSU, Prague) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | Total | Change | Year | Total | Change |
| 1857 | 7,016,531 | - | 1930 | 10,674,386 | 6.6% |
| 1869 | 7,617,230 | 8.6% | 1950 | 8,896,133 | -16.7% |
| 1880 | 8,222,013 | 7.9% | 1961 | 9,571,531 | 7.6% |
| 1890 | 8,665,421 | 5.4% | 1970 | 9,807,697 | 2.5% |
| 1900 | 9,372,214 | 8.2% | 1980 | 10,291,927 | 4.9% |
| 1910 | 10,078,637 | 7.5% | 1991 | 10,302,215 | 0.1% |
| 1921 | 10,009,587 | -0.7% | 2001 | 10,230,060 | -0.7% |
The majority of the inhabitants of the Czech Republic (95%) are ethnically Czech and speak Czech, a member of the Slavic languages. Other ethnic groups include Slovaks, Germans, Roma, Hungarians, Ukrainians and Poles. After the 1993 division, some Slovaks remained in the Czech Republic and comprise roughly 2% of the current population.
Politics
Error: no page names specified (help). Politics of the Czech Republic takes place in a framework of a parliamentary representative democratic republic, whereby the Prime Minister is the head of government, and of a pluriform multi-party system. Executive power is exercised by the government. Legislative power is vested in both the government and the two chambers of parliament, the Chamber of Deputies (Poslanecká sněmovna) and the Senate.
Military
The Czech Armed Forces (Czech: Armáda České republiky) consists of Land and Air Forces and of specialized support units. The country has been a member of NATO since 1999. Military spending is around 1.8% of GDP (2005).
Regions
The Czech Republic consists of 13 regions (kraje, singular - kraj) and one capital city (hlavní město), marked by a *:

| Region | Capital | |
|---|---|---|
| Prague* (Praha) | ||
| Central Bohemian Region (Středočeský kraj) | its offices are located in Prague (Praha) | |
| South Bohemian Region (Jihočeský kraj) | České Budějovice | |
| Plzeň Region (Plzeňský kraj) | Plzeň | |
| Carlsbad Region (Karlovarský kraj) | Karlovy Vary (Carlsbad) | |
| Ústí nad Labem Region (Ústecký kraj) | Ústí nad Labem | |
| Liberec Region (Liberecký kraj) | Liberec | |
| Hradec Králové Region (Královéhradecký kraj) | Hradec Králové | |
| Pardubice Region (Pardubický kraj) | Pardubice | |
| Olomouc Region (Olomoucký kraj) | Olomouc | |
| Moravian-Silesian Region (Moravskoslezský kraj) | Ostrava | |
| South Moravian Region (Jihomoravský kraj) | Brno | |
| Zlín Region (Zlínský kraj) | Zlín | |
| Vysočina Region (Vysočina) | Jihlava |
Economy
One of the most stable and prosperous of the post-Communist states, the Czech Republic has been recovering from recession since mid-1999. Growth in 2000-2001 was led by exports to the European Union, especially Germany, and foreign investment, while domestic demand is reviving. The rate of corruption remains one of the highest among OECD countries.
Uncomfortably high fiscal and current account deficits could be future problems.
Moves to complete banking, telecommunications, and energy privatisation will add to foreign investment, while intensified restructuring among large enterprises and banks and improvements in the financial sector should strengthen output growth.
The Czech government has expressed a desire to adopt the euro currency in 2010, but the introduction of the currency is currently only in the early planning stages.
Tourism
The Czech economy gets a substantial amount of its income from tourism, and there are several centres of tourist activity.
The historic city of Prague is the primary tourist attraction, and the city is also the most common point of entry for tourists visitng other parts of the country. Most other cities in the country attract significant numbers of tourists, but the spa towns such as Karlovy Vary and Mariánské Lázně are particularly popular holiday destinations. Other popular tourist sites are the many castles and chateaux, such as those at Karlštejn, Pernštejn and Český Krumlov. Away from the towns, areas such Český Ráj, Šumava and the Krkonoše mountains attract visitors seeking outdoor pursuits.
The significance of the tourism industry on the country's economy cannot be underestimated; figures from 2001 revealed that the total earnings from tourism reached 118.13 billion CZK, making up 5.5 % of GNP and 9.3% of overall export earnings. The industry employs more than 110,000 persons - over 2% of the population. [3]
Culture
- Cinema of the Czech Republic
- Famous Czech People
- Literature of the Czech Republic
- Music of the Czech Republic
- National Theatre (Prague)
- List of Czech language television channels
- Czech cuisine
Religion
Major religions in the Czech Republic are (2001 census): Roman Catholic (26.7%), Evangelical Church of Czech Brethren (1.1%), Czechoslovak Hussite Church (1.0%), Jehovah's Witnesses (0.22%), Czech and Slovak Orthodox Church (0.22%), other (2.8%). 58.9% is nonreligious, 8.8% gave no answer.
International rankings
- Human Development Index 2003: Rank 31st out of 177 countries.
- Index of Economic Freedom 2005: Rank 33rd out of 155 countries.
- Reporters Without Borders world-wide press freedom index 2005: Rank 9th out of 167 countries.
Miscellaneous topics
- Communications in the Czech Republic
- Foreign relations of the Czech Republic
- Economy of the Czech Republic
- Junák
- List of cities in the Czech Republic
- List of postal codes in the Czech Republic
- List of Czech Republic-related topics
- Military of the Czech Republic
- Public holidays in the Czech Republic
- Tourism in the Czech Republic
- Transportation in the Czech Republic
- Spa towns in the Czech Republic
Reference
- Much of the material in these articles comes from the CIA World Factbook 2000 and the 2003 U.S. Department of State website.
External links
- Chamber of Deputies website, in English
- Czech Press Agency news in English
- CzechTourism - governmental agency aimed at promoting tourism in the Czech Republic
- Travel advisories for Czech Republic - Updated section on travel dangers
- Government website, in English
- Official Czech portal
- Portal of the Public Administration of Czech Republic
- Pictures of the Czech Republic - from slackertravel.com
- Prague Daily Monitor - Czech news in English
- Prague Post - English-language newsweekly
- Presidential website, click for a pop-up overview of English-language content
- Radio Prague - website of the English service of Czech Radio
- Senate website, in English
- Czech Forum, about all the different aspects of the Czech Republic
- Czech Republic at Wikitravel - share your tourist experience.
- Czech R. economy and business indicators Czech Republic key Data on Taxes and Income Tax.
- Message Boards, advices, destination guides and more about info or your trip to Czechia.