1884–85 United States Senate elections: Difference between revisions
No edit summary Tags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit Advanced mobile edit |
No edit summary Tags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit Advanced mobile edit |
||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
| previous_election = 1882–83 United States Senate elections |
| previous_election = 1882–83 United States Senate elections |
||
| previous_year = {{Nowrap|1882 & 1883}} |
| previous_year = {{Nowrap|1882 & 1883}} |
||
| next_election = |
| next_election = 1886–87 United States Senate elections |
||
| next_year = {{Nowrap|1886 & 1887}} |
| next_year = {{Nowrap|1886 & 1887}} |
||
| seats_for_election = 27 of the 76 seats in the [[United States Senate]] (as well as special elections) |
| seats_for_election = 27 of the 76 seats in the [[United States Senate]] (as well as special elections) |
||
Revision as of 20:05, 28 April 2023
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
27 of the 76 seats in the United States Senate (as well as special elections) 39 seats needed for a majority | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
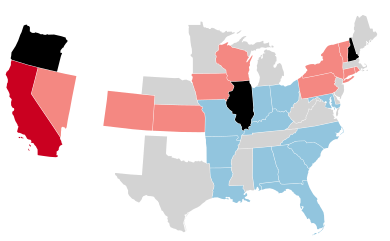 Results of the elections: Republican gain Republican hold Democratic hold Legislature failed to elect | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The 1884–85 United States Senate elections were held on various dates in various states, coinciding with the presidential election of 1884. As these U.S. Senate elections were prior to the ratification of the Seventeenth Amendment in 1913, senators were chosen by state legislatures. Senators were elected over a wide range of time throughout 1884 and 1885, and a seat may have been filled months late or remained vacant due to legislative deadlock.[2] In these elections, terms were up for the senators in Class 3.
With three state legislatures failing to elect their senators in time, both Republicans and Democrats lost seats. Republicans, nevertheless, retained majority control and the Readjusters joined their caucus. By the beginning of the first session, in December 1885, Republicans had won all three vacant seats, increasing their majority.
Results summary
Senate party division, 49th Congress (1885–1887)
- Majority party: Republican (42)
- Minority party: Democratic (34)
- Other parties: (0)
- Total seats: 76
Change in Senate composition
Before the elections
| D8 | D7 | D6 | D5 | D4 | D3 | D2 | D1 | ||
| D9 | D10 | D11 | D12 | D13 | D14 | D15 | D16 | D17 | D18 |
| D28 Ran |
D27 Ran |
D26 Ran |
D25 Ran |
D24 Ran |
D23 Ran |
D22 | D21 | D20 | D19 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D29 Ran |
D30 Ran |
D31 Ran |
D32 Ran |
D33 Unknown |
D34 Retired |
D35 Retired |
D36 Retired |
RA1 | RA2 |
| Majority, with Readjusters in caucus → | R38 Retired | ||||||||
| R29 Ran |
R30 Ran |
R31 Ran |
R32 Ran |
R33 Ran |
R34 Ran |
R35 Unknown |
R36 Unknown |
R37 Retired | |
| R28 Ran |
R27 | R26 | R25 | R24 | R23 | R22 | R21 | R20 | R19 |
| R9 | R10 | R11 | R12 | R13 | R14 | R15 | R16 | R17 | R18 |
| R8 | R7 | R6 | R5 | R4 | R3 | R2 | R1 | ||
After the elections
| D8 | D7 | D6 | D5 | D4 | D3 | D2 | D1 | ||
| D9 | D10 | D11 | D12 | D13 | D14 | D15 | D16 | D17 | D18 |
| D28 Re-elected |
D27 Re-elected |
D26 Re-elected |
D25 Re-elected |
D24 Re-elected |
D23 Re-elected |
D22 | D21 | D20 | D19 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D29 Re-elected |
D30 Hold |
D31 Hold |
D32 Hold |
D33 Hold |
D34 Hold |
V1 D Loss |
V2 R Loss |
V3 R Loss |
RA1 |
| Majority due to three vacancies ↓ | RA2 | ||||||||
| R29 Re-elected |
R30 Re-elected |
R31 Re-elected |
R32 Re-elected |
R33 Re-elected |
R34 Hold |
R35 Hold |
R36 Hold |
R37 Gain | |
| R28 Re-elected |
R27 | R26 | R25 | R24 | R23 | R22 | R21 | R20 | R19 |
| R9 | R10 | R11 | R12 | R13 | R14 | R15 | R16 | R17 | R18 |
| R8 | R7 | R6 | R5 | R4 | R3 | R2 | R1 | ||
Beginning of the first session, December 7, 1885
| D8 | D7 | D6 | D5 | D4 | D3 | D2 | D1 | ||
| D9 | D10 | D11 | D12 | D13 | D14 | D15 | D16 | D17 | D18 |
| D28 | D27 | D26 | D25 | D24 | D23 | D22 | D21 | D20 | D19 |
| D29 | D30 | D31 | D32 | D33 | D34 | RA1 | RA2 | R40 Gain |
R39 Gain |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Majority → | |||||||||
| R29 | R30 | R31 | R32 | R33 | R34 | R35 | R36 | R37 | R38 Gain |
| R28 | R27 | R26 | R25 | R24 | R23 | R22 | R21 | R20 | R19 |
| R9 | R10 | R11 | R12 | R13 | R14 | R15 | R16 | R17 | R18 |
| R8 | R7 | R6 | R5 | R4 | R3 | R2 | R1 | ||
| Key: |
|
|---|
Race summaries
Special elections during the 48th Congress
In this election, the winner was seated in 1885 before March 4.
| State | Incumbent | Results | Candidates | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Senator | Party | Electoral history | |||
| Rhode Island (Class 2) |
William P. Sheffield | Republican | 1884 (Appointed) | Interim appointee retired when successor elected. Winner elected January 20, 1885. Republican hold. |
▌ [data missing] |
Races leading to the 49th Congress
In these regular elections, the winners were elected for the term beginning March 4, 1885; ordered by state.
All of the elections involved the Class 3 seats.
| State | Incumbent | Results | Candidates | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Senator | Party | Electoral history | |||
| Alabama | James L. Pugh | Democratic | 1880 (special) | Incumbent re-elected in August 1884. | ▌ [data missing] |
| Arkansas | James D. Walker | Democratic | 1878 | Incumbent retired. Winner elected in 1885. Democratic hold. |
▌ [data missing] |
| California | James T. Farley | Democratic | 1878 | Incumbent retired. Winner elected in 1885. Republican gain. |
▌ [data missing] |
| Colorado | Nathaniel P. Hill | Republican | 1879 | Incumbent lost renomination. Winner elected in 1885. Republican hold. |
▌ [data missing] |
| Connecticut | Orville H. Platt | Republican | 1879 | Incumbent re-elected in 1885. | ▌ [data missing] |
| Florida | Wilkinson Call | Democratic | 1879 | Incumbent re-elected January 20, 1885.[3] | ▌ [data missing] |
| Georgia | Joseph E. Brown | Democratic | 1880 (special) | Incumbent re-elected in 1885. | ▌ [data missing] |
| Illinois | John A. Logan | Republican | 1879 | Unknown if incumbent ran for re-election. Legislature failed to elect. Republican loss. Incumbent was later elected to continue the vacant term, see below. |
None. |
| Indiana | Daniel W. Voorhees | Democratic | 1877 (Appointed) 1879 (special) |
Incumbent re-elected in 1885. | ▌ [data missing] |
| Iowa | William B. Allison | Republican | 1872 1878 |
Incumbent re-elected January 23, 1884.[4] |
|
| Kansas | John Ingalls | Republican | 1873 1879 |
Incumbent re-elected in 1885. | ▌ [data missing] |
| Kentucky | John Stuart Williams | Democratic | 1879 | Incumbent lost re-election. Winner elected in 1884. Democratic hold. |
▌ [data missing] |
| Louisiana | Benjamin F. Jonas | Democratic | 1879 | Incumbent lost re-election. Winner elected in 1884 or 1885. Democratic hold. |
▌ [data missing] |
| Maryland | James Black Groome | Democratic | 1878 or 1879 | Unknown if incumbent retired or lost re-election. Winner elected in 1884. Democratic hold. |
▌ [data missing] |
| Missouri | George G. Vest | Democratic | 1879 | Incumbent re-elected in 1885. | ▌ [data missing] |
| Nevada | John P. Jones | Republican | 1873 1879 |
Incumbent re-elected in 1885. | ▌ [data missing] |
| New Hampshire | Henry W. Blair | Republican | 1879 | Unknown if incumbent retired or lost re-election. Legislature failed to elect. Republican loss. Incumbent was later appointed, and then elected, to continue the vacant term, see below. |
[data missing] |
| New York | Elbridge G. Lapham | Republican | 1881 (special) | Incumbent retired. Winner elected January 20, 1885. Republican hold. |
|
| North Carolina | Zebulon Vance | Democratic | 1879 | Incumbent re-elected in 1884. |
▌ |
| Ohio | George H. Pendleton | Democratic | 1878 or 1879 | Incumbent lost renomination. Winner elected January 15, 1884.[5] Democratic hold. |
▌ [data missing] |
| Oregon | James H. Slater | Democratic | 1878 or 1879 | Incumbent retired. Legislature failed to elect. Democratic loss. |
[data missing] |
| Pennsylvania | J. Donald Cameron | Republican | 1877 (special) 1879 |
Incumbent re-elected January 20, 1885. |
|
| South Carolina | Wade Hampton III | Democratic | 1878 | Incumbent re-elected in 1884. | ▌ [data missing] |
| Vermont | Justin S. Morrill | Republican | 1866 1872 1878 |
Incumbent re-elected in 1884. | ▌ [data missing] |
| Wisconsin | Angus Cameron | Republican | 1881 | Incumbent retired. Winner elected January 27, 1885. Republican hold. |
▌ [data missing] |
Elections during the 49th Congress
In these elections, the winners were elected in 1885 after March 4, sorted by election date.
| State | Incumbent | Results | Candidates | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Senator | Party | Electoral history | |||
| Delaware (Class 1) |
Thomas F. Bayard | Democratic | 1869 1875 1881 |
Incumbent resigned March 6, 1885 to become U.S. Secretary of State. Winner elected March 18, 1885. |
▌ [data missing] |
| Arkansas (Class 2) |
Augustus Garland | Democratic | 1876 1883 |
Incumbent resigned March 6, 1885 to become U.S. Attorney General. Winner elected March 20, 1885. Democratic hold. |
▌ [data missing] |
| Illinois (Class 3) |
Vacant | Legislature had failed to elect. Winner elected May 19, 1885. Republican gain. |
| ||
| New Hampshire (Class 3) |
Henry W. Blair | Republican | 1879 1885 (Appointed) |
Interim appointee elected June 17, 1885. | ▌ [data missing] |
| Oregon (Class 3) |
Vacant | Legislature had failed to elect. Winner elected November 18, 1885. Republican gain. |
▌ [data missing] | ||
Complete list of races
Maryland
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (November 2022) |
| ||||||||||||||||
80 members of the Maryland General Assembly | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||
Ephraim King Wilson II was elected by an unknown margin of votes, for the Class 3 seat.[6]
New York
The New York election was held January 20, 1885, by the New York State Legislature.
Republican Elbridge G. Lapham had been elected to this seat in a special election in 1881 to succeed Roscoe Conkling who had resigned. Lapham's term would expire on March 3, 1885.
At the State election in November 1883, 19 Republicans and 13 Democrats were elected for a two-year term (1884-1885) in the State Senate. At the State election in November 1884, 73 Republicans and 55 Democrats were elected for the session of 1885 to the Assembly. The 108th New York State Legislature met from January 6 to May 22, 1885, at Albany, New York.
The caucus of Republican State legislators met on January 19, President pro tempore of the State Senate Dennis McCarthy presided. 19 State senators and 73 assemblymen attended. The Evarts faction required the nomination to be made by viva voce vote, which was opposed by the Morton faction, but was carried by a vote of 64 to 28. The caucus nominated Ex-U.S. Secretary of State William M. Evarts on the first ballot.
| Candidate | First ballot |
|---|---|
| William M. Evarts | 61 |
| Levi P. Morton | 28 |
| Chauncey M. Depew | 3 |
The Democratic caucus nominated Ex-Mayor of New York Edward Cooper.
William M. Evarts was the choice of both the Assembly and the State Senate, and was declared elected.
| House | Republican | Democratic | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| State Senate (32 members) |
William M. Evarts | 19 | Edward Cooper | 13 |
| State Assembly (128 members) |
William M. Evarts | 73 | Edward Cooper | 52 |
Note: The votes were cast on January 20, but both Houses met in a joint session on January 21 to compare nominations, and declare the result.
Ohio
In 1884, the Democrats held a majority in the Ohio legislature. In a caucus meeting to determine the party's choice for United States Senator, many Democratic legislators looked to replace the incumbent Senator, Democrat George H. Pendleton, because they disagreed with his advocacy of civil service reform and low tariffs.[7] Some of Pendleton's opponents, led by Oliver Payne, promoted Henry B. Payne for the Senate seat, recalling his opposition to both of those positions during his time in the House.[8] After a secret ballot by the Democratic caucus, Henry B. Payne received 46 out of 80 votes.[9] Because Oliver was a trustee and treasurer of the Standard Oil company, many of the Pendleton supporters immediately alleged that $100,000 from the oil trust had been used to bribe Democratic legislators, and claimed that an open ballot would not have favored Payne.[10][11]
When the full legislature met, Henry B. Payne was elected with 78 votes out of 120.[9] The Democratic legislature initially refused to investigate their members' alleged corruption, but when Republicans regained the majority in the next session, the legislature looked into the allegations and forwarded the results to the federal Senate.[12] The evidence gathered was voluminous, but the Senate declined to expel Payne, who proclaimed his innocence.[11] While there was never enough evidence for definitive proof of bribery, biographer Dewayne Burke wrote that the "circumstantial evidence seems to convict Payne" of the charge.[13]
Pennsylvania
The Pennsylvania election was held January 20, 1885. The Pennsylvania General Assembly convened January 20, 1885. Incumbent Republican J. Donald Cameron, who was elected in an 1877 special election and re-elected in 1879, was a successful candidate for re-election to another term.[14] The results of the vote of both houses combined are as follows:
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | J. Donald Cameron (Inc.) | 163 | 64.94 | |
| Democratic | William A. Wallace | 69 | 27.49 | |
| Republican | A. W. Acheson | 1 | 0.40 | |
| Republican | Charles N. Brumm | 1 | 0.40 | |
| Republican | George Shiras Jr. | 1 | 0.40 | |
| N/A | Not voting | 14 | 5.58 | |
| Totals | 251 | 100.00% | ||
See also
Notes
References
- ^ a b The Readjusters caucused with the Republicans.
- ^ "17th Amendment to the U.S. Constitution: Direct Election of U.S. Senators (1913)". National Archives and Records Administration. February 8, 2022.
- ^ "SELECTING NEW SENATORS". The New York Times. January 20, 1885. p. 1.
- ^ a b Clark 1913, p. 209.
- ^ Burke 1938, p. 28.
- ^ "Our Campaigns - MD US Senate Race - Jan 00, 1884". www.ourcampaigns.com. Retrieved November 5, 2022.
- ^ Burke 1938, p. 22.
- ^ Burke 1938, p. 23.
- ^ a b Walker 1886, p. 3.
- ^ Burke 1938, pp. 23–27.
- ^ a b Weisenburger 1934, p. 326.
- ^ Walker 1886, p. 4.
- ^ Burke 1938, p. 30.
- ^ a b "U.S. Senate Election - 20 January 1885" (PDF). Wilkes University. Retrieved December 22, 2013.
Further reading
- Party Division in the Senate, 1789-Present, via Senate.gov
- Burke, Dewayne (1938). Henry B. Payne: His Congressional Career (M.A. thesis). Ohio State University. Archived from the original on August 26, 2016. Retrieved February 20, 2016.
- Byrd, Robert C. (October 1, 1993). Wolff, Wendy (ed.). The Senate, 1789-1989: Historical Statistics, 1789-1992. United States Senate Historical Office (volume 4 Bicentennial ed.). Washington, DC: U.S. Government Printing Office. ISBN 9780160632563.
- Clark, Dan Elbert (1913). "History of Senatorial Elections in Iowa". Iowa City, Iowa.
- Cox, Harold (January 31, 2007). "Pennsylvania Election Statistics: 1682-2006". The Wilkes University Election Statistics Project. Wilkes University.
- Walker, Albert H. (1886). The Payne Bribery Case and the United States Senate. Hartford, Connecticut: Clark & Smith. OCLC 17693469.
- Weisenburger, Francis Phelps (1934). "Henry B. Payne". Dictionary of American Biography. Vol. XIV. New York, New York: C. Scribner's Sons. pp. 325–326.
- "MR. EVARTS TO BE SENATOR" (PDF). The New York Times. January 20, 1885.
- "EVARTS ELECTED SENATOR" (PDF). The New York Times. January 22, 1885.



