Inner Six: Difference between revisions
avoid dab link |
No edit summary |
||
| (19 intermediate revisions by 12 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|Six founding member countries of the European Communities}} |
{{Short description|Six founding member countries of the European Communities}} |
||
{{About|the grouping of European states|the fictional character|Number Six (Battlestar Galactica)}} |
{{About|the grouping of European states|the fictional character|Number Six (Battlestar Galactica)}} |
||
{{EU history}} |
{{EU history}} |
||
[[File:EC06-1957-58 European Community map.svg|thumb|The six founders of the [[European Communities]] ([[European Coal and Steel Community]], [[European Community]], [[Euratom]])]] |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
The '''Inner Six''' (also known as '''the Six''' or '''the Six founders''') refers to the six founding [[Member state of the European Union|member states]] of the [[European Union]], namely [[Belgium]], [[France]], [[West Germany]], [[Italy]], [[Luxembourg]], and the [[Netherlands]]. They were the original members of the [[European Communities]], which were later succeeded by the European Union. Named for their location on a map of western Europe, the Inner Six contrasted with the "[[Inner Six#Inner Six and Outer Seven|Outer Seven]]", which pursued a free-trade system. |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | The Inner Six are those who responded to the [[Schuman Declaration]]'s call for the pooling of [[coal]] and [[steel]] resources under a common [[High Authority of the European Coal and Steel Community|High Authority]]. The six signed the [[Treaty of Paris (1951)|Treaty of Paris]] creating the [[European Coal and Steel Community]] on 18 April 1951 (which came into force on 23 July 1952). Following on from this, they attempted to create a [[European Defence Community]]: with the idea of allowing [[West Germany]] to rearm under the authority of a common [[Military of the European Union|European military command]], a treaty was signed in 1952. However the plan was rejected by the [[Senate of France]], which also scuppered the draft treaty for a [[European Political Community (1952)|European Political Community]] (which would have created a political federation to ensure democratic control over the new [[European army]]). |
||
| ⚫ | Dependency on overseas [[oil]] and the steady exhaustion of coal deposits led to the idea of an atomic energy community (a separate Community was favoured by Monnet, rather than simply extending the powers of the ECSC as suggested by the [[European Parliament|Common Assembly]]). However, the [[Benelux]] countries ([[Belgium]], the [[Netherlands]], and [[Luxembourg]]) and West Germany desired a [[single market|common market]]. In order to reconcile the two ideas, both communities would be created.<ref>[http://www.ena.lu?lang=2&doc=5599 1957-1968 Successes and crises] [[European NAvigator]]</ref> Thus, the six went on to sign the [[Treaties of Rome]] in 1957, establishing the [[European Economic Community]] and the [[European Atomic Energy Community]]. The institutions of these communities would later be merged in 1967, leading to them collectively being known as the "[[European Communities]]". |
||
==Inner Six and Outer Seven== |
|||
The |
The "Inner Six" were in contrast to the "'''Outer Seven'''" group of countries who formed the [[European Free Trade Association]] rather than engage in [[supranational union|supranational]] [[European integration]]. Five of the Outer Seven would themselves later join the European Communities. |
||
{| class="wikitable" |
{| class="wikitable" |
||
| Line 27: | Line 37: | ||
*{{flag|United Kingdom}}}} |
*{{flag|United Kingdom}}}} |
||
|} |
|} |
||
| ⚫ | |||
The six would continue in their co-operation until 1973 when they were joined by two of the Outer Seven (UK and Denmark) and Ireland. |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | The Inner Six are those who responded to the [[Schuman Declaration]]'s call for the pooling of [[coal]] and [[steel]] resources under a common [[High Authority of the European Coal and Steel Community|High Authority]]. The six signed the [[Treaty of Paris (1951)|Treaty of Paris]] creating the [[European Coal and Steel Community]] on 18 April 1951 (which came into force on 23 July 1952). Following on from this, they attempted to create a [[European Defence Community]]: with the idea of allowing [[West Germany]] to rearm under the authority of a common [[Military of the European Union|European military command]], a treaty was signed in 1952. However the plan was rejected by the [[Senate of France]], which also scuppered the draft treaty for a [[European Political Community (1952)|European Political Community]] (which would have created a political federation to ensure democratic control over the new [[European army]]). |
||
| ⚫ | Dependency on overseas [[oil]] and the steady exhaustion of coal deposits led to the idea of an atomic energy community (a separate Community was favoured by Monnet, rather than simply extending the powers of the ECSC as suggested by the [[European Parliament|Common Assembly]]). However, the [[Benelux]] countries ([[Belgium]], the [[Netherlands]], and [[Luxembourg]]) and Germany desired a [[single market|common market]]. In order to reconcile the two ideas, both communities would be created.<ref>[http://www.ena.lu?lang=2&doc=5599 1957-1968 Successes and crises] [[European NAvigator]]</ref> Thus, the six went on to sign the [[Treaties of Rome]] in 1957, establishing the [[European Economic Community]] and the [[European Atomic Energy Community]]. The institutions of these communities would later be merged in 1967, leading to them collectively being known as the "[[European Communities]]". |
||
==Enlargement and Brexit: Nine, Ten, Twelve, Fifteen, and beyond== |
==Enlargement and Brexit: Nine, Ten, Twelve, Fifteen, and beyond== |
||
The events of the 1956 [[Suez Crisis]] showed the United Kingdom that it could no longer operate alone, instead turning to the [[United States]] and the [[European Communities]]. |
The events of the 1956 [[Suez Crisis]] showed the United Kingdom that it could no longer operate alone, instead turning to the [[United States]] and the [[European Communities]]. The United Kingdom, along with Denmark, Ireland and Norway, applied for membership in 1960. However, then–[[French President]] [[Charles de Gaulle]] saw British membership of the Community as a [[Trojan horse]] for United States interests, and hence stated he would veto British membership.<ref>[http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/europe/6102536.stm France's own lesson from Suez] [[BBC News]]</ref> The four countries resubmitted their applications on 11 May 1967 and with [[Georges Pompidou]] succeeding Charles de Gaulle as French President, the veto was lifted. Negotiations began in 1970 and two years later the accession treaties were signed with all but Norway acceding to the Community (Norway rejected membership in a [[1972 Norwegian European Communities membership referendum|1972 referendum]]). |
||
In 1981 [[Greece]] joined the European Community, bringing the number to ten. After its democratic revolution, Portugal would also leave [[European Free Trade Association|EFTA]] to join the Communities in 1986, along with [[Spain]]. The twelve were joined by Sweden, Austria and [[Finland]] (which had joined EFTA in 1986) in 1995, leaving only Norway and Switzerland as the remaining members of the original outer seven, although EFTA had gained two new members ([[Iceland]] and [[Liechtenstein]]) in the intervening time. On the other hand, membership of the Communities, now the [[European Union]] (EU), had reached 28. With the approval of [[Brexit]], which saw the |
In 1981 [[Greece]] joined the European Community, bringing the number to ten. After its democratic revolution, Portugal would also leave [[European Free Trade Association|EFTA]] to join the Communities in 1986, along with [[Spain]]. The twelve were joined by Sweden, Austria and [[Finland]] (which had joined EFTA in 1986) in 1995, leaving only Norway and Switzerland as the remaining members of the original outer seven, although EFTA had gained two new members ([[Iceland]] and [[Liechtenstein]]) in the intervening time. On the other hand, membership of the Communities, now the [[European Union]] (EU), had reached 28. With the approval of [[Brexit]], which saw the United Kingdom leave the EU on 31 January 2020 after a [[Brexit referendum|June 2016 referendum]] and political negotiations, the EU currently has 27 members. |
||
==Modern "inner" groups== |
==Modern "inner" groups== |
||
| Line 90: | Line 98: | ||
| style="background:#bfb;" |x |
| style="background:#bfb;" |x |
||
|- align="center" |
|- align="center" |
||
| align="left" |{{flagicon|Germany}} [[Germany]] |
| align="left" |{{flagicon|Germany}} [[West Germany]] |
||
| style="background:#bfb;" |x |
| style="background:#bfb;" |x |
||
| style="background:#bfb;" |x |
| style="background:#bfb;" |x |
||
| Line 117: | Line 125: | ||
| style="background:#bfb;" |x |
| style="background:#bfb;" |x |
||
| style="background:#bfb;" |x |
| style="background:#bfb;" |x |
||
| style="background:# |
| style="background:#bfb;" |x |
||
| style="background:#bfb;" |x |
| style="background:#bfb;" |x |
||
| style="background:#bfb;" |x |
| style="background:#bfb;" |x |
||
| Line 163: | Line 171: | ||
* [[Big Four (Western Europe)]] |
* [[Big Four (Western Europe)]] |
||
* [[Craiova Group]] |
* [[Craiova Group]] |
||
| ⚫ | |||
* [[EU Med Group]] |
* [[EU Med Group]] |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
* [[European Economic Area]] |
* [[European Economic Area]] |
||
* [[European Free Trade Association]] |
* [[European Free Trade Association]] |
||
| ⚫ | |||
* [[G6 (EU)]] |
* [[G6 (EU)]] |
||
* [[Multi-speed Europe]] |
* [[Multi-speed Europe]] |
||
| Line 175: | Line 183: | ||
== References == |
== References == |
||
{{ |
{{Reflist}} |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
[[Category:1951 establishments in Europe]] |
[[Category:1951 establishments in Europe]] |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
Latest revision as of 19:31, 14 November 2024
| History of the European Union |
|---|
 |
|
|
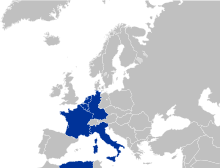
The Inner Six (also known as the Six or the Six founders) refers to the six founding member states of the European Union, namely Belgium, France, West Germany, Italy, Luxembourg, and the Netherlands. They were the original members of the European Communities, which were later succeeded by the European Union. Named for their location on a map of western Europe, the Inner Six contrasted with the "Outer Seven", which pursued a free-trade system.
History
[edit]The Inner Six are those who responded to the Schuman Declaration's call for the pooling of coal and steel resources under a common High Authority. The six signed the Treaty of Paris creating the European Coal and Steel Community on 18 April 1951 (which came into force on 23 July 1952). Following on from this, they attempted to create a European Defence Community: with the idea of allowing West Germany to rearm under the authority of a common European military command, a treaty was signed in 1952. However the plan was rejected by the Senate of France, which also scuppered the draft treaty for a European Political Community (which would have created a political federation to ensure democratic control over the new European army).
Dependency on overseas oil and the steady exhaustion of coal deposits led to the idea of an atomic energy community (a separate Community was favoured by Monnet, rather than simply extending the powers of the ECSC as suggested by the Common Assembly). However, the Benelux countries (Belgium, the Netherlands, and Luxembourg) and West Germany desired a common market. In order to reconcile the two ideas, both communities would be created.[1] Thus, the six went on to sign the Treaties of Rome in 1957, establishing the European Economic Community and the European Atomic Energy Community. The institutions of these communities would later be merged in 1967, leading to them collectively being known as the "European Communities".
Inner Six and Outer Seven
[edit]The "Inner Six" were in contrast to the "Outer Seven" group of countries who formed the European Free Trade Association rather than engage in supranational European integration. Five of the Outer Seven would themselves later join the European Communities.
| EFTA Members (Outer Seven) | |
|---|---|
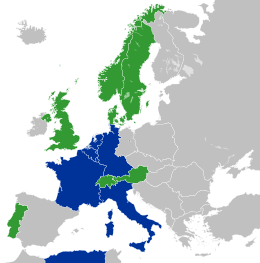
The six would continue in their co-operation until 1973 when they were joined by two of the Outer Seven (UK and Denmark) and Ireland.
Enlargement and Brexit: Nine, Ten, Twelve, Fifteen, and beyond
[edit]The events of the 1956 Suez Crisis showed the United Kingdom that it could no longer operate alone, instead turning to the United States and the European Communities. The United Kingdom, along with Denmark, Ireland and Norway, applied for membership in 1960. However, then–French President Charles de Gaulle saw British membership of the Community as a Trojan horse for United States interests, and hence stated he would veto British membership.[2] The four countries resubmitted their applications on 11 May 1967 and with Georges Pompidou succeeding Charles de Gaulle as French President, the veto was lifted. Negotiations began in 1970 and two years later the accession treaties were signed with all but Norway acceding to the Community (Norway rejected membership in a 1972 referendum). In 1981 Greece joined the European Community, bringing the number to ten. After its democratic revolution, Portugal would also leave EFTA to join the Communities in 1986, along with Spain. The twelve were joined by Sweden, Austria and Finland (which had joined EFTA in 1986) in 1995, leaving only Norway and Switzerland as the remaining members of the original outer seven, although EFTA had gained two new members (Iceland and Liechtenstein) in the intervening time. On the other hand, membership of the Communities, now the European Union (EU), had reached 28. With the approval of Brexit, which saw the United Kingdom leave the EU on 31 January 2020 after a June 2016 referendum and political negotiations, the EU currently has 27 members.
Modern "inner" groups
[edit]Today, there are still some groups within the European Union integrating faster than others, for example the eurozone and Schengen Area (see: Opt-outs in the European Union). The Treaty of Lisbon includes provisions for a group of countries to integrate without the inclusions of others if they do not wish to join in as, following the rejection of the European Constitution, some leaders wished to create an inner, more highly integrated federal Europe within a slower-moving EU.
The Inner Six are today among the most integrated members of the EU.
| Participant | Schengen | AFSJ | CFR | Euro | EEA | ESM | EFC | SRM | Euro+ | CSDP | Prüm | Patent | Divorce | Symbols |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | |
| x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | |
| x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | |
| x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | |
| x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | |
| x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | o | o |
x – member
o – non-member
See also
[edit]- Arraiolos meeting
- Big Four (Western Europe)
- Craiova Group
- EU Med Group
- EU three
- Enlargement of the European Union
- European Economic Area
- European Free Trade Association
- G6 (EU)
- Multi-speed Europe
- Opt-outs in the European Union
- Schengen Agreement
- Visegrád Group
