Chemical elements in East Asian languages: Difference between revisions
Double sharp (talk | contribs) |
Double sharp (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
The semantic (meaning) part is also the [[radical (Chinese character)|radical]] of the character. It refers to the element's usual state at [[room temperature]] and [[standard pressure]]. Only four radicals are used for elements: {{lang|zh-Hant|釒}}/{{lang|zh-Hans|钅}} (''jīn'' "gold; metal") for solid metals, {{lang|zh|石}} (''shí'' "stone, rock") for solid non-metals, {{lang|zh|水}}/{{lang|zh|氵}} (''shuǐ'' "water") for liquids, and {{lang|zh|气}} (''qì'' "air, steam") for gases. |
The semantic (meaning) part is also the [[radical (Chinese character)|radical]] of the character. It refers to the element's usual state at [[room temperature]] and [[standard pressure]]. Only four radicals are used for elements: {{lang|zh-Hant|釒}}/{{lang|zh-Hans|钅}} (''jīn'' "gold; metal") for solid metals, {{lang|zh|石}} (''shí'' "stone, rock") for solid non-metals, {{lang|zh|水}}/{{lang|zh|氵}} (''shuǐ'' "water") for liquids, and {{lang|zh|气}} (''qì'' "air, steam") for gases. |
||
The phonetic (sound) part represents the character's pronunciation and is a partial transliteration of the element. For each element character, this is a unique phonetic component. Since 118 elements have been discovered, over 100 phonetic components are used in naming the elements. Because many characters in modern Chinese are homophones, including for tone, two different phonetic components can be pronounced the same. Current practice dictates that new names should avoid being homophonous with previous element names or with [[Organic nomenclature in Chinese|organic functional groups]]. However, this rule was not rigorously followed in the past, and confusingly, the names of tin (锡) and selenium (硒) are pronounced the same, including tone, as ''xī''. |
The phonetic (sound) part represents the character's pronunciation and is a partial transliteration of the element. For each element character, this is a unique phonetic component. Since 118 elements have been discovered, over 100 phonetic components are used in naming the elements. Because many characters in modern Chinese are homophones, including for tone, two different phonetic components can be pronounced the same. Current practice dictates that new names should avoid being homophonous with previous element names or with [[Organic nomenclature in Chinese|organic functional groups]]. However, this rule was not rigorously followed in the past, and confusingly, the names of tin (锡) and selenium (硒) are pronounced the same, including tone, as ''xī'' in Mainland China. (On Taiwan tin is ''xí'' while selenium is ''xī''.) |
||
锡 (tin) and 硒 (selenium) are not homophones in [[Nanjing dialect|Nanjing Mandarin]], which was the prestige dialect of Chinese when most elements were named, which was until the late 19th century. The phonetic component of 锡, 易 (''yì''), was accurate when the character was invented around 3000 years ago, but not now because of sound change. In [[Middle Chinese]] 锡 was an [[Checked tone|entering tone]] character, a closed syllable ending in -p/-t/-k (or -ʔ in some modern dialects). But 硒 was constructed in the late 19th century using the (still accurate) phonetic 西 (''xī''), which in Middle Chinese was a [[Four tones (Middle Chinese)|level tone]] character, an open syllable with a vowel ending. In Beijing Mandarin, the variety on which Standard Modern Chinese is based, stop consonant endings of syllables were dropped, and the entering tone was merged into the other tones in a complex and irregular manner by the 16th-17th centuries, and 锡 and 西 both became Tone 1 (high tone) characters. In dialects that preserve the entering tone, like Nanjing Mandarin and Shanghainese and Cantonese, 锡 retains a -k or -ʔ ending and 锡 and 西 (硒) are pronounced differently. |
锡 (tin) and 硒 (selenium) are not homophones in [[Nanjing dialect|Nanjing Mandarin]], which was the prestige dialect of Chinese when most elements were named, which was until the late 19th century. The phonetic component of 锡, 易 (''yì''), was accurate when the character was invented around 3000 years ago, but not now because of sound change. In [[Middle Chinese]] 锡 was an [[Checked tone|entering tone]] character, a closed syllable ending in -p/-t/-k (or -ʔ in some modern dialects). But 硒 was constructed in the late 19th century using the (still accurate) phonetic 西 (''xī''), which in Middle Chinese was a [[Four tones (Middle Chinese)|level tone]] character, an open syllable with a vowel ending. In Beijing Mandarin, the variety on which Standard Modern Chinese is based, stop consonant endings of syllables were dropped, and the entering tone was merged into the other tones in a complex and irregular manner by the 16th-17th centuries, and 锡 and 西 both became Tone 1 (high tone) characters. In dialects that preserve the entering tone, like Nanjing Mandarin and Shanghainese and Cantonese, 锡 retains a -k or -ʔ ending and 锡 and 西 (硒) are pronounced differently. |
||
This sometimes causes difficulty in verbal communication, as Sn and Se can both be divalent and tetravalent. Thus, SnO<sub>2</sub> 二氧化锡 and SeO<sub>2</sub> 二氧化硒 are pronounced identically, as ''èryǎnghuàxī''. To avoid further confusion, [[P.R.C.]] authorities avoided using the name 矽 ''xī'' (or any tonal variants) for silicon. |
This sometimes causes difficulty in verbal communication, as Sn and Se can both be divalent and tetravalent. Thus, SnO<sub>2</sub> 二氧化锡 and SeO<sub>2</sub> 二氧化硒 are pronounced identically, as ''èryǎnghuàxī''. To avoid further confusion, [[P.R.C.]] authorities avoided using the name 矽 ''xī'' (or any tonal variants) for silicon. (On Taiwan 矽 is pronounced ''xì''.) |
||
{| class="wikitable" |
{| class="wikitable" |
||
Revision as of 07:28, 9 August 2022
The topic of this article may not meet Wikipedia's general notability guideline. (October 2019) |
| Part of a series on the |
| Periodic table |
|---|
The names for chemical elements in East Asian languages, along with those for some chemical compounds (mostly organic), are among the newest words to enter the local vocabularies. Except for those metals well-known since antiquity, the names of most elements were created after modern chemistry was introduced to East Asia in the 18th and 19th century, with more translations being coined for those elements discovered later.
While most East Asian languages use—or have used—the Chinese script, only the Chinese language uses logograms as the predominant way of naming elements. Native phonetic writing systems are primarily used for element names in Japanese (Katakana), Korean (Hangul) and Vietnamese (chữ Quốc ngữ).
Chinese
In Chinese, characters for the elements are the last officially created and recognized characters in the Chinese writing system. Unlike characters for unofficial varieties of Chinese (e.g., written Cantonese) or other now-defunct ad hoc characters (e.g., those by the Empress Wu), the names for the elements are official, consistent, and taught (with Mandarin pronunciation) to every Chinese and Taiwanese student who has attended public schools (usually by the first year of middle school). New names and symbols are decided upon by the China National Committee for Terminology in Science and Technology.[1]
Native characters
Some metallic elements were already familiar to the Chinese, as their ores were already excavated and used extensively in China for construction, alchemy, and medicine. These include the long-established group of "Five Metals" (五金) — gold (金), silver (銀/银), copper (銅/铜), iron (鐵/铁), and tin (錫/锡) — as well as lead (鉛/铅) and mercury (汞).
Some non-metals were already named in Chinese as well, because their minerals were in widespread use. For example,
- boron (硼) as part of borax
- carbon (碳) in the form of charcoal
- sulfur (硫) had been used to make gunpowder since at least the 10th century in China.
Characters based on European pronunciations
However, the Chinese did not know about most of the elements until they were isolated during the Industrial Age. These new elements therefore required new characters, which were invented using the phono-semantic principle. Each character consists of two parts, one to signify the meaning and the other to hint at the sound:
The semantic (meaning) part is also the radical of the character. It refers to the element's usual state at room temperature and standard pressure. Only four radicals are used for elements: 釒/钅 (jīn "gold; metal") for solid metals, 石 (shí "stone, rock") for solid non-metals, 水/氵 (shuǐ "water") for liquids, and 气 (qì "air, steam") for gases.
The phonetic (sound) part represents the character's pronunciation and is a partial transliteration of the element. For each element character, this is a unique phonetic component. Since 118 elements have been discovered, over 100 phonetic components are used in naming the elements. Because many characters in modern Chinese are homophones, including for tone, two different phonetic components can be pronounced the same. Current practice dictates that new names should avoid being homophonous with previous element names or with organic functional groups. However, this rule was not rigorously followed in the past, and confusingly, the names of tin (锡) and selenium (硒) are pronounced the same, including tone, as xī in Mainland China. (On Taiwan tin is xí while selenium is xī.)
锡 (tin) and 硒 (selenium) are not homophones in Nanjing Mandarin, which was the prestige dialect of Chinese when most elements were named, which was until the late 19th century. The phonetic component of 锡, 易 (yì), was accurate when the character was invented around 3000 years ago, but not now because of sound change. In Middle Chinese 锡 was an entering tone character, a closed syllable ending in -p/-t/-k (or -ʔ in some modern dialects). But 硒 was constructed in the late 19th century using the (still accurate) phonetic 西 (xī), which in Middle Chinese was a level tone character, an open syllable with a vowel ending. In Beijing Mandarin, the variety on which Standard Modern Chinese is based, stop consonant endings of syllables were dropped, and the entering tone was merged into the other tones in a complex and irregular manner by the 16th-17th centuries, and 锡 and 西 both became Tone 1 (high tone) characters. In dialects that preserve the entering tone, like Nanjing Mandarin and Shanghainese and Cantonese, 锡 retains a -k or -ʔ ending and 锡 and 西 (硒) are pronounced differently.
This sometimes causes difficulty in verbal communication, as Sn and Se can both be divalent and tetravalent. Thus, SnO2 二氧化锡 and SeO2 二氧化硒 are pronounced identically, as èryǎnghuàxī. To avoid further confusion, P.R.C. authorities avoided using the name 矽 xī (or any tonal variants) for silicon. (On Taiwan 矽 is pronounced xì.)
| Semantic | Phonetic | Element | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| 釒/钅 + | 里 lǐ | = 鋰/锂 (lǐ) | lithium |
| 釒/钅 + | 甲 jiǎ | = 鉀/钾 (jiǎ) | kalium, Latin name for potassium |
| 釒/钅 + | 內/内 nèi or nà † | = 鈉/钠 (nà) | natrium, Latin name for sodium |
| 釒/钅 + | 弟 dì or tì † | = 銻/锑 (Taiwan tì / Mainland tī*) | stibium, Latin name for antimony |
| 釒/钅 + | 臬 niè | = 鎳/镍 (niè) | nickel |
| 釒/钅 + | 鬲 gé | = 鎘/镉 (gé) | cadmium |
| 釒/钅 + | 烏/乌 wū | = 鎢/钨 (wū) | wolframium, Latin name for tungsten |
| 釒/钅 + | 必 bì | = 鉍/铋 (bì) | bismuth |
| 釒/钅 + | 由 yóu | = 鈾/铀 (Taiwan yòu* / Mainland yóu) |
uranium |
| 釒/钅 + | 呂/吕 lǚ | = 鋁/铝 (lǚ) | aluminium |
| 石 + | 典 diǎn | = 碘 (diǎn) | iodine |
| 气 + | 亥 hài | = 氦 (hài) | helium |
| 气 + | 弗 fú | = 氟 (fú) | fluorine |
| 气 + | 乃 nǎi | = 氖 (nǎi) | neon |
| 石 + | 夕 xī | = 矽 (Taiwan xì* / Mainland xī) | silicon. Mainly used in R.O.C. (Taiwan), Hong Kong, and Macau |
| 圭 guī | = 硅 (guī) | silicon. Derived from Japanese transliteration '珪' (kei, けい) of archaic Dutch keiaarde. Mostly used in P.R.C. |
- † 內/内 is primarily pronounced as nèi, but less commonly as nà, the source of 納/纳. Likewise, the primary pronunciation of 弟 is dì, but the alternate reading of tì gave rise to 銻/锑.
- * The derived pronunciation differs (in tone or in sound) from the pronunciation of the element.
The "water" radical (水) is not used much here, as only two elements (bromine and mercury) are truly liquid at standard room temperature and pressure. Their characters are not based on the European pronunciation of the elements' names. Bromine (溴), the only liquid nonmetal at room temperature, is explained in the following section. Mercury (汞), now grouped with the heavy metals, was long classified as a kind of fluid in ancient China.
Meaning-based characters
A few characters, though, are not created using the above "phono-semantic" design, but are "semantic-semantic", that is, both of its parts indicate meanings. One part refers to the element's usual state (like the semanto-phonetic characters), while the other part indicates some additional property or function of the element. In addition, the second part also indicates the pronunciation of the element. Such elements are:
| Semantic | Semantic | Element | English | Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 釒/钅 + | 白 bái (white) | = 鉑/铂 bó[note 1] | platinum | The character is repurposed.[note 2] |
| 氵 + | 臭 chòu (stinky) | = 溴 xiù[note 1] | bromine | odorous (Greek βρῶμος brómos also means "stench") |
| 气 + | 羊 yáng, short for 養/养 yǎng (to nourish/foster) | = 氧 yǎng[note 3] | oxygen | A continuous supply of oxygenated air nourishes almost all animals |
| 气 + | 巠/𢀖 jīng, short for 輕/轻 qīng (light-weight) | = 氫/氢 qīng[note 3] | hydrogen | the lightest of all elements |
| 气 + | 彔/录 lù, short for 綠/绿 lǜ (green) | = 氯/氯 lǜ[note 3] | chlorine | greenish yellow in color |
| 气 + | 炎 yán, short for 淡 dàn (diluted) | = 氮 dàn[note 3] | nitrogen | dilutes breathable air |
| 石 + | 粦 lín, short for 燐 lín (glow) | = 磷 lín | phosphorus | emits a faint glow in the dark |
- ^ a b The pronunciation of these characters come from the second semantic characters' nearly obsolete pronunciations. Nowadays 白 (white) is normally pronounced bái in the standard Mandarin dialect, although traditionally bó was preferred. Similarly, 臭 (stinky) is almost always pronounced chòu, as opposed to xiù, now an archaic reading.
- ^ The original meaning of 鉑/铂 is "thin sheet of gold" (now obsolete). The character was not associated with platinum until modern time, since platinum was known in the Old World only after the Age of Discovery.
- ^ a b c d The apparent mismatch in pronunciation with the phonetic component is because the pronunciation is inherited from another character that provides the meaning. For example, the ultimate source of the pronunciation of 氧 yǎng (oxygen) is not 羊 yáng (sheep), but 養/养 yǎng (to nourish/foster).
Usage in the nomenclature for simple inorganic compounds
Simple covalent binary inorganic compounds EmXn are named as
- n X 化 (huà) m E (with n and m written as Chinese numerals),
where X is more electronegative than E, using the IUPAC formal electronegativity order. 化 as a full noun or verb means 'change; transform(ation)'. As a noun suffix, it is equivalent to the English suffixes -ized/-ated/-ified. It is the root of the word 化学 (huàxué) 'chemistry'.
For example, P4S10 is called 十硫化四磷 (shíliúhuàsìlín) (literally: 'ten sulfur of four phosphorus', 'decasulfide of tetraphosphorus'). As in English nomenclature, if m = 1, the numerical prefix of E is usually dropped in covalent compounds. For example, CO is called 一氧化碳 (yīyǎnghuàtàn) (literally: 'one oxygen of carbon', 'monoxide of carbon').
However, for compounds named as salts, numerical prefixes are dropped altogether, as in English. Thus, calcium chloride, CaCl2, is named 氯化钙 (literally: 'chloride of calcium'). The Chinese name for FeCl3, 氯化铁, literally means 'chlorinated iron' and is akin to the archaic English names 'muriated iron' or 'muriate of iron'. In this example, 氯 is 'chlorine' and 铁 is 'iron'.
There is a Chinese analog of the -ic/-ous nomenclature for higher/lower oxidation states: -ous is translated as 亚 (yà, 'minor; secondary'): for example, FeCl2 is 氯化亚铁 and FeCl3 is 氯化铁. In a four-way contrast, hypo- is translated as 次 (cì, 'inferior; following') and per- is translated as 高 (gāo, 'high, upper'). For example, the acid HClO is 次氯酸 "inferior chlorine acid", HClO2 is 亚氯酸, HClO3 is 氯酸, and HClO4 is 高氯酸. In this example, the character 酸 (suān, 'sour') means (organic or inorganic) acid. The more modern Stock nomenclature in which oxidation state is explicitly specified can also be used: thus, tin(IV) oxide (SnO2) is simply 氧化锡(IV).
Recently discovered elements
In 2015, IUPAC recognised the discovery of four new elements. In November 2016, IUPAC published their formal names and symbols: nihonium (113Nh), moscovium (115Mc), tennessine (117Ts), and oganesson (118Og).
Subsequently, in January 2017, the China National Committee for Terms in Sciences and Technologies published four naming characters for these elements.[1] The National Academy for Educational Research under the Ministry of Education of the Republic of China on Taiwan published an almost identical list (the only differences being the use of the traditional Chinese metal radical '釒' in place of the simplified Chinese form '钅' for nihonium and moscovium) in April 2017.[2]
For traditional Chinese, nihonium and moscovium were then existing characters; while in simplified Chinese, only moscovium already existed in the Unicode Standard. The missing characters were added to Unicode version 11.0 as urgently-needed characters in June 2018.[3]
The Chinese characters for these symbols are:
- Nihonium: Traditional: U+9268 鉨 CJK UNIFIED IDEOGRAPH-9268 Simplfied: U+9FED 鿭 CJK UNIFIED IDEOGRAPH-9FED
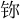 (nǐ)
(nǐ) - Moscovium: Traditional: U+93CC 鏌 CJK UNIFIED IDEOGRAPH-93CC Simplfied: U+9546 镆 CJK UNIFIED IDEOGRAPH-9546 (mò)
- Tennessine: Both Traditional and Simplfied: U+9FEC 鿬 CJK UNIFIED IDEOGRAPH-9FEC
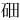 (tián)
(tián) - Oganesson: Both Traditional and Simplfied: U+9FEB 鿫 CJK UNIFIED IDEOGRAPH-9FEB
 (ào)
(ào)
In the periodic table
Pronunciations for some elements differ between Mainland China and Taiwan, as described in the article. Simplified characters and Mainland Chinese pronunciations are shown above.[4] Some of the characters for the superheavy elements may not be visible depending on fonts.
Notes
| English | Z | Mainland China | Taiwan | Hong Kong/Macau |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| silicon | 14 | 硅 guī | 矽 xì | 硅 gwai1, 矽 zik6 |
| technetium | 43 | 锝 dé | 鎝 tǎ | 鎝 daap1, 鍀 dak1 |
| lutetium | 71 | 镥 lǔ | 鎦 liú | 鑥 lou5, 鎦 lau4 |
| astatine | 85 | 砹 ài | 砈 è | 砹 ngaai6, 砈 ngo5 |
| francium | 87 | 钫 fāng | 鍅 fǎ | 鈁 fong1, 鍅 faat3 |
| neptunium | 93 | 镎 ná | 錼 nài | 錼 noi6, 鎿 naa4 |
| plutonium | 94 | 钚 bù | 鈽 bù | 鈈 bat1 |
| americium | 95 | 镅 méi | 鋂 méi | 鎇 mei4, 鋂 mui4 |
| berkelium | 97 | 锫 péi | 鉳 běi | 錇 pui4, 鉳 bak1 |
| californium | 98 | 锎 kāi | 鉲 kǎ | 鐦 hoi1, 鉲 kaa1 |
| einsteinium | 99 | 锿 āi | 鑀 ài | 鎄 oi1, 鑀 oi3 |
A minority of the "new characters" are not completely new inventions, as they coincide with archaic characters, whose original meanings have long been lost to most people. For example, 鈹 (beryllium), 鉻 (chromium), 鑭 (lanthanum), and 鏷 (protactinium), are obscure characters meaning "needle", "hook", "harrow", and "raw iron", respectively.
The majority of the elements' names are the same in Simplified Chinese and Traditional Chinese, merely being variants of each other, since most of the names were translated by a single body of standardization before the PRC-ROC split. However, since francium and the transuranium elements were discovered during or after the split, they have different names in Taiwan and in Mainland China. In Hong Kong, both Taiwanese and Mainland Chinese names are used.[5] A few pronunciations also differ even when the characters are analogous: cobalt gǔ (PRC) / gū (ROC); palladium bǎ (PRC) / bā (ROC); tin xī (PRC) / xí (ROC); antimony tī (PRC) / tì (ROC); polonium pō (PRC) / pò (ROC); uranium yóu (PRC) / yòu (ROC); bohrium bō (PRC) / pō (ROC).[4]
The isotopes of hydrogen – protium (1H), deuterium (D) and tritium (T) – are written 氕 piē, 氘 dāo and 氚 chuān, respectively, in both simplified and traditional writing. 鑀 is used in Taiwan for both einsteinium (mainland China: 锿) and ionium, a previous name for the isotope thorium-230.[citation needed]
Japanese
Like other words in the language, elements' names in Japanese can be native, from China (Sino-Japanese) or from Europe (gairaigo).
Names based on European pronunciations
Even though the Japanese language also uses Chinese characters (kanji), it primarily employs katakana to transliterate names of the elements from European languages (often German/Dutch or Latin [via German] or English). For example,
| English | Japanese | Note |
|---|---|---|
| antimony | anchimon (アンチモン) | This form without the final vowel (i from y) is likely from Dutch (antimoon) or German (Antimon) |
| tungsten | tangusuten (タングステン) | from English; other major European languages refer to this element as wolfram or tungsten with some additional syllable (-o, -e, etc.). |
| sodium | natoriumu (ナトリウム) | natrium in Latin |
| uranium | uran (ウラン) | Uran in German |
| iodine | yōso (ヨウ素 / 沃素) | -yō (ヨウ, "io-" [joː], like Dutch jood [joːt]) + -so (素, "element/component"). Chinese uses 碘 (diǎn), the second syllable of iodine. |
| fluorine | fusso (弗素) | futsu (弗) approximates flu-. Similar to the Chinese: 氟, plus the "air" radical (气). As 弗 is not a commonly used kanji, it is often written フッ素, using katakana. |
Native names
On the other hand, elements known since antiquity are Chinese loanwords, which are mostly identical to their Chinese counterparts, albeit in the Shinjitai, for example, iron (鉄) is tetsu (Tang-dynasty loan) and lead (鉛) is namari (native reading). While all elements in Chinese are single-character in the official system, some Japanese elements have two characters. Often this parallels colloquial or everyday names for such elements in Chinese, such as 水銀/水银 (pinyin: shuǐyín) for mercury and 硫黃/硫黄 (pinyin: liúhuáng) for sulfur. A special case is tin (錫, suzu), which is more often written in katakana (スズ).
| English | Japanese | Chinese | Note |
|---|---|---|---|
| mercury | suigin (水銀) | 汞 (gǒng) | lit. "watery silver" aka. quicksilver, like the element's symbol, Hg (Latin/Greek hydro-argyrum, "water-silver"). In the Greater China Region, 水銀/水银 is more generally used than 汞, because 汞 is not taught until the chemistry class but 水銀/水银 is the word used in daily life; for example, when people talk about the mercury liquid in the thermometer, most people would say "水銀/水银" but not 汞. This kind of thermometer is called "水銀溫度計/水银温度计" (lit. "watery silver thermometer") in Chinese instead of "汞溫度計/汞温度计" (lit. "mercury thermometer"), which is not being used at all. In Japanese too, 汞 exists but is extremely rare and literary, having an alternative obsolete reading mizugane. |
| sulfur | iō, formerly iwō (硫黄) | 硫 (liú) | 黄 (ō) means "yellow", to distinguish 硫 from other characters pronounced the same. |
| zinc | aen (亜鉛) | 鋅/锌 (xīn) | meaning "light lead"; 鉛 is "lead" in Japanese and Chinese. |
| platinum | hakkin (白金) | 鉑 (bó) | lit. "white gold". Like 水銀/水银 and 汞 in Chinese, 白金 is the "daily" word, and 鉑/铂 is the formal name and usually won't be taught until the chemistry class. In mainland China, jewelry stores usually use the word "白金" or "铂金". |
| arsenic | hiso (砒素) | 砷 (shēn) | hi (ヒ) < (砒霜) hishima, the Chinese name for arsenic trioxide (pīshuāng). In modern Chinese, arsenic is instead shēn (砷), an approximation of the second syllable of arsenic.
The kanji 砒 is quite rare. Often written ヒ素 using katakana. |
| boron | hōso (硼素, "borax element") | 硼 (péng) | Hō (ホウ) < hōsa (硼砂), the Chinese name for borax (péngshā). Boron is still called péng in modern Chinese.
The kanji 硼 is extremely rare. Mostly written ホウ素 using katakana. |
Meaning-based names
Some names were later invented to describe properties or characteristics of the element. They were mostly introduced around the 18th century to Japan, and they sometimes differ drastically from their Chinese counterparts. The following comparison shows that Japanese does not use the radical system for naming elements like Chinese.
| English | Japanese | Chinese | Note |
|---|---|---|---|
| hydrogen | suiso (水素, "water's element") | 氫/氢 (qīng) | translation of the hydro- prefix, or translation of the Dutch word for hydrogen, waterstof ("Water substance") |
| carbon | tanso (炭素, "coal element") | 碳 (tàn) | translation of the Dutch word for carbon, koolstof ("coal substance"). |
| nitrogen | chisso (窒素, "the suffocating element") | 氮 (dàn) | translation of the Dutch word for nitrogen, stikstof ("suffocating substance"). While nitrogen is not toxic per se, air-breathing animals cannot survive breathing it alone (without sufficient oxygen mixed in). |
| oxygen | sanso (酸素, "acid's element") | 氧 (yǎng) |
similar to the Dutch word for oxygen, zuurstof ("sour substance") or the Greek-based oxygen ("acid maker"). |
| silicon | keiso (硅素 / 珪素) | 硅 (guī) | same as Chinese; the kanji 硅 is extremely rare. Often written ケイ素 using katakana. Its origin lies in the Dutch word keiaarde; kei is a partial calque. The Chinese word is an orthographical loan from Japanese. |
| phosphorus | rin (燐) | 磷 (lín) | similar to Chinese, except the "fire" radical replacing the "stone" radical. The kanji 燐 is rare. Usually written リン using katakana. |
| chlorine | enso (塩素, "salt's element") | 氯 (lǜ) | it and sodium make up common table salt (NaCl); 塩 is the Shinjitai version of 鹽. |
| bromine | shūso (臭素, "the stinky element") | 溴 (xiù) | similar to Chinese, except the lack of the "water" radical. |
Korean
As Hanja (Sino-Korean characters) are now rarely used in Korea, all of the elements are written in Hangul. Since many Korean scientific terms were translated from Japanese sources, the pattern of naming is mostly similar to that of Japanese. Namely, the classical elements are loanwords from China, with new elements from European languages. But recently, some elements' names were changed. For example:
| English | Korean (before 2014) | Source | (South) Korean (after 2014) |
|---|---|---|---|
| gold | geum (금) | from Chinese jin (金) | geum (금) |
| silver | eun (은) | from Chinese yin (銀) | eun (은) |
| antimony | antimon (안티몬) | from German | antimoni (안티모니) |
| tungsten | teongseuten (텅스텐) | from English | teongseuten (텅스텐) |
| sodium | nateuryum (나트륨) | from Latin or German (Na for natrium) | sodyum (소듐) |
| potassium | kalyum (칼륨) | from Latin or German kalium | potasyum (포타슘) |
| manganese | manggan (망간) | from German Mangan | mangganijeu (망가니즈) |
Pre-modern (18th-century) elements often are the Korean pronunciation of their Japanese equivalents, e.g.,
| English | Korean (Hangul, hanja) |
|---|---|
| hydrogen | suso (수소, 水素) |
| carbon | tanso (탄소, 炭素) |
| nitrogen | jilso (질소, 窒素) |
| oxygen | sanso (산소, 酸素) |
| chlorine | yeomso (염소, 鹽素) |
| zinc | ayeon (아연, 亞鉛) |
| mercury | sueun (수은, 水銀) |
Vietnamese
Some of the elements known since antiquity and medieval times are loanwords from Chinese, such as copper (đồng from 銅), tin (thiếc from 錫), mercury (thuỷ ngân from 水銀), sulfur (lưu huỳnh from 硫黄), oxygen (dưỡng khí from 氧氣; ôxy is the more common name) and platinum (bạch kim from 白金; platin is another common name). Others have native or old Sino-Vietnamese names, such as sắt for iron, bạc for silver, chì for lead, vàng for gold, kền for nickel (niken is the more common name) and kẽm for zinc. In either case, now they are written in the Vietnamese alphabet. Before the Latin alphabet was introduced, sắt was rendered as 𨫊, bạc as 鉑, chì as 𨨲, vàng as 鐄, kền as 𨪝 and kẽm as 𨯘 in Chữ Nôm.
The majority of elements are shortened and localized pronunciations of the European names (usually from French). For example:
- Phosphorus becomes phốtpho.
- The -ine suffix is absent, e.g., chlorine, iodine and fluorine become clo, iốt and flo, respectively; compare French chlore, iode, fluor.
- The -um suffix is lost, e.g., caesium becomes xêzi, pronounced /sezi/; compare the French césium, pronounced /sezjɔm/ (whereas the English is /sizi-/).
- Similarly, beryllium, tellurium, lithium, natrium (sodium), and lanthanum become berili, telua, liti, natri, and lantan respectively
- The -gen suffix is lost, e.g., nitrogen, oxygen and hydrogen become nitơ, ôxy and hiđrô, respectively
A minority of elements, mostly those not suffixed with -ium, retain their full name, e.g.,
- Tungsten (aka wolfram) becomes volfram.
- Bismuth becomes bitmut.
- Aluminium becomes nhôm (銋), because the ending -nium has a similar pronunciation. It was the first element to be known in English in Vietnam.
- Elements with the -on suffix (e.g. noble gases) seem to be inconsistent. Boron and silicon are respectively shortened to bo and silic. On the other hand, neon, argon, krypton, xenon and radon do not have common shorter forms.
- Unlike the other halogens, astatine retains its suffix (astatin in Vietnamese).
- Antimony is shortened to antimon, and arsenic to asen; these names are similar to the German ones (Antimon and Arsen, respectively).
Some elements have multiple names, for instance, potassium is known as pô-tát and kali (from kalium, the element's Latin name).
See also
References
- ^ a b "新元素113号、115号、117号、118号的中文定名征集" (in Chinese). 2017-01-15.
- ^ "Chemical nouns -- overview of the names of chemical elements". Retrieved 17 July 2017.
- ^ "Unicode® 11.0.0". Unicode.org. Retrieved 7 June 2018.
- ^ a b Language Log: Names of the chemical elements in Chinese
- ^ Wong, Kin-on James; Cheuk, Kwok-hung; Lei, Keng-lon; Leung, Ho-ming; Leung, Man-wai; Pang, Hei-tung; Pau, Chiu-wah; Tang, Kin-hung; Wai, Pui-wah; Fong, Wai-hung Raymond (1999). "English-Chinese Glossary of Terms Commonly Used in the Teaching of Chemistry in Secondary Schools" (PDF). Education Bureau. Hong Kong Education City Limited. Retrieved 29 January 2015.
- Wright, David (2000). Translating Science: The Transmission of Western Chemistry into Late Imperial China, 1840–1900. Leiden; Boston: Brill. See especially Chapter Seven, "On Translation".
External links
Periodic tables
- Interactive table in Traditional Chinese
- Interactive table in Simplified Chinese
- Interactive table in Japanese
- Interactive table in Korean
- Interactive table in Vietnamese
- English-Chinese periodic table of elements
