Nazca plate: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
minor formatting, typo(s) fixed: east-west → east–west |
||
| (45 intermediate revisions by 32 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ |
{{Short description|Oceanic tectonic plate in the eastern Pacific Ocean basin}} |
||
| ⚫ | |||
{{Infobox tectonic plate |
{{Infobox tectonic plate |
||
| image = File:NazcaPlate.png |
| image = File:NazcaPlate.png |
||
| alt = The Nazca Plate |
|||
| type = [[List of tectonic plates#Minor plates|Minor]] |
| type = [[List of tectonic plates#Minor plates|Minor]] |
||
| area = 15,600,000 km<sup>2</sup><ref>{{cite web|url=http://geology.about.com/library/bl/blplate_size_table.htm|title=Sizes of Tectonic or Lithospheric Plates |
| area = 15,600,000 km<sup>2</sup><ref>{{cite web |url=http://geology.about.com/library/bl/blplate_size_table.htm |title=Sizes of Tectonic or Lithospheric Plates |work=About.com Geology |access-date=4 January 2016 |archive-date=9 February 2007 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070209033841/http://geology.about.com/library/bl/blplate_size_table.htm |url-status=dead }}</ref> |
||
| move_direction = |
| move_direction = north-east |
||
| move_speed = 40- |
| move_speed = 40-53 mm/year |
||
| geo_features = [[Pacific Ocean]] |
| geo_features = [[Pacific Ocean]] |
||
}} |
}} |
||
The '''Nazca |
The '''Nazca plate''' or '''Nasca plate''',<ref>{{Cite book |title=Oxford Atlas of the World 26th Ed. |publisher=Oxford University Press |year=2019 |isbn=978-0-19-006581-2 |location=New York, NY |pages=74}}</ref> named after the [[Nazca]] region of southern [[Peru]], is an oceanic [[list of tectonic plates|tectonic plate]] in the eastern [[Pacific Ocean]] basin off the west coast of [[South America]]. The ongoing [[subduction]], along the [[Peru–Chile Trench]], of the Nazca plate under the [[South American plate]] is largely responsible for the [[Andes|Andean orogeny]]. The Nazca plate is bounded on the west by the [[Pacific plate]] and to the south by the [[Antarctic plate]] through the [[East Pacific Rise]] and the [[Chile Rise]], respectively. The movement of the Nazca plate over several [[Hotspot (geology)|hotspots]] has created some [[volcanic islands]] as well as east–west running [[seamount]] chains that subduct under [[South America]]. Nazca is a relatively young plate in terms of the age of its rocks and its existence as an independent plate, having been formed from the breakup of the [[Farallon plate]] about 23 million years ago. The oldest rocks of the plate are about 50 million years old.<ref>{{cite web |title=Sea Floor Spreading in the Pacific (Plate Boundaries Shown) |first=Steven |last=Dutch |url=https://www.uwgb.edu/dutchs/GeolColBk/PacificSFS-PB.HTM |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100317130720/https://www.uwgb.edu/dutchs/GeolColBk/PacificSFS-PB.HTM |archive-date=17 March 2010 |date=10 August 2009 |publisher=University of Wisconsin – Green Bay}}</ref> |
||
==Boundaries== |
==Boundaries== |
||
===East Pacific and Chile Rise=== |
===East Pacific and Chile Rise=== |
||
{{Main|East Pacific Rise|Chile Rise}} |
{{Main|East Pacific Rise|Chile Rise}} |
||
A [[triple junction]], the [[Chile Triple Junction]],<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.nsm.buffalo.edu/courses/gly481-581/McGuire05_2.pdf |
A [[triple junction]], the [[Chile Triple Junction]],<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.nsm.buffalo.edu/courses/gly481-581/McGuire05_2.pdf |title=Tectonics of South America: Chile Triple Junction |date=8 April 2004 |author=Kelly McGuire |access-date=27 February 2016 |archive-date=19 January 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200119100719/http://www.nsm.buffalo.edu/courses/gly481-581/McGuire05_2.pdf |url-status=live }}</ref> occurs on the seafloor of the [[Pacific Ocean]] off [[Taitao Peninsula|Taitao]] and [[Tres Montes Peninsula]] at the southern coast of [[Chile]]. Here, three [[tectonics|tectonic]] plates meet: the Nazca plate, the [[South American plate]], and the [[Antarctic plate]]. |
||
===Peru–Chile Trench=== |
===Peru–Chile Trench=== |
||
{{See also|Peru–Chile Trench}} |
{{See also|Peru–Chile Trench}} |
||
The eastern margin is a [[convergent boundary]] [[subduction |
The eastern margin is a [[convergent boundary]] [[subduction]] zone under the South American plate and the [[Andes Mountains]], forming the [[Peru–Chile Trench]]. The southern side is a [[divergent boundary]] with the Antarctic plate, the [[Chile Rise]], where [[seafloor spreading]] permits [[magma]] to rise. The western side is a divergent boundary with the [[Pacific plate]], forming the [[East Pacific Rise]]. The northern side is a divergent boundary with the [[Cocos plate]], the [[Galapagos Rise]]. |
||
The subduction of the Nazca plate under southern Chile has a history of producing massive [[earthquake]]s, including the largest ever recorded on earth, the [[moment magnitude scale|moment magnitude]] 9.5 [[1960 Valdivia earthquake]]. |
The subduction of the Nazca plate under southern Chile has a history of producing massive [[earthquake]]s, including the largest ever recorded on earth, the [[moment magnitude scale|moment magnitude]] 9.5 [[1960 Valdivia earthquake]]. |
||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
{{Main|Easter hotspot|Juan Fernández hotspot|Galápagos hotspot}} |
{{Main|Easter hotspot|Juan Fernández hotspot|Galápagos hotspot}} |
||
A second triple junction occurs at the northwest corner of the plate where the Nazca, Cocos, and Pacific |
A second triple junction occurs at the northwest corner of the plate where the Nazca, Cocos, and Pacific plates all join off the coast of [[Colombia]]. Yet another triple junction occurs at the southwest corner at the intersection of the Nazca, Pacific, and Antarctic plates off the coast of southern [[Chile]]. At each of these triple junctions an ''[[:wikt:anomaly|anomalous]]'' microplate exists, the [[Galapagos microplate]] at the northern junction and the [[Juan Fernandez microplate]] at the southern junction. The [[Easter Plate|Easter Island microplate]] is a third microplate that is located just north of the Juan Fernandez Microplate and lies just west of [[Easter Island]]. |
||
===Aseismic ridges=== |
===Aseismic ridges=== |
||
{{Main|Nazca Ridge|Juan Fernández Ridge|Carnegie Ridge|}} |
{{Main|Nazca Ridge|Juan Fernández Ridge|Carnegie Ridge|}} |
||
The '''Carnegie Ridge''' is a |
The '''Carnegie Ridge''' is a {{convert|1350|km|mi|adj=mid|-long}} and up to {{convert|300|km|mi|adj=mid|-wide}} feature on the ocean floor of the northern Nazca plate that includes the [[Galápagos Islands|Galápagos archipelago]] at its western end. It is being subducted under South America with the rest of the Nazca plate. |
||
===Fracture zones=== |
|||
The [[Darwin Gap]] is the area between the Nazca Plate and the coast of [[Chile]], where [[Charles Darwin]] experienced the [[1835 Concepción earthquake|earthquake of 1835]]. It is expected that this area will be the [[epicenter]] of a major quake in the near future.<ref>{{cite magazine|title=Darwin Gap quake will shake Chile again|url=https://www.newscientist.com/article/dn20048-darwin-gap-quake-will-shake-chile-again.html|magazine=New Scientist|date=30 Jan 2011|author=Kate Ravilious|access-date=8 Feb 2011}}</ref> |
|||
==Plate motion== |
==Plate motion== |
||
The absolute motion of the Nazca |
The absolute motion of the Nazca plate has been calibrated at {{cvt|3.7|cm/yr}} east motion (88°), one of the fastest absolute motions of any tectonic plate. The subducting Nazca plate, which exhibits unusual [[flat slab subduction]], is tearing as well as deforming as it is subducted (Barzangi and Isacks). The subduction has formed and continues to form the [[volcano|volcanic]] [[Andes]] Mountain Range. Deformation of the Nazca plate even affects the [[Geography of Bolivia|geography]] of [[Bolivia]], far to the east (Tinker et al.). The [[1994 Bolivia earthquake]] occurred on the Nazca plate; this had a magnitude of 8.2 <math>M_w</math>, which at that time was the strongest instrumentally recorded earthquake occurring deeper than {{cvt|300|km}}. |
||
Aside from the [[Juan Fernández Islands]], this area has very few other islands that are affected by the earthquakes |
Aside from the [[Juan Fernández Islands]], this area has very few other islands that are affected by the earthquakes resulting from complicated movements at these junctions. |
||
==Geologic history== |
==Geologic history== |
||
{{See also|Farallon |
{{See also|Farallon plate}} |
||
The precursor of |
The precursor of the Nazca plate, [[Juan de Fuca plate]], and the [[Cocos plate]] was the [[Farallon plate]], which split in the late [[Oligocene]], about 22.8 [[myr|Mya]], a date arrived at by interpreting [[Geomagnetism|magnetic anomalies]]. Subduction under the South American continent began about 140 Mya, although the formation of the high parts of the Central Andes and the Bolivian [[orocline]] did not occur until 45 Mya. It has been suggested that the mountains were forced up by the subduction of the older and heavier parts of the plate, which sank more quickly into the [[Mantle (geology)|mantle]].<ref>{{cite news |title=Mountains on a plate form the Andes |url=http://www.universityworldnews.com/article.php?story=20120321111927290 |publisher=University World News |date=25 March 2012 |issue=214 |access-date=8 February 2016 |archive-date=13 September 2015 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150913114457/http://www.universityworldnews.com/article.php?story=20120321111927290 |url-status=live }}</ref> |
||
==See also== |
==See also== |
||
*[[2010 Chile earthquake]] |
*[[2010 Chile earthquake]] |
||
*[[Caribbean |
*[[Caribbean plate]] |
||
==References== |
==References== |
||
| Line 58: | Line 55: | ||
===Bibliography=== |
===Bibliography=== |
||
*[https://web.archive.org/web/20100211011746/http://www.extremescience.com/PlateTectonicsmap.htm Extreme Science site: "A Lesson in Plate |
* [https://web.archive.org/web/20100211011746/http://www.extremescience.com/PlateTectonicsmap.htm Extreme Science site: "A Lesson in Plate Tectonics"] The basics explained. |
||
*[http://www.earth.columbia.edu/news/2002/story12-05-02.html Galapagos rise junction (map)] |
* [http://www.earth.columbia.edu/news/2002/story12-05-02.html Galapagos rise junction (map)] |
||
*[http://www.pmel.noaa.gov/vents/s-epr.html Juan Fernandez and Easter microplate (map)] |
* [http://www.pmel.noaa.gov/vents/s-epr.html Juan Fernandez and Easter microplate (map)] |
||
*Muawia Barazangi and Bryan L. Isacks, "Spatial distribution of earthquakes and subduction of the Nazca plate beneath South America" in ''Geology'' Vol. 4, No. 11, pp. 686–692. [https://web.archive.org/web/20120229132304/http://www.gsajournals.org/gsaonline/?request=get-abstract&doi=10.1130%2F0091-7613(1976)4%3C686:SDOEAS%3E2.0.CO%3B2 Abstract] |
* Muawia Barazangi and Bryan L. Isacks, "Spatial distribution of earthquakes and subduction of the Nazca plate beneath South America" in ''Geology'' Vol. 4, No. 11, pp. 686–692. [https://web.archive.org/web/20120229132304/http://www.gsajournals.org/gsaonline/?request=get-abstract&doi=10.1130%2F0091-7613(1976)4%3C686:SDOEAS%3E2.0.CO%3B2 Abstract] |
||
*Mark Andrew Tinker, Terry C. Wallace, [[Susan L. Beck]], Stephen Myers, and Andrew Papanikolas, "Geometry and state of stress of the Nazca plate beneath Bolivia and its implication for the evolution of the Bolivian orocline" in ''Geology'' '''24'''(5), pp. 387–390 [https://web.archive.org/web/20120229132313/http://www.gsajournals.org/gsaonline/?request=get-abstract&doi=10.1130%2F0091-7613(1996)024%3C0387:GASOSO%3E2.3.CO%3B2 Abstract] |
*Mark Andrew Tinker, Terry C. Wallace, [[Susan L. Beck]], Stephen Myers, and Andrew Papanikolas, "Geometry and state of stress of the Nazca plate beneath Bolivia and its implication for the evolution of the Bolivian orocline" in ''Geology'' '''24'''(5), pp. 387–390 [https://web.archive.org/web/20120229132313/http://www.gsajournals.org/gsaonline/?request=get-abstract&doi=10.1130%2F0091-7613(1996)024%3C0387:GASOSO%3E2.3.CO%3B2 Abstract] |
||
*Cahill, T. and B. Isacks (1992). "Seismicity and shape of the subducted Nazca plate." ''Journal Geophysical Research'' '''97''' (12) |
* Cahill, T. and B. Isacks (1992). "Seismicity and shape of the subducted Nazca plate." ''Journal Geophysical Research'' '''97''' (12) |
||
*James, D. (1978). "Subduction of the Nazca plate beneath Central Peru." ''Geology'' '''6''' (3) pp 174–178 |
* James, D. (1978). "Subduction of the Nazca plate beneath Central Peru." ''Geology'' '''6''' (3) pp 174–178 |
||
*[http://www-odp.tamu.edu/publications/170_SR/VOLUME/CHAPTERS/SR170_07.PDF Martin Meschede and Udo Barckhausen, "Plate tectonic evolution of the Cocos-Nazca spreading center"] |
* [http://www-odp.tamu.edu/publications/170_SR/VOLUME/CHAPTERS/SR170_07.PDF Martin Meschede and Udo Barckhausen, "Plate tectonic evolution of the Cocos-Nazca spreading center"] |
||
| ⚫ | |||
{{Central America plates}} |
{{Central America plates}} |
||
| ⚫ | |||
{{Authority control}} |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
[[Category:Tectonic plates]] |
[[Category:Tectonic plates]] |
||
[[Category:Geology of Chile]] |
[[Category:Geology of Chile]] |
||
[[Category:Natural history of Oceania]] |
|||
[[Category:Natural history of South America]] |
[[Category:Natural history of South America]] |
||
[[Category:Geology of the Pacific Ocean]] |
[[Category:Geology of the Pacific Ocean]] |
||
Latest revision as of 12:20, 9 November 2024
| Nazca plate | |
|---|---|
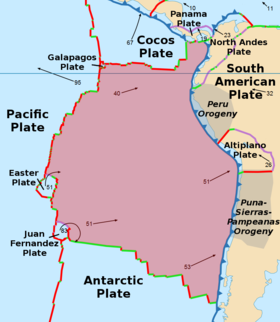 | |
| Type | Minor |
| Approximate area | 15,600,000 km2[1] |
| Movement1 | north-east |
| Speed1 | 40-53 mm/year |
| Features | Pacific Ocean |
| 1Relative to the African plate | |
The Nazca plate or Nasca plate,[2] named after the Nazca region of southern Peru, is an oceanic tectonic plate in the eastern Pacific Ocean basin off the west coast of South America. The ongoing subduction, along the Peru–Chile Trench, of the Nazca plate under the South American plate is largely responsible for the Andean orogeny. The Nazca plate is bounded on the west by the Pacific plate and to the south by the Antarctic plate through the East Pacific Rise and the Chile Rise, respectively. The movement of the Nazca plate over several hotspots has created some volcanic islands as well as east–west running seamount chains that subduct under South America. Nazca is a relatively young plate in terms of the age of its rocks and its existence as an independent plate, having been formed from the breakup of the Farallon plate about 23 million years ago. The oldest rocks of the plate are about 50 million years old.[3]
Boundaries
[edit]East Pacific and Chile Rise
[edit]A triple junction, the Chile Triple Junction,[4] occurs on the seafloor of the Pacific Ocean off Taitao and Tres Montes Peninsula at the southern coast of Chile. Here, three tectonic plates meet: the Nazca plate, the South American plate, and the Antarctic plate.
Peru–Chile Trench
[edit]The eastern margin is a convergent boundary subduction zone under the South American plate and the Andes Mountains, forming the Peru–Chile Trench. The southern side is a divergent boundary with the Antarctic plate, the Chile Rise, where seafloor spreading permits magma to rise. The western side is a divergent boundary with the Pacific plate, forming the East Pacific Rise. The northern side is a divergent boundary with the Cocos plate, the Galapagos Rise.
The subduction of the Nazca plate under southern Chile has a history of producing massive earthquakes, including the largest ever recorded on earth, the moment magnitude 9.5 1960 Valdivia earthquake.
Intraplate features
[edit]Hotspots
[edit]A second triple junction occurs at the northwest corner of the plate where the Nazca, Cocos, and Pacific plates all join off the coast of Colombia. Yet another triple junction occurs at the southwest corner at the intersection of the Nazca, Pacific, and Antarctic plates off the coast of southern Chile. At each of these triple junctions an anomalous microplate exists, the Galapagos microplate at the northern junction and the Juan Fernandez microplate at the southern junction. The Easter Island microplate is a third microplate that is located just north of the Juan Fernandez Microplate and lies just west of Easter Island.
Aseismic ridges
[edit]The Carnegie Ridge is a 1,350-kilometre-long (840 mi) and up to 300-kilometre-wide (190 mi) feature on the ocean floor of the northern Nazca plate that includes the Galápagos archipelago at its western end. It is being subducted under South America with the rest of the Nazca plate.
Plate motion
[edit]The absolute motion of the Nazca plate has been calibrated at 3.7 cm/year (1.5 in/year) east motion (88°), one of the fastest absolute motions of any tectonic plate. The subducting Nazca plate, which exhibits unusual flat slab subduction, is tearing as well as deforming as it is subducted (Barzangi and Isacks). The subduction has formed and continues to form the volcanic Andes Mountain Range. Deformation of the Nazca plate even affects the geography of Bolivia, far to the east (Tinker et al.). The 1994 Bolivia earthquake occurred on the Nazca plate; this had a magnitude of 8.2 , which at that time was the strongest instrumentally recorded earthquake occurring deeper than 300 km (190 mi).
Aside from the Juan Fernández Islands, this area has very few other islands that are affected by the earthquakes resulting from complicated movements at these junctions.
Geologic history
[edit]The precursor of the Nazca plate, Juan de Fuca plate, and the Cocos plate was the Farallon plate, which split in the late Oligocene, about 22.8 Mya, a date arrived at by interpreting magnetic anomalies. Subduction under the South American continent began about 140 Mya, although the formation of the high parts of the Central Andes and the Bolivian orocline did not occur until 45 Mya. It has been suggested that the mountains were forced up by the subduction of the older and heavier parts of the plate, which sank more quickly into the mantle.[5]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ "Sizes of Tectonic or Lithospheric Plates". About.com Geology. Archived from the original on 9 February 2007. Retrieved 4 January 2016.
- ^ Oxford Atlas of the World 26th Ed. New York, NY: Oxford University Press. 2019. p. 74. ISBN 978-0-19-006581-2.
- ^ Dutch, Steven (10 August 2009). "Sea Floor Spreading in the Pacific (Plate Boundaries Shown)". University of Wisconsin – Green Bay. Archived from the original on 17 March 2010.
- ^ Kelly McGuire (8 April 2004). "Tectonics of South America: Chile Triple Junction" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 19 January 2020. Retrieved 27 February 2016.
- ^ "Mountains on a plate form the Andes". No. 214. University World News. 25 March 2012. Archived from the original on 13 September 2015. Retrieved 8 February 2016.
Bibliography
[edit]- Extreme Science site: "A Lesson in Plate Tectonics" The basics explained.
- Galapagos rise junction (map)
- Juan Fernandez and Easter microplate (map)
- Muawia Barazangi and Bryan L. Isacks, "Spatial distribution of earthquakes and subduction of the Nazca plate beneath South America" in Geology Vol. 4, No. 11, pp. 686–692. Abstract
- Mark Andrew Tinker, Terry C. Wallace, Susan L. Beck, Stephen Myers, and Andrew Papanikolas, "Geometry and state of stress of the Nazca plate beneath Bolivia and its implication for the evolution of the Bolivian orocline" in Geology 24(5), pp. 387–390 Abstract
- Cahill, T. and B. Isacks (1992). "Seismicity and shape of the subducted Nazca plate." Journal Geophysical Research 97 (12)
- James, D. (1978). "Subduction of the Nazca plate beneath Central Peru." Geology 6 (3) pp 174–178
- Martin Meschede and Udo Barckhausen, "Plate tectonic evolution of the Cocos-Nazca spreading center"


