Chalkidiki: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (18 intermediate revisions by 13 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|Peninsula in Macedonia, Greece}} |
{{Short description|Peninsula in Macedonia, Greece}} |
||
{{Infobox |
{{Infobox Greece place |
||
| name = Chalkidiki |
|||
| |
| name_local = <small>Περιφερειακή ενότητα</small><br />Χαλκιδικής |
||
| |
| type = regional unit |
||
| |
| image_skyline = 2010 Dimi Chalkidikis numbered.svg |
||
| |
| caption_skyline = Municipalities of Chalkidiki |
||
| |
| image_map = Nomos Chalidikis.png |
||
| |
| map_caption = Chalkidiki within Greece |
||
| |
| coordinates = {{coord|40|20|N|23|30|E|display=inline,title}} |
||
| |
| georegion = [[Macedonia (Greece)|Macedonia]] |
||
| |
| periph = [[Central Macedonia]] |
||
| |
| seat = [[Polygyros]] |
||
| |
| area = 2918 <!-- 2917.877 --> |
||
| |
| elevation = |
||
| |
| population = 102085 |
||
| |
| population_as_of = 2021 |
||
| |
| demonym = |
||
| |
| postal_code = 63x xx |
||
| |
| area_code = 237x0, 239x0 |
||
| |
| licence = ΧΚ |
||
| |
| website = {{URL|www.halkidiki.gov.gr}} |
||
| pushpin_label_position = |
|||
| pushpin_map_alt = |
|||
| pushpin_map_caption = |
|||
| coordinates = {{coord|40|20|N|23|30|E|display=inline,title}} |
|||
| coor_pinpoint = |
|||
| coordinates_footnotes = |
|||
| subdivision_type = Country |
|||
| subdivision_name = {{flag|Greece}} |
|||
| subdivision_type1 = [[modern regions of Greece|Region]] |
|||
| subdivision_name1 = |
|||
| established_title = |
|||
| established_date = 2011 |
|||
| founder = |
|||
| seat_type = Capital |
|||
| seat = [[Polygyros]] |
|||
| government_footnotes = |
|||
| leader_party = |
|||
| leader_title = Vice Governor |
|||
| leader_name = Ioannis Giorgos |
|||
| unit_pref = Metric |
|||
| area_footnotes = |
|||
| area_total_km2 = 2918 <!-- 2917.877 --> |
|||
| area_land_km2 = |
|||
| area_water_km2 = |
|||
| area_water_percent = |
|||
| area_note = |
|||
| elevation_footnotes = |
|||
| elevation_m = |
|||
| population_footnotes = |
|||
| population_total = 101324 |
|||
| population_as_of = 2021 |
|||
| population_density_km2 = auto |
|||
| population_demonym = |
|||
| population_note = |
|||
| timezone = [[Eastern European Time|EET]] |
|||
| utc_offset = +2 |
|||
| timezone1_DST = [[EEST]] |
|||
| utc_offset1_DST = +3 |
|||
| postal_code_type = [[Postal codes in Greece|Postal codes]] |
|||
| postal_code = 63x xx |
|||
| area_code_type = [[Telephone numbers in Greece|Area codes]] |
|||
| area_code = 237x0, 239x0 |
|||
| blank_name = [[Vehicle registration plates of Greece|Vehicle plates]] |
|||
| blank_info = ΧΚ |
|||
| iso_code = GR-64 |
|||
| website = {{URL|www.halkidiki.gov.gr}} |
|||
| footnotes = |
|||
| subdivision_type2 = Geographic region |
|||
| subdivision_name2 = {{Flagicon image|Flag of Greek Macedonia.svg|size=23px}} |
|||
[[Macedonia (Greece) | Macedonia]] |
|||
}} |
}} |
||
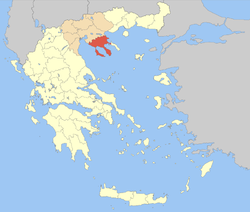
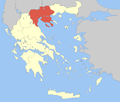
'''Chalkidiki''' ({{IPAc-en|k|æ|l|ˈ|k|ɪ|d|ᵻ|k|i}}; {{langx|el|Χαλκιδική|Chalkidikḗ}} {{IPA-el|xalciðiˈci|}}, alternatively '''Halkidiki'''), also known as '''Chalcidice''', is a [[peninsula]] and [[regional units of Greece|regional unit of Greece]], part of the region of [[Central Macedonia]], in the [[Geographic regions of Greece|geographic region]] of [[Macedonia (Greece)|Macedonia]] in [[Northern Greece]]. The autonomous [[Mount Athos]] region constitutes the easternmost part of the peninsula, but not of the regional unit. |
|||
'''Chalkidiki''' ({{IPAc-en|k|æ|l|ˈ|k|ɪ|d|ᵻ|k|i}}; {{lang-el|Χαλκιδική|Chalkidikḗ}} {{IPA-el|xalciðiˈci|}}, alternatively '''Halkidiki'''), also known as '''Chalcidice''', is a [[peninsula]] and [[regional units of Greece|regional unit of Greece]], part of the region of [[Central Macedonia]], in the [[Geographic regions of Greece|geographic region]] of [[Macedonia (Greece)|Macedonia]] in [[Northern Greece]]. The autonomous [[Mount Athos]] region constitutes the easternmost part of the peninsula, but not of the regional unit. |
|||
The capital of Chalkidiki is the town of [[Polygyros]], located in the centre of the peninsula, while the largest town is [[Nea Moudania]]. Chalkidiki is a popular summer tourist destination. |
The capital of Chalkidiki is the town of [[Polygyros]], located in the centre of the peninsula, while the largest town is [[Nea Moudania]]. Chalkidiki is a popular summer tourist destination. |
||
==Name== |
==Name== |
||
''Chalkidiki'' also spelled ''Halkidiki'' ({{IPAc-en|k|æ|l|ˈ|k|ɪ|d|ᵻ|k|i}}) or ''Chalcidice'' ({{IPAc-en|k|æ|l|ˈ|s|ɪ|d|ᵻ|s|i}}) |
''Chalkidiki'' also spelled ''Halkidiki'' ({{IPAc-en|k|æ|l|ˈ|k|ɪ|d|ᵻ|k|i}}) or ''Chalcidice'' ({{IPAc-en|k|æ|l|ˈ|s|ɪ|d|ᵻ|s|i}}) is named after the ancient Greek city-state of [[Chalcis]] in [[Euboea]], which colonised the area in the 8th century BC. |
||
==Geography== |
==Geography== |
||
[[File:Chalcidice.jpg|thumb|left|Map of ancient Chalcidice]] |
[[File:Chalcidice.jpg|thumb|left|Map of ancient Chalcidice]] |
||
Chalkidiki consists of a large peninsula in the northwestern [[Aegean Sea]], resembling a hand with three 'fingers' (though in Greek these peninsulas are often referred to as 'legs'). From west to east, these are [[Kassandra, Chalkidiki|Kassandra]] (highest peak 345 m), [[Sithonia]] (highest peak Mt Itamos 817 m), and [[Mount Athos]], a special polity within Greece known for its monasteries and its highest peak reaching 2,033 metres above sea level. These 'fingers' are separated by two gulfs, the [[Toronean Gulf]] and the [[Singitic Gulf]]. |
|||
The [[Cholomontas]] mountains lie in the north-central part of Chalkidiki, with the highest peak reaching 1,165 metres above sea level. |
|||
Chalkidiki borders on the regional unit of Thessaloniki to the north, and is bounded by the [[Thermaic Gulf]] on the west, and the [[Strymonian Gulf]] and Ierissos Gulf on the east (which are separated by the Brostomnitsa peninsula). |
|||
The [[Mount Cholomon|Cholomontas]] mountains lie in the north-central part of Chalkidiki, with the highest peak reaching 1,165 metres above sea level. Chalkidiki has a few rivers running from Mt Cholomontas south to the sea, these include the Havrias, Vatonias (Olynthios) and Psychros rivers. Chalkidiki also has a few islands including the inhabited [[Ammouliani]] and [[Diaporos Island|Diaporos]] both in the Singitic Gulf. |
|||
Its largest towns are [[Nea Moudania]] ({{Lang|el|Νέα Μουδανιά}}), [[Kallikrateia|Nea Kallikrateia]] ({{Lang|el|Νέα Καλλικράτεια}}) and the capital town of [[Polygyros]] ({{Lang|el|Πολύγυρος}}). |
Its largest towns are [[Nea Moudania]] ({{Lang|el|Νέα Μουδανιά}}), [[Kallikrateia|Nea Kallikrateia]] ({{Lang|el|Νέα Καλλικράτεια}}) and the capital town of [[Polygyros]] ({{Lang|el|Πολύγυρος}}). |
||
| Line 93: | Line 44: | ||
===Climate=== |
===Climate=== |
||
The climate of Chalkidiki is mainly [[Mediterranean climate|Mediterranean]] ([[Koppen]]: ''Csa'') with cool, wet winters and hot, relatively dry summers. Snowfalls are possible but not long-lasting during the winter months, while occasional thunderstorms may occur during the summer. |
The climate of Chalkidiki is mainly [[Mediterranean climate|Mediterranean]] ([[Koppen]]: ''Csa'') with cool, wet winters and hot, relatively dry summers. Snowfalls are possible but not long-lasting during the winter months, while occasional thunderstorms may occur during the summer. Few areas such as [[Neos Marmaras]] have a [[hot semi-arid climate]] ([[Köppen climate classification]]: ''BSh''). <ref>https://www.meteo.gr/Monthly_Bulletins.cfm {{Bare URL inline|date=August 2024}}</ref> <ref>https://penteli.meteo.gr/stations/marmaras/ {{Bare URL inline|date=August 2024}}</ref> |
||
{{Weather box |
|||
|location= [[Neos Marmaras]] 6 m a.s.l. |
|||
| width = 70% |
|||
|metric first=yes |
|||
|single line=yes |
|||
|Jan high C=12.2 |
|||
|Feb high C=14.1 |
|||
|Mar high C=15.6 |
|||
|Apr high C=19.5 |
|||
|May high C=24.3 |
|||
|Jun high C=29.3 |
|||
|Jul high C=32.1 |
|||
|Aug high C=32.4 |
|||
|Sep high C=27.8 |
|||
|Oct high C=22.2 |
|||
|Nov high C=18.1 |
|||
|Dec high C=14.0 |
|||
|Jan mean C= 9.4 |
|||
|Feb mean C= 11.0 |
|||
|Mar mean C=12.2 |
|||
|Apr mean C=15.4 |
|||
|May mean C=20.0 |
|||
|Jun mean C=24.9 |
|||
|Jul mean C=27.7 |
|||
|Aug mean C=28.0 |
|||
|Sep mean C=23.9 |
|||
|Oct mean C=18.9 |
|||
|Nov mean C=15.2 |
|||
|Dec mean C=11.3 |
|||
|Jan low C= 6.5 |
|||
|Feb low C= 7.9 |
|||
|Mar low C= 8.7 |
|||
|Apr low C=11.3 |
|||
|May low C=15.6 |
|||
|Jun low C=20.5 |
|||
|Jul low C=23.2 |
|||
|Aug low C=23.6 |
|||
|Sep low C=20.0 |
|||
|Oct low C=15.6 |
|||
|Nov low C=12.2 |
|||
|Dec low C= 8.6 |
|||
|rain colour = green |
|||
|Jan rain mm=62.4 |
|||
|Feb rain mm=28.9 |
|||
|Mar rain mm=50.1 |
|||
|Apr rain mm=27.4 |
|||
|May rain mm=21.7 |
|||
|Jun rain mm=33.9 |
|||
|Jul rain mm= 28.0 |
|||
|Aug rain mm= 11.6 |
|||
|Sep rain mm=29.5 |
|||
|Oct rain mm=36.8 |
|||
|Nov rain mm=41.8 |
|||
|Dec rain mm=60.3 |
|||
| Jan record high C = 20.7 |
|||
| Feb record high C = 22.8 |
|||
| Mar record high C = 22.8 |
|||
| Apr record high C = 26.5 |
|||
| May record high C = 32.4 |
|||
| Jun record high C = 36.4 |
|||
| Jul record high C = 39.9 |
|||
| Aug record high C = 41.6 |
|||
| Sep record high C = 37.0 |
|||
| Oct record high C = 29.3 |
|||
| Nov record high C = 26.1 |
|||
| Dec record high C = 19.8 |
|||
| Jan record low C = -4.2 |
|||
| Feb record low C = -0.5 |
|||
| Mar record low C = 0.6 |
|||
| Apr record low C = 4.2 |
|||
| May record low C = 10.5 |
|||
| Jun record low C = 13.1 |
|||
| Jul record low C = 16.3 |
|||
| Aug record low C = 18.6 |
|||
| Sep record low C = 13.2 |
|||
| Oct record low C = 9.9 |
|||
| Nov record low C = 3.7 |
|||
| Dec record low C = -0.6 |
|||
|source = [[National Observatory of Athens]] (Feb 2014 - Jul 2024), <ref>{{cite web | url=https://www.meteo.gr/Monthly_Bulletins.cfm | title=N.O.A Monthly Bulletins }}|source 2= </ref> <br /> Neos Marmaras N.O.A station <ref>{{cite web | url=https://penteli.meteo.gr/stations/marmaras/ | title=Latest Conditions in Neos Marmaras </ref> and [[World Meteorological Organization]]<ref name="WMO">{{cite web | url=https://oscar.wmo.int/surface/#/search/station/stationReportDetails/0-300-1-marmaras | title=World Meteorological Organization | accessdate=14 July 2023}}</ref> |
|||
}} |
|||
==History== |
==History== |
||
| Line 105: | Line 144: | ||
The first Greek settlers in this area came from [[Chalcis]] and [[Eretria]], ancient [[Ionians|ionian]] cities in [[Euboea]], around the 8th century BC who founded cities such as [[Mende (Chalcidice)|Mende]],<ref>Thucydides, Book 4, 123</ref> [[Toroni]] and [[Scione]]<ref>N. G. L. Hammond, ''A History of Macedonia, Vol.{{nbsp}}1: Historical Geography and Prehistory'' (Clarendon Press, 1972), p.{{nbsp}}426.</ref> a second wave came from [[Andros]] in the 6th century BC<ref>The Cyclades: Discovering the Greek Islands of the Aegean By John Freely p. 82</ref> who founded cities such as [[Akanthos (Greece)|Akanthos]].<ref>Thucydides, Book 4, p.{{nbsp}}84</ref> The ancient city of [[Stageira]] was the birthplace of the great philosopher [[Aristotle]]. Chalkidiki was an important theatre of war during the [[Peloponnesian War]] between [[Classical Athens|Athens]] and [[Sparta]]. Later, the Greek colonies of the peninsula were conquered by [[Philip II of Macedon]] and Chalkidiki became part of [[Macedonia (ancient kingdom)]]. After the end of the [[Macedonian Wars|wars]] between the Macedonians and the Romans, the region became part of the [[Roman Empire]], along with the rest of Greece. At the end of the Roman Republic (in 43 BC) a Roman colony was settled in Cassandreia, which was later (in 30 BC) resettled by Augustus.<ref>[http://olympias.lib.uoi.gr/jspui/bitstream/123456789/6116/1/13.%20%CE%97%20%CF%81%CF%89%CE%BC%CE%B1%CF%8A%CE%BA%CE%AE%20%CE%B1%CF%80%CE%BF%CE%B9%CE%BA%CE%AF%CE%B1.pdf] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170424175948/http://olympias.lib.uoi.gr/jspui/bitstream/123456789/6116/1/13.%20%CE%97%20%CF%81%CF%89%CE%BC%CE%B1%CF%8A%CE%BA%CE%AE%20%CE%B1%CF%80%CE%BF%CE%B9%CE%BA%CE%AF%CE%B1.pdf|date=2017-04-24}} D. C. Samsaris,''The Roman Colony of Cassandreia in Macedonia (Colonia Iulia Augusta Cassandrensis)'' (in Greek), ''Dodona'' 16(1), 1987, 353–437</ref> |
The first Greek settlers in this area came from [[Chalcis]] and [[Eretria]], ancient [[Ionians|ionian]] cities in [[Euboea]], around the 8th century BC who founded cities such as [[Mende (Chalcidice)|Mende]],<ref>Thucydides, Book 4, 123</ref> [[Toroni]] and [[Scione]]<ref>N. G. L. Hammond, ''A History of Macedonia, Vol.{{nbsp}}1: Historical Geography and Prehistory'' (Clarendon Press, 1972), p.{{nbsp}}426.</ref> a second wave came from [[Andros]] in the 6th century BC<ref>The Cyclades: Discovering the Greek Islands of the Aegean By John Freely p. 82</ref> who founded cities such as [[Akanthos (Greece)|Akanthos]].<ref>Thucydides, Book 4, p.{{nbsp}}84</ref> The ancient city of [[Stageira]] was the birthplace of the great philosopher [[Aristotle]]. Chalkidiki was an important theatre of war during the [[Peloponnesian War]] between [[Classical Athens|Athens]] and [[Sparta]]. Later, the Greek colonies of the peninsula were conquered by [[Philip II of Macedon]] and Chalkidiki became part of [[Macedonia (ancient kingdom)]]. After the end of the [[Macedonian Wars|wars]] between the Macedonians and the Romans, the region became part of the [[Roman Empire]], along with the rest of Greece. At the end of the Roman Republic (in 43 BC) a Roman colony was settled in Cassandreia, which was later (in 30 BC) resettled by Augustus.<ref>[http://olympias.lib.uoi.gr/jspui/bitstream/123456789/6116/1/13.%20%CE%97%20%CF%81%CF%89%CE%BC%CE%B1%CF%8A%CE%BA%CE%AE%20%CE%B1%CF%80%CE%BF%CE%B9%CE%BA%CE%AF%CE%B1.pdf] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170424175948/http://olympias.lib.uoi.gr/jspui/bitstream/123456789/6116/1/13.%20%CE%97%20%CF%81%CF%89%CE%BC%CE%B1%CF%8A%CE%BA%CE%AE%20%CE%B1%CF%80%CE%BF%CE%B9%CE%BA%CE%AF%CE%B1.pdf|date=2017-04-24}} D. C. Samsaris,''The Roman Colony of Cassandreia in Macedonia (Colonia Iulia Augusta Cassandrensis)'' (in Greek), ''Dodona'' 16(1), 1987, 353–437</ref> |
||
During the following centuries, Chalkidiki was part of the [[Byzantine Empire]] (East Roman Empire). On a [[chrysobull]] of Emperor [[Basil I]], dated 885, the ''Holy Mountain'' ([[Mount Athos]]) was proclaimed a place of monks, and no laymen or farmers or cattle-breeders were allowed to be settled there. With the support of [[Nikephoros II Phokas]], the [[Great Lavra (Athos)|Great Lavra monastery]] was founded soon afterwards. Today, over 2,000 monks from Greece and many other |
During the following centuries, Chalkidiki was part of the [[Byzantine Empire]] (East Roman Empire). On a [[chrysobull]] of Emperor [[Basil I]], dated 885, the ''Holy Mountain'' ([[Mount Athos]]) was proclaimed a place of monks, and no laymen or farmers or cattle-breeders were allowed to be settled there. With the support of [[Nikephoros II Phokas]], the [[Great Lavra (Athos)|Great Lavra monastery]] was founded soon afterwards. Today, over 2,000 monks from Greece and many other Orthodox Christian countries, such as Romania, Moldova, Georgia, Bulgaria, Serbia, and Russia, live an ascetic life in Athos, isolated from the rest of the world. Athos with its monasteries has been self-governing ever since. |
||
After a short period of domination by the Latin [[Kingdom of Thessalonica]], the area became again Byzantine until its conquest by the [[Ottoman Empire|Ottomans]] in 1430. During the Ottoman period, the peninsula was important for its [[gold mining]]. In 1821, the [[Greek War of Independence]] started and the Greeks of Chalkidiki revolted under the command of [[Emmanouel Pappas]], a member of [[Filiki Eteria]], and other local fighters. The revolt was progressing slowly and unsystematically. The insurrection was confined to the peninsulas of Mount Athos and Kassandra. One of the main goals was to restrain and detain the coming of the Ottoman army from [[Istanbul]], until the revolution in the south (mainly [[Peloponnese]]) became stable. Finally, the revolt resulted in a decisive Ottoman victory at Kassandra. The survivors, among them Papas, were rescued by the [[Psara|Psarian]] fleet, which took them mainly to [[Skiathos]], [[Skopelos]] and [[Skyros]]. The Ottomans proceeded in retaliation and many villages were burnt. |
After a short period of domination by the Latin [[Kingdom of Thessalonica]], the area became again Byzantine until its conquest by the [[Ottoman Empire|Ottomans]] in 1430. During the Ottoman period, the peninsula was important for its [[gold mining]]. In 1821, the [[Greek War of Independence]] started and the Greeks of Chalkidiki revolted under the command of [[Emmanouel Pappas]], a member of [[Filiki Eteria]], and other local fighters. The revolt was progressing slowly and unsystematically. The insurrection was confined to the peninsulas of Mount Athos and Kassandra. One of the main goals was to restrain and detain the coming of the Ottoman army from [[Istanbul]], until the revolution in the south (mainly [[Peloponnese]]) became stable. Finally, the revolt resulted in a decisive Ottoman victory at Kassandra. The survivors, among them Papas, were rescued by the [[Psara|Psarian]] fleet, which took them mainly to [[Skiathos]], [[Skopelos]] and [[Skyros]]. The Ottomans proceeded in retaliation and many villages were burnt. |
||
| Line 111: | Line 150: | ||
Finally, the peninsula was incorporated into the [[Greek Kingdom]] in 1912 after the [[Balkan Wars]]. Many Greek refugees from [[East Thrace]] and [[Anatolia]] (modern Turkey) were settled in parts of Chalkidiki after the 1922 [[Greco-Turkish War (1919–1922)|Greco-Turkish war]], adding to the indigenous Greek population. |
Finally, the peninsula was incorporated into the [[Greek Kingdom]] in 1912 after the [[Balkan Wars]]. Many Greek refugees from [[East Thrace]] and [[Anatolia]] (modern Turkey) were settled in parts of Chalkidiki after the 1922 [[Greco-Turkish War (1919–1922)|Greco-Turkish war]], adding to the indigenous Greek population. |
||
In the 1980s, a tourism boom came to Chalkidiki and took over agriculture as the primary industry.<ref>{{Cite web|date=2018-03-18|title=THE HISTORY OF KASSANDRA, HALKIDIKI!!|url=https://transferthessaloniki.eu/history-kassandra-halkidiki/|access-date=2021-03-09|website=Transfer Thessaloniki|language=en-US}}</ref> In June 2003, at the holiday resort of [[Porto Carras]] located in Neos Marmaras, Sithonia, leaders of the [[European Union]] presented the first draft of the European Constitution (see [[History of the European Constitution]] for developments after this point). |
In the 1980s, a tourism boom came to Chalkidiki and took over agriculture as the primary industry.<ref>{{Cite web|date=2018-03-18|title=THE HISTORY OF KASSANDRA, HALKIDIKI!!|url=https://transferthessaloniki.eu/history-kassandra-halkidiki/|access-date=2021-03-09|website=Transfer Thessaloniki|language=en-US|archive-date=2021-07-09|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210709190657/https://transferthessaloniki.eu/history-kassandra-halkidiki/|url-status=dead}}</ref> In June 2003, at the holiday resort of [[Porto Carras]] located in Neos Marmaras, Sithonia, leaders of the [[European Union]] presented the first draft of the European Constitution (see [[History of the European Constitution]] for developments after this point). |
||
===Ancient sites=== |
===Ancient sites=== |
||
| Line 121: | Line 160: | ||
[[File:Toroni1.jpg|thumb|Beach in [[Toroni]]]] |
[[File:Toroni1.jpg|thumb|Beach in [[Toroni]]]] |
||
[[File:Porto Carras Sithonia.jpg|thumb|Exterior view of ''[[Porto Carras]]'' Hotel in [[Sithonia]]]] |
[[File:Porto Carras Sithonia.jpg|thumb|Exterior view of ''[[Porto Carras]]'' Hotel in [[Sithonia]]]] |
||
[[File:Sani Resort.jpg|thumb|Sani Resort in Sani |
[[File:Sani Resort.jpg|thumb|Sani Resort in Sani, Chalkidiki]] |
||
*[[Acanthus (Greece)|Acanthus]] (near [[Ierissos]]) |
*[[Acanthus (Greece)|Acanthus]] (near [[Ierissos]]) |
||
| Line 220: | Line 259: | ||
==Population== |
==Population== |
||
The autonomous monastic state of [[Mount Athos]] which is often considered to be geographically part of Chalkidiki recorded an additional 1,746 people in the 2021 census. The population is mostly Orthodox Christian monks. |
|||
{{Historical populations |
|||
{| class=wikitable |
|||
|align = none |
|||
! Year !! Population |
|||
|1991<ref name = elstat>{{cite web |title=Απογραφές πληθυσμού 1991,2001,2011 σύμφωνα με την κωδικοποίηση της Απογραφής 2011 |url=https://www.statistics.gr/documents/20181/1210503/Kallikratis_me_plithismous_1991_2011.xls |publisher=[[Hellenic Statistical Authority]] |lang=el|access-date=17 April 2024}}</ref>|85471 |
|||
|- |
|||
|2001<ref name=elstat/>|96849 |
|||
| 1991 || 85,426 |
|||
|2011<ref name=elstat/>|105908 |
|||
|- |
|||
|2021<ref name="census21"/>|102085 |
|||
| 2001 || 96,849 |
|||
}} |
|||
|- |
|||
| 2011 || 105,908 |
|||
|} |
|||
==Television== |
==Television== |
||
| Line 237: | Line 274: | ||
==Transport== |
==Transport== |
||
*Motorways: |
*Motorways: |
||
** |
**[[A24 motorway (Greece)|A24 motorway]] connects [[Thessaloniki]] and [[Thessaloniki International Airport, "Macedonia"|"Macedonia" Airport]] with [[Nea Moudania]] and [[Kallithea, Chalkidiki|Kallithea]] in Kassandra. |
||
*Chalkidiki has no [[Rail transport|railroads]] or [[airports]]. |
*Chalkidiki has no [[Rail transport|railroads]] or [[airports]]. |
||
*A bus system, KTEL, serves major |
*A bus system, KTEL, serves major towns. |
||
In September 2018 it was announced that [[Line 2 (Thessaloniki Metro)|Line 2]] of the [[Thessaloniki Metro]] could be extended in the future in order to serve commuters to and from some areas of Chalkidiki.<ref name="am 83 deth">{{Cite web |url=http://www.ametro.gr/?p=13667 |title=ΑΤΤΙΚΟ ΜΕΤΡΟ: "Το Μέτρο στη πόλη μας" με το πρώτο του βαγόνι. Συμμετοχή της Αττικό Μετρό Α.Ε. στην 83η Δ.Ε.Θ. |website=www.ametro.gr |language=el |trans-title=Attiko Metro: "The Metro in our city" with the first carriage. The participation of Attiko Metro S.A. at the 83rd Thessaloniki International Fair |access-date=2018-09-08}}</ref> |
In September 2018 it was announced that [[Line 2 (Thessaloniki Metro)|Line 2]] of the [[Thessaloniki Metro]] could be extended in the future in order to serve commuters to and from some areas of Chalkidiki.<ref name="am 83 deth">{{Cite web |url=http://www.ametro.gr/?p=13667 |title=ΑΤΤΙΚΟ ΜΕΤΡΟ: "Το Μέτρο στη πόλη μας" με το πρώτο του βαγόνι. Συμμετοχή της Αττικό Μετρό Α.Ε. στην 83η Δ.Ε.Θ. |website=www.ametro.gr |language=el |trans-title=Attiko Metro: "The Metro in our city" with the first carriage. The participation of Attiko Metro S.A. at the 83rd Thessaloniki International Fair |access-date=2018-09-08}}</ref> |
||
| Line 252: | Line 289: | ||
*[[Aristobulus of Cassandreia]] (375–301 BC), historian, architect |
*[[Aristobulus of Cassandreia]] (375–301 BC), historian, architect |
||
*[[Aristotle]] (384 BC in [[Stageira]]–322 BC), philosopher |
*[[Aristotle]] (384 BC in [[Stageira]]–322 BC), philosopher |
||
*[[Andronicus of Olynthus]] ( |
*[[Andronicus of Olynthus]] ({{circa|370 BC}}), Phrourarchus of Tyre, appointed by Antigonus |
||
*[[Callisthenes]] (360–328 BC), historian |
*[[Callisthenes]] (360–328 BC), historian |
||
*[[Crates (engineer)|Crates of Olynthus]], Alexander's hydraulic engineer |
*[[Crates (engineer)|Crates of Olynthus]], Alexander's hydraulic engineer |
||
*Bubalus of Cassandreia (304 BC), ''keles'' (horse) competing in the flat race of the Lykaia<ref>[[Arcadia (region)|Arkadia]]{{snd}}[[Lycaeus|Lykaion]]{{snd}}[https://web.archive.org/web/20071201121839/http://epigraphy.packhum.org/inscriptions/main?url=oi%3Fikey%3D32707%26bookid%3D12 Epigraphical Database]</ref> |
*Bubalus of Cassandreia (304 BC), ''keles'' (horse) competing in the flat race of the Lykaia<ref>[[Arcadia (region)|Arkadia]]{{snd}}[[Lycaeus|Lykaion]]{{snd}}[https://web.archive.org/web/20071201121839/http://epigraphy.packhum.org/inscriptions/main?url=oi%3Fikey%3D32707%26bookid%3D12 Epigraphical Database]</ref> |
||
*[[Poseidippus of Cassandreia]] ( |
*[[Poseidippus of Cassandreia]] ({{circa|310}}–240 BC), comic poet |
||
*Erginus (son of Simylus) from Cassandreia, [[citharede]] winner in [[Soteria (festival)|Soteria]] |
*Erginus (son of Simylus) from Cassandreia, [[citharede]] winner in [[Soteria (festival)|Soteria]] {{circa|260 BC}}<ref>[[Phocis (ancient region)|Phocis]]{{snd}}[[Delphi]]{{snd}}[https://web.archive.org/web/20071201131137/http://epigraphy.packhum.org/inscriptions/oi?ikey=239145&bookid=452®ion=3&subregion=7 Epigraphical Database]</ref> |
||
*[[Stamatios Kapsas]], revolutionary of the [[Greek War of Independence]] (1821–1830) |
*[[Stamatios Kapsas]], revolutionary of the [[Greek War of Independence]] (1821–1830) |
||
*[[Xenophon Paionidis]] (1863–1933), architect |
*[[Xenophon Paionidis]] (1863–1933), architect |
||
Latest revision as of 16:02, 22 October 2024
Chalkidiki
Περιφερειακή ενότητα Χαλκιδικής | |
|---|---|
 Municipalities of Chalkidiki | |
| Coordinates: 40°20′N 23°30′E / 40.333°N 23.500°E | |
| Country | Greece |
| Geographic region | Macedonia |
| Administrative region | Central Macedonia |
| Seat | Polygyros |
| Area | |
• Total | 2,918 km2 (1,127 sq mi) |
| Population (2021)[1] | |
• Total | 102,085 |
| • Density | 35/km2 (91/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+2 (EET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+3 (EEST) |
| Postal code | 63x xx |
| Area code(s) | 237x0, 239x0 |
| Vehicle registration | ΧΚ |
| Website | www |
Chalkidiki (/kælˈkɪdɪki/; Greek: Χαλκιδική, romanized: Chalkidikḗ [xalciðiˈci], alternatively Halkidiki), also known as Chalcidice, is a peninsula and regional unit of Greece, part of the region of Central Macedonia, in the geographic region of Macedonia in Northern Greece. The autonomous Mount Athos region constitutes the easternmost part of the peninsula, but not of the regional unit.
The capital of Chalkidiki is the town of Polygyros, located in the centre of the peninsula, while the largest town is Nea Moudania. Chalkidiki is a popular summer tourist destination.
Name
[edit]Chalkidiki also spelled Halkidiki (/kælˈkɪdɪki/) or Chalcidice (/kælˈsɪdɪsi/) is named after the ancient Greek city-state of Chalcis in Euboea, which colonised the area in the 8th century BC.
Geography
[edit]
Chalkidiki consists of a large peninsula in the northwestern Aegean Sea, resembling a hand with three 'fingers' (though in Greek these peninsulas are often referred to as 'legs'). From west to east, these are Kassandra (highest peak 345 m), Sithonia (highest peak Mt Itamos 817 m), and Mount Athos, a special polity within Greece known for its monasteries and its highest peak reaching 2,033 metres above sea level. These 'fingers' are separated by two gulfs, the Toronean Gulf and the Singitic Gulf.
Chalkidiki borders on the regional unit of Thessaloniki to the north, and is bounded by the Thermaic Gulf on the west, and the Strymonian Gulf and Ierissos Gulf on the east (which are separated by the Brostomnitsa peninsula).
The Cholomontas mountains lie in the north-central part of Chalkidiki, with the highest peak reaching 1,165 metres above sea level. Chalkidiki has a few rivers running from Mt Cholomontas south to the sea, these include the Havrias, Vatonias (Olynthios) and Psychros rivers. Chalkidiki also has a few islands including the inhabited Ammouliani and Diaporos both in the Singitic Gulf.
Its largest towns are Nea Moudania (Νέα Μουδανιά), Nea Kallikrateia (Νέα Καλλικράτεια) and the capital town of Polygyros (Πολύγυρος).
There are several summer resorts on the beaches of all three fingers where other minor towns and villages are located, such as at Yerakini (Gerakina Beach) and Psakoudia in central Chalkidiki, Kallithea, Chanioti and Pefkochori in the Kassandra peninsula, Nikiti and Neos Marmaras (Porto Carras) in the Sithonia peninsula, and Ouranoupolis at Mount Athos. A popular village in winter is Arnaia for its architecture and mountain scenery.
Climate
[edit]The climate of Chalkidiki is mainly Mediterranean (Koppen: Csa) with cool, wet winters and hot, relatively dry summers. Snowfalls are possible but not long-lasting during the winter months, while occasional thunderstorms may occur during the summer. Few areas such as Neos Marmaras have a hot semi-arid climate (Köppen climate classification: BSh). [2] [3]
| Climate data for Neos Marmaras 6 m a.s.l. | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 20.7 (69.3) |
22.8 (73.0) |
22.8 (73.0) |
26.5 (79.7) |
32.4 (90.3) |
36.4 (97.5) |
39.9 (103.8) |
41.6 (106.9) |
37.0 (98.6) |
29.3 (84.7) |
26.1 (79.0) |
19.8 (67.6) |
41.6 (106.9) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 12.2 (54.0) |
14.1 (57.4) |
15.6 (60.1) |
19.5 (67.1) |
24.3 (75.7) |
29.3 (84.7) |
32.1 (89.8) |
32.4 (90.3) |
27.8 (82.0) |
22.2 (72.0) |
18.1 (64.6) |
14.0 (57.2) |
21.8 (71.2) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 9.4 (48.9) |
11.0 (51.8) |
12.2 (54.0) |
15.4 (59.7) |
20.0 (68.0) |
24.9 (76.8) |
27.7 (81.9) |
28.0 (82.4) |
23.9 (75.0) |
18.9 (66.0) |
15.2 (59.4) |
11.3 (52.3) |
18.2 (64.7) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 6.5 (43.7) |
7.9 (46.2) |
8.7 (47.7) |
11.3 (52.3) |
15.6 (60.1) |
20.5 (68.9) |
23.2 (73.8) |
23.6 (74.5) |
20.0 (68.0) |
15.6 (60.1) |
12.2 (54.0) |
8.6 (47.5) |
14.5 (58.1) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −4.2 (24.4) |
−0.5 (31.1) |
0.6 (33.1) |
4.2 (39.6) |
10.5 (50.9) |
13.1 (55.6) |
16.3 (61.3) |
18.6 (65.5) |
13.2 (55.8) |
9.9 (49.8) |
3.7 (38.7) |
−0.6 (30.9) |
−4.2 (24.4) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 62.4 (2.46) |
28.9 (1.14) |
50.1 (1.97) |
27.4 (1.08) |
21.7 (0.85) |
33.9 (1.33) |
28.0 (1.10) |
11.6 (0.46) |
29.5 (1.16) |
36.8 (1.45) |
41.8 (1.65) |
60.3 (2.37) |
432.4 (17.02) |
| Source: National Observatory of Athens (Feb 2014 - Jul 2024), [4] Neos Marmaras N.O.A station [5] and World Meteorological Organization[6] | |||||||||||||
History
[edit]



The first Greek settlers in this area came from Chalcis and Eretria, ancient ionian cities in Euboea, around the 8th century BC who founded cities such as Mende,[7] Toroni and Scione[8] a second wave came from Andros in the 6th century BC[9] who founded cities such as Akanthos.[10] The ancient city of Stageira was the birthplace of the great philosopher Aristotle. Chalkidiki was an important theatre of war during the Peloponnesian War between Athens and Sparta. Later, the Greek colonies of the peninsula were conquered by Philip II of Macedon and Chalkidiki became part of Macedonia (ancient kingdom). After the end of the wars between the Macedonians and the Romans, the region became part of the Roman Empire, along with the rest of Greece. At the end of the Roman Republic (in 43 BC) a Roman colony was settled in Cassandreia, which was later (in 30 BC) resettled by Augustus.[11]
During the following centuries, Chalkidiki was part of the Byzantine Empire (East Roman Empire). On a chrysobull of Emperor Basil I, dated 885, the Holy Mountain (Mount Athos) was proclaimed a place of monks, and no laymen or farmers or cattle-breeders were allowed to be settled there. With the support of Nikephoros II Phokas, the Great Lavra monastery was founded soon afterwards. Today, over 2,000 monks from Greece and many other Orthodox Christian countries, such as Romania, Moldova, Georgia, Bulgaria, Serbia, and Russia, live an ascetic life in Athos, isolated from the rest of the world. Athos with its monasteries has been self-governing ever since.
After a short period of domination by the Latin Kingdom of Thessalonica, the area became again Byzantine until its conquest by the Ottomans in 1430. During the Ottoman period, the peninsula was important for its gold mining. In 1821, the Greek War of Independence started and the Greeks of Chalkidiki revolted under the command of Emmanouel Pappas, a member of Filiki Eteria, and other local fighters. The revolt was progressing slowly and unsystematically. The insurrection was confined to the peninsulas of Mount Athos and Kassandra. One of the main goals was to restrain and detain the coming of the Ottoman army from Istanbul, until the revolution in the south (mainly Peloponnese) became stable. Finally, the revolt resulted in a decisive Ottoman victory at Kassandra. The survivors, among them Papas, were rescued by the Psarian fleet, which took them mainly to Skiathos, Skopelos and Skyros. The Ottomans proceeded in retaliation and many villages were burnt.
Finally, the peninsula was incorporated into the Greek Kingdom in 1912 after the Balkan Wars. Many Greek refugees from East Thrace and Anatolia (modern Turkey) were settled in parts of Chalkidiki after the 1922 Greco-Turkish war, adding to the indigenous Greek population.
In the 1980s, a tourism boom came to Chalkidiki and took over agriculture as the primary industry.[12] In June 2003, at the holiday resort of Porto Carras located in Neos Marmaras, Sithonia, leaders of the European Union presented the first draft of the European Constitution (see History of the European Constitution for developments after this point).
Ancient sites
[edit]







- Acanthus (near Ierissos)
- Acrothoi
- Aege
- Alapta
- Aphytis (Afytos)
- Apollonia (near Polygyros)
- Cleonae (Chalcidice)
- Galepsus
- Mekyberna
- Mende
- Neapolis, Chalcidice
- Olophyxus
- Olynthus
- Palaiochori "Neposi" castle
- Polichrono
- Potidaea
- Scione
- Scolus
- Sermylia (Ormylia)
- Stageira
- Spartolus
- Thyssus
- Torone
- Treasury of the Acanthians
- Xerxes Canal
Archaeology
[edit]In June 2022, archaeologists announced the discovery of a poorly preserved single-edged sabre among the ruins of a monastery on the coast of Chalcidice. Alongside the curved sword, excavators revealed evidence of a fire, a large cache of 14th-century glazed pottery vessels, as well as other weapons, including axes and arrowheads.[13]
Economy
[edit]Agriculture
[edit]The peninsula is notable for its olive oil and its green olives production. Also various types of honey and wine are produced.
Tourism
[edit]Chalkidiki has been a popular summer tourist destination since the late 1950s when people from Thessaloniki started spending their summer holidays in the coastal villages. In the beginning tourists rented rooms in the houses of locals. By the 1960s, tourists from Austria and Germany started to visit Chalkidiki more frequently. Since the start of the big tourist boom in the 1970s, the whole region has been captured by tourism.[14] In the region there is a golf course, with plans for four others in the future.
Mining
[edit]Gold was mined in the region during antiquity by Philip II of Macedon and the next rulers. Since 2013, a revival of mining for gold and other minerals has occurred, and a number of concessions have been granted to Eldorado Gold of Canada. Critics claim that mining adversely affects tourism and the environment.[15]
Administration
[edit]The Chalkidiki regional unit is subdivided into five municipalities (numbered as in the infobox map):[16]
- Aristotelis (2)
- Kassandra (4)
- Nea Propontida (3)
- Polygyros (1)
- Sithonia (5)
Prefecture
[edit]As a part of Greece's 2011 local government reform, the Chalkidiki regional unit (περιφερειακή ενότητα, perifereiakí enótita) was created out of the former Chalkidiki prefecture (νομός, nomós); the regional unit has the same territory as the former prefecture. As par of the reforms, Chalkidiki's five municipalities (δήμοι, dhími) were created by combining former municipalities, which were in turn demoted to municipal units (δημοτικές ενότητες, dhimotikés enótites), according to the table below.[16]
| Municipalities | Municipal Units[a] | Seat |
|---|---|---|
| Aristotelis | Arnaia | Ierissos |
| Panagia | ||
| Stagira-Akanthos | ||
| Kassandra | Kassandra | Kassandreia |
| Pallini | ||
| Nea Propontida | Kallikrateia | Nea Moudania |
| Moudania | ||
| Triglia | ||
| Polygyros | Polygyros | Polygyros |
| Anthemountas | ||
| Zervochoria | ||
| Ormylia | ||
| Sithonia | Sithonia | Nikiti |
| Toroni |
Provinces
[edit]Before the abolishment of the provinces of Greece in 2006, the Chalkidiki prefecture was subdivided into the following provinces:[17]
| Province | Seat |
|---|---|
| Arnaia Province | Arnaia |
| Chalkidiki Province | Polygyros |
Population
[edit]The autonomous monastic state of Mount Athos which is often considered to be geographically part of Chalkidiki recorded an additional 1,746 people in the 2021 census. The population is mostly Orthodox Christian monks.
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1991[18] | 85,471 | — |
| 2001[18] | 96,849 | +13.3% |
| 2011[18] | 105,908 | +9.4% |
| 2021[1] | 102,085 | −3.6% |
Television
[edit]- TV Halkidiki – Nea Moudania
- Super TV – Nea Moudania
Transport
[edit]- Motorways:
- A24 motorway connects Thessaloniki and "Macedonia" Airport with Nea Moudania and Kallithea in Kassandra.
- Chalkidiki has no railroads or airports.
- A bus system, KTEL, serves major towns.
In September 2018 it was announced that Line 2 of the Thessaloniki Metro could be extended in the future in order to serve commuters to and from some areas of Chalkidiki.[19]
Notable inhabitants
[edit]
- Paeonius of Mende (late 5th century BC), sculptor
- Philippus of Mende, Plato's student, astronomer
- Nicomachus, Aristotle's father
- Aristobulus of Cassandreia (375–301 BC), historian, architect
- Aristotle (384 BC in Stageira–322 BC), philosopher
- Andronicus of Olynthus (c. 370 BC), Phrourarchus of Tyre, appointed by Antigonus
- Callisthenes (360–328 BC), historian
- Crates of Olynthus, Alexander's hydraulic engineer
- Bubalus of Cassandreia (304 BC), keles (horse) competing in the flat race of the Lykaia[20]
- Poseidippus of Cassandreia (c. 310–240 BC), comic poet
- Erginus (son of Simylus) from Cassandreia, citharede winner in Soteria c. 260 BC[21]
- Stamatios Kapsas, revolutionary of the Greek War of Independence (1821–1830)
- Xenophon Paionidis (1863–1933), architect
- Manolis Mitsias, singer
- Sokratis Malamas (1957 in Sykia), singer
- Paola Foka (1982 Sykia), singer[22]
See also
[edit]- Chalkidian League
- List of settlements in Chalkidiki
- Mount Athos
- Petralona cave
- Vavdos Folklore Collection
Notes
[edit]- ^ Prior to the implementation of the Kallikratis Plan these municipal units were municipalities.
References
[edit]- ^ a b "Αποτελέσματα Απογραφής Πληθυσμού - Κατοικιών 2021, Μόνιμος Πληθυσμός κατά οικισμό" [Results of the 2021 Population - Housing Census, Permanent population by settlement] (in Greek). Hellenic Statistical Authority. 29 March 2024.
- ^ https://www.meteo.gr/Monthly_Bulletins.cfm [bare URL]
- ^ https://penteli.meteo.gr/stations/marmaras/ [bare URL]
- ^ "N.O.A Monthly Bulletins".|source 2=
- ^ {{cite web | url=https://penteli.meteo.gr/stations/marmaras/ | title=Latest Conditions in Neos Marmaras
- ^ "World Meteorological Organization". Retrieved 14 July 2023.
- ^ Thucydides, Book 4, 123
- ^ N. G. L. Hammond, A History of Macedonia, Vol. 1: Historical Geography and Prehistory (Clarendon Press, 1972), p. 426.
- ^ The Cyclades: Discovering the Greek Islands of the Aegean By John Freely p. 82
- ^ Thucydides, Book 4, p. 84
- ^ [1] Archived 2017-04-24 at the Wayback Machine D. C. Samsaris,The Roman Colony of Cassandreia in Macedonia (Colonia Iulia Augusta Cassandrensis) (in Greek), Dodona 16(1), 1987, 353–437
- ^ "THE HISTORY OF KASSANDRA, HALKIDIKI!!". Transfer Thessaloniki. 2018-03-18. Archived from the original on 2021-07-09. Retrieved 2021-03-09.
- ^ Tom Metcalfe (2022-06-07). "Rusty saber, possibly wielded by medieval Turkish pirates, unearthed in Greece". livescience.com. Retrieved 2022-08-16.
- ^ Deltsou, Eleftheria (2007). "Second homes and tourism in a Greek village". Ethnologia Europaea: Journal of European Ethnology. 37 (1–2): 124.
- ^ Suzanne Daley (January 13, 2013). "Greece Sees Gold Boom, but at a Price". The New York Times. Retrieved January 14, 2013.
- ^ a b "ΦΕΚ A 87/2010, Kallikratis reform law text" (in Greek). Government Gazette.
- ^ "Detailed census results 1991" (PDF). (39 MB) (in Greek and French)
- ^ a b c "Απογραφές πληθυσμού 1991,2001,2011 σύμφωνα με την κωδικοποίηση της Απογραφής 2011" (in Greek). Hellenic Statistical Authority. Retrieved 17 April 2024.
- ^ "ΑΤΤΙΚΟ ΜΕΤΡΟ: "Το Μέτρο στη πόλη μας" με το πρώτο του βαγόνι. Συμμετοχή της Αττικό Μετρό Α.Ε. στην 83η Δ.Ε.Θ." [Attiko Metro: "The Metro in our city" with the first carriage. The participation of Attiko Metro S.A. at the 83rd Thessaloniki International Fair]. www.ametro.gr (in Greek). Retrieved 2018-09-08.
- ^ Arkadia – Lykaion – Epigraphical Database
- ^ Phocis – Delphi – Epigraphical Database
- ^ "Xronia Polla Paola Foka, Who Turns 38 Today". Greek City Times. 25 June 2020. Retrieved 2021-02-23.
External links
[edit] Media related to Chalkidiki at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Chalkidiki at Wikimedia Commons