Patriarchal cross: Difference between revisions
Tags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit Advanced mobile edit |
No edit summary |
||
| (27 intermediate revisions by 16 users not shown) | |||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
[[Image:PatriarchsCross.svg|frame|Patriarchal cross]] |
[[Image:PatriarchsCross.svg|frame|Patriarchal cross]] |
||
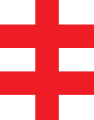
The '''Patriarchal cross''' is a variant of the [[Christian cross]], the [[religious symbol]] of [[Christianity]], and also known as the [[Cross of Lorraine]]. Similar to the |
The '''Patriarchal cross''' is a variant of the [[Christian cross]], the [[religious symbol]] of [[Christianity]], and is also known as the [[Cross of Lorraine]]. Similar to the [[Latin cross]], the patriarchal cross possesses a smaller crossbar placed above the main one so that both crossbars are near the top. Sometimes the patriarchal cross has a short, slanted crosspiece near its foot ([[Russian Orthodox cross]]). This slanted, lower crosspiece often appears in [[Byzantine Greeks|Byzantine Greek]] and [[Eastern Europe]]an [[iconography]], as well as in other [[Eastern Orthodox Church|Eastern Orthodox]] [[Church architecture|churches]]{{citation needed|date=July 2018}}. In most renditions of the [[Cross of Lorraine]], the horizontal bars are "graded" with the upper bar being the shorter, though variations with the bars of equal length are also seen. |
||
== Imagery == |
== Imagery == |
||
<!-- Deleted image removed: [[Image:Slavcross.png|150px|thumb|A three-bar cross (black) inside a cross [[bottony]] (the letters are the Greek abbreviation for "Jesus Christ" - ΙΗΣΟΥΣ ΧΡΙΣΤΟΣ ''Iesous Christos'').]] --> |
<!-- Deleted image removed: [[Image:Slavcross.png|150px|thumb|A three-bar cross (black) inside a cross [[bottony]] (the letters are the Greek abbreviation for "Jesus Christ" - ΙΗΣΟΥΣ ΧΡΙΣΤΟΣ ''Iesous Christos'').]] --> |
||
The top beam represents the plaque bearing the inscription "[[Jesus]] the Nazarene, King of the Jews" (often abbreviated in the [[Latin]]ate "[[INRI]]" and in the Greek as "[[INBI]]"). A popular view is that the slanted bottom beam is a footrest |
The top beam represents the plaque bearing the inscription "[[Jesus]] the Nazarene, King of the Jews" (often abbreviated in the [[Latin]]ate "[[INRI]]" and in the Greek as "[[INBI]]"). A popular view is that the slanted bottom beam is a footrest; however, there is no evidence of footrests ever being used during the crucifixion, and it has a deeper meaning. The bottom beam may represent a balance of justice. Some sources suggest that as one of the thieves being crucified with Jesus repented of his sin and believed in Jesus as the Messiah and was thus with Christ in [[Bosom of Abraham|Paradise]], the other thief rejected and mocked Jesus and therefore descended into [[Hades in Christianity#Eastern Orthodox|Hades]]. |
||
Many symbolic interpretations of the double-cross have been put forth. One of them says that the first horizontal line symbolized the secular power and the other horizontal line the ecclesiastic power of [[Byzantine emperor|Byzantine emperors]],{{Citation needed|date=November 2007}} and also that the first cross bar represents the death, and the second cross the resurrection, of [[Jesus Christ]]. |
Many symbolic interpretations of the double-cross have been put forth. One of them says that the first horizontal line symbolized the secular power and the other horizontal line the ecclesiastic power of [[Byzantine emperor|Byzantine emperors]],{{Citation needed|date=November 2007}} and also that the first cross bar represents the death, and the second cross the resurrection, of [[Jesus Christ]]. |
||
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
==Hungary== |
==Hungary== |
||
The two-barred cross has been one of the main elements in the [[coat of arms of Hungary]] at least since 1190. It appeared during the reign of [[Béla III of Hungary|King Béla III]],{{sfn|Engel|2001|p=86}} who was raised in the Byzantine court. He was for a time heir to the throne of the [[Byzantine Empire]] and betrothed to the emperor's daughter. When the emperor's wife gave birth to a son, the emperor dissolved his daughter's betrothal to Béla and removed Béla's title of despotes. Soon after Béla left [[Constantinople]] when he inherited the Hungarian throne in 1172. The cross started appearing floating in the coat of arms and on the coins from this era. During the middle ages, the two-barred cross became associated with the [[Árpád dynasty]] and the [[Kingdom of Hungary]] along with the [[Árpád stripes]]. The symbol found its way to [[Western Europe]] through Hungary, because [[René of Anjou|René the Good]], who was related to the [[Capetian House of Anjou|House Anjou]] of Hungary, laid claim to four kingdoms, including [[Kingdom of Hungary|Hungary]]. He placed the symbol on his flags before the [[battle of Nancy]].{{sfn|Monter|2007|pp=22–23}} He won the battle and regained his lost [[Duchy of Lorraine]]. Thus the symbol became known in Western-Europe as the [[Cross of Lorraine]]. |
The two-barred cross has been one of the main elements in the [[coat of arms of Hungary]] at least since 1190. It appeared during the reign of [[Béla III of Hungary|King Béla III]],{{sfn|Engel|2001|p=86}} who was raised in the Byzantine court. He was for a time heir to the throne of the [[Byzantine Empire]] and betrothed to the emperor's daughter. When the emperor's wife gave birth to a son, the emperor dissolved his daughter's betrothal to Béla and removed Béla's title of despotes. Soon after Béla left [[Constantinople]] when he inherited the Hungarian throne in 1172. The cross started appearing floating in the coat of arms and on the coins from this era. During the middle ages, the two-barred cross became associated with the [[Árpád dynasty]] and the [[Kingdom of Hungary]] along with the [[Árpád stripes]]. The symbol found its way to [[Western Europe]] through Hungary, because [[René of Anjou|René the Good]], who was related to the [[Capetian House of Anjou|House Anjou]] of Hungary, laid claim to four kingdoms, including [[Kingdom of Hungary|Hungary]]. He placed the symbol on his flags before the [[battle of Nancy]].{{sfn|Monter|2007|pp=22–23}} He won the battle and regained his lost [[Duchy of Lorraine]]. Thus the symbol became known in Western-Europe as the [[Cross of Lorraine]]. |
||
<gallery> |
<gallery> |
||
File:Istvan-ChroniconPictum.jpg|[[Stephen I of Hungary|Saint Stephen]], the first [[King of Hungary]] (1000–1038). |
File:Istvan-ChroniconPictum.jpg|[[Stephen I of Hungary|Saint Stephen]], the first [[King of Hungary]] (1000–1038). |
||
File:Coa Hungary Country History Bela III (1172-1196).svg|[[Coat of arms of Hungary]] under king [[Béla III]] |
File:Coa Hungary Country History Bela III (1172-1196).svg|[[Coat of arms of Hungary]] under king [[Béla III]] |
||
File:IV. Béla aranypecsétje.jpg|The seal of King [[Béla IV of Hungary]] (1235–1270) from his Golden Bull |
|||
File:Magyar zászló a königsfeldeni kolostorból - 14. század első fele.jpg|Hungarian flag from [[Königsfelden Monastery]] from the first half of the 14th century, from the monastery of [[Agnes of Austria (1281–1364)|Agnes of Habsburg]], widow of King [[Andrew III of Hungary]] (1290–1301) |
|||
File:I. Nagy Lajos király (1342-1382) második kettős felségpecsétjének hátlapja (1366-1382).jpg|Reverse of the second double seal (1366–1382) of King [[Louis I of Hungary|Louis I the Great]] (1342–1382). This was later become the predecessor to the modern coat of arms of Slovakia. |
|||
File:Luxemburgi Zsigmond király (1387-1437) első kettős felségpecsétjének hátlapja (1384-1405).jpg|Reverse of the first double seal (1387–1405) of King [[Sigismund, Holy Roman Emperor|Sigismund of Luxembourg]] (1387–1437) |
|||
File:Coat of arms of Hungary.svg|[[Coat of arms of Hungary]] |
File:Coat of arms of Hungary.svg|[[Coat of arms of Hungary]] |
||
File:Gabor arkangyal.jpg|[[Archangel Gabriel]] holds the [[Holy Crown of Hungary|Holy Crown]] and the apostolic double cross as the symbols of Hungary, [[Hősök tere]], Budapest, Hungary |
File:Gabor arkangyal.jpg|[[Archangel Gabriel]] holds the [[Holy Crown of Hungary|Holy Crown]] and the apostolic double cross as the symbols of Hungary, [[Hősök tere]], Budapest, Hungary |
||
File:Globus cruciger of Hungary and Royal Scepter of Hungary. Matthias Church, Budapešť 0523.jpg|The {{lang|la|[[globus cruciger]]}} of Hungary (right) is unique in having a patriarchal cross instead of a simple cross |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
</gallery> |
</gallery> |
||
== Lithuania and Belarus == |
== Lithuania and Belarus == |
||
Another form of the cross was used by the [[Jagiellonian dynasty]]. This cross now features on the coat of arms of [[Lithuania]], where it appears on the shield of the [[Coat of arms of Lithuania|Vytis]]. It is also the badge of the Lithuanian Air Force and forms the country's highest award for bravery, the [[Order of the Cross of Vytis]]. |
Another form of the cross was used by the [[Jagiellonian dynasty]]. This cross now features on the coat of arms of [[Lithuania]], where it appears on the shield of the [[Coat of arms of Lithuania|Vytis]]. It is also the badge of the Lithuanian Air Force and forms the country's highest award for bravery, the [[Order of the Cross of Vytis]]. The Jagiellonian cross is also used on the coat of arms and flags of [[Counties of Lithuania|every Lithuanian county]], yet not following any heraldic rules. |
||
The Patriarchal Cross appears on the |
The Patriarchal Cross appears on the [[National emblem of Belarus#Pahonia|Pahonia]], used at various times as the coat of arms of Grand Duchy of Lithuania for centuries and of [[Belarus]]. |
||
<gallery> |
<gallery> |
||
File:POL Jagiellonów COA.svg|Coat of arms of King [[ |
File:POL Jagiellonów COA.svg|Coat of arms of King [[Władysław II Jagiełło]] |
||
File:Coat of arms of Lithuania.svg|The [[coat of arms of Lithuania]], with the patriarchal cross on the knight's shield |
File:Coat of arms of Lithuania.svg|The [[coat of arms of Lithuania]], with the patriarchal cross on the knight's shield |
||
File:Coat of arms of Belarus (1991–1995).svg| |
File:Coat of arms of Belarus (1991–1995).svg|[[National emblem of Belarus#Pahonia|Pahonia]] used at various times as the coat of arms of [[Belarus]], preserving the original name and appearance since the times of Grand Duchy of Lithuania. |
||
File:Emblem of the Lithuanian Air Force.svg|The badge of the [[Lithuanian Air Force]] |
File:Emblem of the Lithuanian Air Force.svg|The badge of the [[Lithuanian Air Force]] |
||
</gallery> |
</gallery> |
||
== Great Moravia == |
|||
The [[Byzantine Empire|Byzantine]] Christianization came to the [[Great Moravia|Morava Empire]] in the year 863, provided at the request of [[Rastislav of Moravia|Rastislav]] sent Byzantine Emperor [[Michael III]].<ref>Spiesz ''et al.'' 2006, p. 22.</ref> The symbol often referred to as the patriarchal cross, appeared in the Byzantine Empire in large numbers in the 10th century. For a long time, it was thought to have been given to [[Stephen I of Hungary|Saint Stephen]] by the [[pope]] as the symbol of the apostolic Kingdom of Hungary. |
|||
== Russia == |
== Russia == |
||
| Line 69: | Line 67: | ||
== Slovakia == |
== Slovakia == |
||
The territory of present-day [[Slovakia]] was an integral [[Upper Hungary|part]] of the [[Kingdom of Hungary]] from the 10th century until the [[Treaty of Trianon]] in 1920. Many of its cities gained privileges and coats of arms from the [[List of Hungarian monarchs|Hungarian kings]], often containing the kings' own [[Coat of arms of Hungary|coat of arms]]. |
The territory of present-day [[Slovakia]] was an integral [[Upper Hungary|part]] of the [[Kingdom of Hungary]] from the 10th century until the [[Treaty of Trianon]] in 1920. Many of its cities gained privileges and coats of arms from the [[List of Hungarian monarchs|Hungarian kings]], often containing the kings' own [[Coat of arms of Hungary|coat of arms]]. |
||
=== First Slovak Republic (1939–1945) === |
|||
<gallery> |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
File:War ensign of the First Slovak Republic.svg|[[War flag]] of the [[First Slovak Republic]], used by a country's military forces |
|||
File:Flag of the President of Slovakia (1939-1945).svg|Presidential standard of First Slovak Republic |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
File:Flag of the Hlinka party (1938–1945) variant 2.svg|Flag of the Hlinka's Slovak People's Party |
|||
</gallery> |
|||
=== Slovak Republic (since 1993) === |
|||
<gallery> |
<gallery> |
||
File:Coat of arms of Slovakia.svg|[[Coat of arms of Slovakia]] |
File:Coat of arms of Slovakia.svg|[[Coat of arms of Slovakia]] |
||
File:Flag of Slovakia.svg|[[Flag of Slovakia]] |
|||
File:Flag of the President of Slovakia.svg|Presidential standard of Slovakia |
|||
File:Coat of Arms of Nitra.svg|Coat of arms of the city of [[Nitra]], Slovakia |
File:Coat of Arms of Nitra.svg|Coat of arms of the city of [[Nitra]], Slovakia |
||
| ⚫ | |||
File:Coat of Arms of Žilina.svg|Coat of arms of the city of [[Žilina]], Slovakia |
|||
File:Coat of Arms of Žilina Region.svg|Coat of arms of [[Žilina Region]], Slovakia |
|||
File:Coat of Arms of Skalica.svg|Coat of arms of the city of [[Skalica]], Slovakia |
File:Coat of Arms of Skalica.svg|Coat of arms of the city of [[Skalica]], Slovakia |
||
File:Coat of Arms of Levoča.svg|Coat of arms of the city of [[Levoča]], Slovakia |
File:Coat of Arms of Levoča.svg|Coat of arms of the city of [[Levoča]], Slovakia |
||
| ⚫ | |||
File:Coat of Arms of Zvolen.svg|Coat of arms of the city of [[Zvolen]], Slovakia |
File:Coat of Arms of Zvolen.svg|Coat of arms of the city of [[Zvolen]], Slovakia |
||
| ⚫ | |||
</gallery> |
</gallery> |
||
| Line 88: | Line 99: | ||
{{Portal|Christianity}} |
{{Portal|Christianity}} |
||
*[[Papal cross]] |
*[[Papal cross]] |
||
*[[Lorraine cross]] |
|||
*[[Two-barred cross]] |
*[[Two-barred cross]] |
||
| Line 97: | Line 109: | ||
{{Refbegin}} |
{{Refbegin}} |
||
* {{cite book |last=Engel |first=Pál |year=2001 |title=The Realm of St Stephen: A History of Medieval Hungary, 895–1526 |publisher= I.B. Tauris Publishers |isbn=1-86064-061-3 }} |
* {{cite book |last=Engel |first=Pál |year=2001 |title=The Realm of St Stephen: A History of Medieval Hungary, 895–1526 |publisher= I.B. Tauris Publishers |isbn=1-86064-061-3 }} |
||
* {{cite book |last=Monter |first=William |year=2007 |title=A Bewitched Duchy: Lorraine and its Dukes, |
* {{cite book |last=Monter |first=William |year=2007 |title=A Bewitched Duchy: Lorraine and its Dukes, 1477–1736 |publisher=Librairie Droz |isbn=978-2-600-01165-5 }} |
||
{{refend}} |
|||
{{Christian crosses}} |
{{Christian crosses}} |
||
Latest revision as of 17:24, 11 December 2024
This article needs additional citations for verification. (September 2014) |

The Patriarchal cross is a variant of the Christian cross, the religious symbol of Christianity, and is also known as the Cross of Lorraine. Similar to the Latin cross, the patriarchal cross possesses a smaller crossbar placed above the main one so that both crossbars are near the top. Sometimes the patriarchal cross has a short, slanted crosspiece near its foot (Russian Orthodox cross). This slanted, lower crosspiece often appears in Byzantine Greek and Eastern European iconography, as well as in other Eastern Orthodox churches[citation needed]. In most renditions of the Cross of Lorraine, the horizontal bars are "graded" with the upper bar being the shorter, though variations with the bars of equal length are also seen.
Imagery
[edit]The top beam represents the plaque bearing the inscription "Jesus the Nazarene, King of the Jews" (often abbreviated in the Latinate "INRI" and in the Greek as "INBI"). A popular view is that the slanted bottom beam is a footrest; however, there is no evidence of footrests ever being used during the crucifixion, and it has a deeper meaning. The bottom beam may represent a balance of justice. Some sources suggest that as one of the thieves being crucified with Jesus repented of his sin and believed in Jesus as the Messiah and was thus with Christ in Paradise, the other thief rejected and mocked Jesus and therefore descended into Hades.
Many symbolic interpretations of the double-cross have been put forth. One of them says that the first horizontal line symbolized the secular power and the other horizontal line the ecclesiastic power of Byzantine emperors,[citation needed] and also that the first cross bar represents the death, and the second cross the resurrection, of Jesus Christ.
Other variations
[edit]The Russian Orthodox cross can be considered a modified version of the Patriarchal cross, having two smaller crossbeams, one at the top and one near the bottom, in addition to the longer crossbeam. One suggestion is the lower crossbeam represents the footrest (suppedaneum) to which the feet of Jesus were nailed. In some earlier representations (and still currently in the Greek Church) the crossbar near the bottom is straight or slanted upwards. In later Slavic and other traditions, it came to be depicted as slanted, with the side to the viewer's left usually being higher.
One tradition says that this comes from the idea that as Jesus Christ took his last breath, the bar to which his feet were nailed broke, thus slanting to the side. Another tradition holds that the slanted bar represents the repentant thief and the unrepentant thief that were crucified with Christ, the one to Jesus' right-hand repenting and rising to be with God in Paradise, and one on his left falling to Hades and separation from God. In this manner, it also reminds the viewer of the Last Judgment. Still another explanation of the slanted crossbar would suggest the Cross Saltire, as tradition holds that the Apostle St. Andrew introduced Christianity to lands north and west of the Black Sea: today's Ukraine, Russia, Belarus, Moldova, and Romania.
-
Roman Catholic metropolitan archbishop's coat of arms (version with pallium
-
The Russian cross, with slanted cross-bar (suppedaneum)
-
A variation of the Russian cross, so called "Calvary cross"
-
Archangels' cross
-
Archangels' cross variant
Byzantine Empire
[edit]The Patriarchal cross first regularly appeared on the coinage of the Byzantine Empire starting with the second reign of the Emperor Justinian II, whose second reign was from 705–711. At the beginning of the second reign, the Emperor was depicted on the solidus holding a globus cruciger with a Patriarchal cross at the top of the globe.[1] Until then, the standard practice was to show the globus cruciger with an ordinary cross. The Emperor Theodosius III, who ruled from 715 to 717, made the Patriarchal cross a standard feature of the gold, silver and bronze coinage minted in Constantinople.[2] After his short reign ended, the practice was discontinued under his successor, Leo III, due to his iconoclastic views, and was not revived again until the middle of the eighth century by Artavasdus.
-
A solidus of Emperor Theodosius III (r. 715–717) holding a globus cruciger surmounted by a patriarchal cross.
-
A histamenon of co-Emperors Nikephoros II (r. 963–969) and Basil II (r. 976–1025) depicted "wielding the sceptre" (patriarchal cross).
-
A miliaresion of Emperor Michael VII Doukas (r. 1071–1078) depicting a middle Byzantine cross-crosslet variant of the patriarchal cross.
-
A fresco of Serbian Emperor Stefan Dušan holding the patriarchal cross in the manner of a Byzantine Emperor.
Hungary
[edit]The two-barred cross has been one of the main elements in the coat of arms of Hungary at least since 1190. It appeared during the reign of King Béla III,[3] who was raised in the Byzantine court. He was for a time heir to the throne of the Byzantine Empire and betrothed to the emperor's daughter. When the emperor's wife gave birth to a son, the emperor dissolved his daughter's betrothal to Béla and removed Béla's title of despotes. Soon after Béla left Constantinople when he inherited the Hungarian throne in 1172. The cross started appearing floating in the coat of arms and on the coins from this era. During the middle ages, the two-barred cross became associated with the Árpád dynasty and the Kingdom of Hungary along with the Árpád stripes. The symbol found its way to Western Europe through Hungary, because René the Good, who was related to the House Anjou of Hungary, laid claim to four kingdoms, including Hungary. He placed the symbol on his flags before the battle of Nancy.[4] He won the battle and regained his lost Duchy of Lorraine. Thus the symbol became known in Western-Europe as the Cross of Lorraine.
-
Saint Stephen, the first King of Hungary (1000–1038).
-
Coat of arms of Hungary under king Béla III
-
The seal of King Béla IV of Hungary (1235–1270) from his Golden Bull
-
Hungarian flag from Königsfelden Monastery from the first half of the 14th century, from the monastery of Agnes of Habsburg, widow of King Andrew III of Hungary (1290–1301)
-
Reverse of the second double seal (1366–1382) of King Louis I the Great (1342–1382). This was later become the predecessor to the modern coat of arms of Slovakia.
-
Reverse of the first double seal (1387–1405) of King Sigismund of Luxembourg (1387–1437)
-
Archangel Gabriel holds the Holy Crown and the apostolic double cross as the symbols of Hungary, Hősök tere, Budapest, Hungary
Lithuania and Belarus
[edit]Another form of the cross was used by the Jagiellonian dynasty. This cross now features on the coat of arms of Lithuania, where it appears on the shield of the Vytis. It is also the badge of the Lithuanian Air Force and forms the country's highest award for bravery, the Order of the Cross of Vytis. The Jagiellonian cross is also used on the coat of arms and flags of every Lithuanian county, yet not following any heraldic rules.
The Patriarchal Cross appears on the Pahonia, used at various times as the coat of arms of Grand Duchy of Lithuania for centuries and of Belarus.
-
Coat of arms of King Władysław II Jagiełło
-
The coat of arms of Lithuania, with the patriarchal cross on the knight's shield
-
The badge of the Lithuanian Air Force
Russia
[edit]During 1577–1625 the Russian use of the cross was between the heads of the double-headed eagle in the coat of arms of Russia.
Slovakia
[edit]The territory of present-day Slovakia was an integral part of the Kingdom of Hungary from the 10th century until the Treaty of Trianon in 1920. Many of its cities gained privileges and coats of arms from the Hungarian kings, often containing the kings' own coat of arms.
First Slovak Republic (1939–1945)
[edit]-
Coat of arms of First Slovak Republic
-
War flag of the First Slovak Republic, used by a country's military forces
-
Presidential standard of First Slovak Republic
-
Emblem of the Hlinka's Slovak People's Party
-
Flag of the Hlinka's Slovak People's Party
Slovak Republic (since 1993)
[edit]-
Presidential standard of Slovakia
-
Coat of arms of the city of Nitra, Slovakia
-
Coat of arms of Nitra Region, Slovakia
-
Coat of arms of the city of Žilina, Slovakia
-
Coat of arms of Žilina Region, Slovakia
-
Coat of arms of the city of Skalica, Slovakia
-
Coat of arms of the city of Levoča, Slovakia
-
Coat of arms of the city of Zvolen, Slovakia
Typefaces
[edit]Unicode defines the character ☦ (Russian cross) and ☨ (Cross of Lorraine) in the Miscellaneous Symbols range at code point U+2626 and U+2628 respectively.
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Breckenridge, James (1959). The Numismatic Iconography of Justinian II. The American Numismatic Society. p. 23.
- ^ Sear, David (1987). Byzantine Coins and Their Values. Seaby. pp. 283–84. ISBN 0900652713.
- ^ Engel 2001, p. 86.
- ^ Monter 2007, pp. 22–23.
Sources
[edit]- Engel, Pál (2001). The Realm of St Stephen: A History of Medieval Hungary, 895–1526. I.B. Tauris Publishers. ISBN 1-86064-061-3.
- Monter, William (2007). A Bewitched Duchy: Lorraine and its Dukes, 1477–1736. Librairie Droz. ISBN 978-2-600-01165-5.