Microsporidia: Difference between revisions
m →As hyperparasites: add punctuation |
Lavateraguy (talk | contribs) take account of the possibility/likelihood of sampling bias |
||
| (20 intermediate revisions by 14 users not shown) | |||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
| image_caption = [[Sporoblast]] of<br />''[[Fibrillanosema crangonycis]]'' |
| image_caption = [[Sporoblast]] of<br />''[[Fibrillanosema crangonycis]]'' |
||
| display_parents = 6 |
| display_parents = 6 |
||
| taxon = |
| taxon = Microsporidiomycota |
||
| authority = Benny 2007 |
|||
| authority = Balbiani, 1882<ref>{{cite journal | last1 = Balbiani | first1 = G | year = 1882 | title = Sur les microsporidies ou psorospermies des Articulés | url = https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/item/112005#page/1166/mode/1up | journal = C. R. Acad. Sci. | volume = 95 | pages = 1168–71 }}</ref> |
|||
| subdivision_ranks = Classes |
| subdivision_ranks = Classes & orders |
||
| subdivision_ref = <ref name="OOF2022"/> |
|||
| subdivision = [[#Classification|See text]]. |
|||
| subdivision = |
|||
* [[Paramicrosporidiales]] |
|||
* [[Morellosporales]] |
|||
* [[Nucleophagales]] |
|||
* [[Chytridiopsidea]] |
|||
** [[Hesseida]] |
|||
** [[Chytridiopsida]] |
|||
* [[Metchnikovellea]] |
|||
** [[Metchnikovellida]] |
|||
* [[Microsporidea]] |
|||
** [[Neopereziida]] |
|||
** [[Ovavesiculida]] |
|||
** [[Amblyosporida]] |
|||
** [[Glugeida]] |
|||
** [[Nosematida]] |
|||
| synonyms = |
| synonyms = |
||
* Microsporidia <small>Balbiani, 1882</small><ref>{{cite journal | last1 = Balbiani | first1 = G | year = 1882 | title = Sur les microsporidies ou psorospermies des Articulés | url = https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/item/112005#page/1166/mode/1up | journal = C. R. Acad. Sci. | volume = 95 | pages = 1168–71 }}</ref> |
|||
* Microsporidiida <small>Labbé, 1899</small> |
* Microsporidiida <small>Labbé, 1899</small> |
||
* Cnidosporidia <small>Doflein 190?</small> |
|||
* Microsporea <small>Delphy, 1936 [1963], Levine et al., 1980</small><ref>Delphy, J. 1936. Sous-règne des Protozoaires. In: Perrier, R. (ed.). ''La Faune de la France en tableaux synoptiques illustrés'', vol 1A. Delagrave: Paris.</ref><ref>{{cite journal | last1 = Levine | first1 = N. D. | display-authors = etal | year = 1980 | title = A Newly Revised Classification of the Protozoa | url = https://www.researchgate.net/publication/16209026 | journal = The Journal of Protozoology | volume = 27 | issue = 1 | pages = 37–58 | doi = 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1980.tb04228.x | pmid = 6989987 | doi-access = free }}</ref> |
* Microsporea <small>Delphy, 1936 [1963], Levine et al., 1980</small><ref>Delphy, J. 1936. Sous-règne des Protozoaires. In: Perrier, R. (ed.). ''La Faune de la France en tableaux synoptiques illustrés'', vol 1A. Delagrave: Paris.</ref><ref>{{cite journal | last1 = Levine | first1 = N. D. | display-authors = etal | year = 1980 | title = A Newly Revised Classification of the Protozoa | url = https://www.researchgate.net/publication/16209026 | journal = The Journal of Protozoology | volume = 27 | issue = 1 | pages = 37–58 | doi = 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1980.tb04228.x | pmid = 6989987 | doi-access = free }}</ref> |
||
* Microsporidea <small>Corliss & Levine |
* Microsporidea <small>Corliss & Levine 1963</small><ref name=corliss>{{cite journal |vauthors=Corliss JO, Levine ND |year=1963 |title=Establishment of the Microsporidea as a new class in the protozoan subphylum Cnidospora |journal=The Journal of Protozoology |volume=10 |issue=Suppl |pages=26–27 |doi=10.1111/jeu.1963.10.issue-s3 }}</ref> |
||
* Microspora <small>Sprague, 1969, 1977</small><ref>Sprague, V. (1977). Classification and phylogeny of the Microsporidia. In: ''Comparative pathobiology''. vol. 2, Systematics of the Microsporidia. Lee A. Bulla & Thomas C. Cheng (ed.). pp. |
* Microspora <small>Sprague, 1969, 1977</small><ref>Sprague, V. (1977). Classification and phylogeny of the Microsporidia. In: ''Comparative pathobiology''. vol. 2, Systematics of the Microsporidia. Lee A. Bulla & Thomas C. Cheng (ed.). pp. 1–30. New York: Plenum Press, [https://books.google.com/books?id=wpnwAAAAMAAJ]. |
||
</ref> |
</ref> |
||
* Microsporida <small>Tuzet et al. 1971</small> |
* Microsporida <small>Tuzet et al. 1971</small> |
||
}} |
}} |
||
'''Microsporidia''' are a group of [[spore]]-forming [[unicellular]] [[parasite]]s. These spores contain an extrusion apparatus that has a coiled polar tube ending in an anchoring disc at the apical part of the spore. |
'''Microsporidia''' are a group of [[spore]]-forming [[unicellular]] [[parasite]]s. These spores contain an extrusion apparatus that has a coiled polar tube ending in an anchoring disc at the apical part of the spore.<ref name="Franzen, C. 2005">Franzen, C. (2005). How do Microsporidia invade cells?. Folia Parasitologica, 52(1–2), 36–40. doi.org/10.14411/fp.2005.005</ref> They were once considered [[protozoa]]ns or [[protist]]s, but are now known to be [[fungi]],<ref>{{cite journal | last1 = Hibbett | first1 = D.S. | display-authors = etal | year = 2007 | title = A higher level phylogenetic classification of the Fungi | url = http://www.umich.edu/~mycology/resources/Publications/Hibbett-et-al.-2007.pdf | journal = Mycological Research | volume = 111 | issue = 5| pages = 509–47 | doi = 10.1016/j.mycres.2007.03.004 | pmid = 17572334 | s2cid = 4686378 }}</ref> or a sister group to [[fungus|true fungi]].<ref name=Silar2016>{{Cite book|last1=Silar|first1=Philippe |title=Protistes Eucaryotes : Origine, Evolution et Biologie des Microbes Eucaryotes |publisher=HAL |year=2016 |page=462 |isbn=978-2-9555841-0-1 | url=https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-01263138/document}}</ref> These fungal microbes are obligate eukaryotic parasites that use a unique mechanism to infect host cells.<ref name="Franzen, C. 2005"/> They have recently been discovered in a 2017 Cornell study to infect [[Beetle|Coleoptera]] on a large scale. So far, about 1500 of the probably more than one million<ref name="Hawksworth, D. 2001">{{cite journal|last1=Hawksworth|first1=David |title=The magnitude of fungal diversity: The 1.5 million spices estimate revisited|journal=Mycological Research|volume=105 |issue=12 |year=2001 |page=1422 |doi=10.1017/S0953756201004725 }}</ref> species are named. Microsporidia are restricted to animal [[host (biology)|host]]s, and all major groups of animals host microsporidia. Most infect [[insect]]s, but they are also responsible for common diseases of [[crustacea]]ns and [[fish]]. The named species of microsporidia usually infect one host species or a group of closely related taxa. Approximately 10 percent of the known species are parasites of vertebrates — several species, most of which are opportunistic, can infect humans, in whom they can cause [[microsporidiosis]]. |
||
After infection they influence their hosts in various ways and all organs and tissues are invaded, though generally by different species of microsporidia. Some species are lethal, and a few are used in biological control of insect pests. [[Parasitic castration]], gigantism, or change of host sex are all potential effects of microsporidian parasitism (in insects). In the most advanced cases of parasitism the microsporidium rules the host cell completely and controls its metabolism and reproduction, forming a [[xenoma]].<ref name="lund">Ronny Larsson, Lund University (Department of Cell and Organism Biology) [http://www.cob.lu.se/microsporidia/proj_descr.html#spores ''Cytology and taxonomy of the microsporidia''] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090912100619/http://www.cob.lu.se/microsporidia/proj_descr.html#spores |date=2009-09-12 }} 2004.</ref> |
After infection they influence their hosts in various ways and all organs and tissues are invaded, though generally by different species of specialised microsporidia. Some species are lethal, and a few are used in biological control of insect pests. [[Parasitic castration]], gigantism, or change of host sex are all potential effects of microsporidian parasitism (in insects). In the most advanced cases of parasitism the microsporidium rules the host cell completely and controls its metabolism and reproduction, forming a [[xenoma]].<ref name="lund">Ronny Larsson, Lund University (Department of Cell and Organism Biology) [http://www.cob.lu.se/microsporidia/proj_descr.html#spores ''Cytology and taxonomy of the microsporidia''] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090912100619/http://www.cob.lu.se/microsporidia/proj_descr.html#spores |date=2009-09-12 }} 2004.</ref> |
||
Replication takes place within the host's cells, which are infected by means of unicellular [[spore]]s. These vary from 1–40 μm, making them some of the smallest [[eukaryote]]s.{{citation needed|date=June 2012}}<!-- see 'Talk' --> Microsporidia that infect [[mammal]]s are 1.0–4.0 μm.<ref name=pmid15777637>{{Cite journal | last1 = Didier | first1 = ES. | title = Microsporidiosis: an emerging and opportunistic infection in humans and animals | journal = Acta Trop | volume = 94 | issue = 1 | pages = 61–76 |date=Apr 2005 | doi = 10.1016/j.actatropica.2005.01.010 | pmid = 15777637 }}</ref> They also have the smallest eukaryotic [[genome]]s. |
Replication takes place within the host's cells, which are infected by means of unicellular [[spore]]s. These vary from 1–40 μm, making them some of the smallest [[eukaryote]]s.{{citation needed|date=June 2012}}<!-- see 'Talk' --> Microsporidia that infect [[mammal]]s are 1.0–4.0 μm.<ref name=pmid15777637>{{Cite journal | last1 = Didier | first1 = ES. | title = Microsporidiosis: an emerging and opportunistic infection in humans and animals | journal = Acta Trop | volume = 94 | issue = 1 | pages = 61–76 |date=Apr 2005 | doi = 10.1016/j.actatropica.2005.01.010 | pmid = 15777637 }}</ref> They also have the smallest eukaryotic [[genome]]s. |
||
The terms "microsporidium" (pl. "microsporidia") and "microsporidian" are used as vernacular names for members of the group. The name ''Microsporidium'' <small>Balbiani, 1884</small><ref>Balbiani, G. 1884. Les Psorospermies des Articulés ou Microsporidies, pp. 150-168, 184. In: ''Leçons sur les sporozoaires''. Paris: Doin, [https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/bibliography/932#/summary].</ref> is also used as a catchall genus for [[incertae sedis]] members.<ref>Hoffman, G. (1999). ''Parasites of North American Freshwater Fishes'', 2nd edn, University of California Press, Berkeley, California, USA, p. 89, [https://books.google.com/books?id=ZU5iqP3NJpMC |
The terms "microsporidium" (pl. "microsporidia") and "microsporidian" are used as vernacular names for members of the group. The name ''Microsporidium'' <small>Balbiani, 1884</small><ref>Balbiani, G. 1884. Les Psorospermies des Articulés ou Microsporidies, pp. 150-168, 184. In: ''Leçons sur les sporozoaires''. Paris: Doin, [https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/bibliography/932#/summary].</ref> is also used as a catchall genus for [[incertae sedis]] members.<ref>Hoffman, G. (1999). ''Parasites of North American Freshwater Fishes'', 2nd edn, University of California Press, Berkeley, California, USA, p. 89, [https://books.google.com/books?id=ZU5iqP3NJpMC&dq=genus%20Microsporidium&pg=PA89].</ref> |
||
[[File:Glugea stephani.jpg|thumb|300px|[[Xenoma]] on flatfish caused by ''[[Glugea]] stephani'']] |
[[File:Glugea stephani.jpg|thumb|300px|[[Xenoma]] on flatfish caused by ''[[Glugea]] stephani'']] |
||
| Line 42: | Line 59: | ||
== Infection == |
== Infection == |
||
In the gut of the host the spore germinates |
In the gut of the host the spore germinates; it builds up osmotic pressure until its rigid wall ruptures at its thinnest point at the apex. The posterior vacuole swells, forcing the polar filament to rapidly eject the infectious content into the cytoplasm of the potential host. Simultaneously the material of the filament is rearranged to form a tube which functions as a hypodermic needle and penetrates the gut epithelium. |
||
Once inside the host cell, a [[sporoplasm]] grows, dividing or forming a [[multinucleate]] [[plasmodium (life cycle)|plasmodium]], before producing new spores. The life cycle varies considerably. Some have a simple [[asexual reproduction|asexual]] life cycle,<ref name="pmid17394631">{{cite journal |author=Ironside JE |title=Multiple losses of sex within a single genus of Microsporidia |journal=BMC Evolutionary Biology |volume=7|pages=48 |year=2007 |pmid=17394631 |pmc=1853083 |doi=10.1186/1471-2148-7-48}}</ref> while others have a complex life cycle involving multiple hosts and both asexual and [[sexual reproduction]]. Different types of spores may be produced at different stages, probably with different functions including [[autoinfection]] (transmission within a single host). |
Once inside the host cell, a [[sporoplasm]] grows, dividing or forming a [[multinucleate]] [[plasmodium (life cycle)|plasmodium]], before producing new spores. The life cycle varies considerably. Some have a simple [[asexual reproduction|asexual]] life cycle,<ref name="pmid17394631">{{cite journal |author=Ironside JE |title=Multiple losses of sex within a single genus of Microsporidia |journal=BMC Evolutionary Biology |volume=7|pages=48 |year=2007 |pmid=17394631 |pmc=1853083 |doi=10.1186/1471-2148-7-48 |doi-access=free }}</ref> while others have a complex life cycle involving multiple hosts and both asexual and [[sexual reproduction]]. Different types of spores may be produced at different stages, probably with different functions including [[autoinfection]] (transmission within a single host). |
||
== Medical implications == |
== Medical implications == |
||
In animals and humans, microsporidia often cause chronic, debilitating diseases rather than lethal infections. Effects on the host include reduced longevity, fertility, weight, and general vigor. [[Vertical transmission]] of microsporidia is frequently reported. |
In animals and humans, microsporidia often cause chronic, debilitating diseases rather than lethal infections. Effects on the host include reduced longevity, fertility, weight, and general vigor. [[Vertical transmission]] of microsporidia is frequently reported. |
||
In the case of insect hosts, vertical transmission often occurs as [[transovarial]] transmission, where the microsporidian parasites pass from the ovaries of the female host into eggs and eventually multiply in the infected larvae. ''[[Amblyospora|Amblyospora salinaria]]'' n. sp. which infects the mosquito ''[[Culex salinarius]]'' Coquillett, and ''[[Amblyospora|Amblyospora californica]]'' which infects the mosquito ''[[Culex|Culex tarsalis]]'' Coquillett, provide typical examples of transovarial transmission of microsporidia.<ref>{{cite journal |vauthors=Andreadis TG, Hall DW |title=Development, ultrastructure, and mode of transmission of Amblyospora sp. (Microspora) in the mosquito |journal=The Journal of Protozoology |volume=26 |issue=3 |pages=444–52 |date=August 1979 |pmid=536933 |doi=10.1111/j.1550-7408.1979.tb04651.x}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |vauthors=Andreadis TG, Hall DW |title=Significance of transovarial infections of Amblyospora sp. (Microspora:Thelohaniidae) in relation to parasite maintenance in the mosquito Culex salinarius |journal=Journal of Invertebrate Pathology |volume=34 |issue=2 |pages=152–7 |date=September 1979 |pmid=536610 |doi=10.1016/0022-2011(79)90095-8}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |vauthors=Jahn GC, Hall DW, Zam SG |year=1986 |title=A comparison of the life cycles of two Amblyospora (Microspora: Amblyosporidae) in the mosquitoes ''Culex salinarius'' and ''Culex tarsalis'' Coquillett |journal=Journal of the Florida Anti-Mosquito Association |volume=57 |issue=1 |pages=24–27}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |vauthors=Becnel JJ, Andreadis TG |title=''Amblyospora salinaria'' n. sp. (Microsporidia: amblyosporidae), parasite of ''Culex salinarius'' (Diptera: culicidae): its life cycle stages in an intermediate host |journal=Journal of Invertebrate Pathology |volume=71 |issue=3 |pages=258–62 |date=May 1998 |pmid=9538031 |doi=10.1006/jipa.1998.4729|url=https://zenodo.org/record/1229866 }}</ref> Microsporidia, specifically the mosquito-infecting ''[[Vavraia culicis]]'', are being explored as a possible 'evolution-proof' malaria-control method.<ref>{{Cite book|first1=Jacob C. |last1=Koella |first2=Lena |last2=Lorenz |first3=Irka |last3=Bargielowski |year=2009 |title=Chapter 12 Microsporidians as Evolution-Proof Agents of Malaria Control?|volume=68|pages=315–327 |pmid=19289199|doi=10.1016/S0065-308X(08)00612-X|series=Advances in Parasitology|isbn=978-0-12-374787-7}}</ref> Microsporidian infection of ''[[Anopheles gambiae]]'' (the principal vector of ''[[Plasmodium falciparum]]'' malaria) reduces malarial infection within the mosquito, and shortens the mosquito lifespan.<ref>{{cite journal |vauthors=Bargielowski I, Koella JC |title=A Possible Mechanism for the Suppression of Plasmodium berghei Development in the Mosquito Anopheles gambiae by the Microsporidian Vavraia culicis |journal=PLOS ONE |volume=4 |issue=3 |pages=e4676 |year=2009 |pmid=19277119 |pmc=2651578 |doi=10.1371/journal.pone.0004676 |editor1-last=Baylis |editor1-first=Matthew|bibcode=2009PLoSO...4.4676B |doi-access=free }}</ref> As the majority of malaria-infected mosquitoes naturally die before the malaria parasite is mature enough to transmit, any increase in mosquito mortality through microsporidian-infection may reduce malaria transmission to humans. In May 2020, researchers reported that ''Microsporidia MB'', a symbiont in the midgut and ovaries of ''[[Anopheles gambiae#Discovery and elements|An. arabiensis]]'', significantly impaired transmission of ''P. falciparum'', had "no overt effect" on the fitness of host mosquitoes, and was transmitted vertically (through inheritance).<ref>{{cite journal |display-authors = etal |last1 = Herren |first1 = JK |last2 = Mbaisi |first2 = L |last3 = Mararo |first3 = E |title=A microsporidian impairs ''Plasmodium falciparum'' transmission in ''Anopheles arabiensis'' mosquitoes |journal=Nature Communications |volume=11 |issue=2187 |year=2020 |page = 2187 |doi=10.1038/s41467-020-16121-y|pmid = 32366903 |pmc = 7198529 |bibcode = 2020NatCo..11.2187H |doi-access = free }}</ref> |
In the case of insect hosts, vertical transmission often occurs as [[transovarial]] transmission, where the microsporidian parasites pass from the ovaries of the female host into eggs and eventually multiply in the infected larvae. ''[[Amblyospora|Amblyospora salinaria]]'' n. sp. which infects the mosquito ''[[Culex salinarius]]'' Coquillett, and ''[[Amblyospora|Amblyospora californica]]'' which infects the mosquito ''[[Culex|Culex tarsalis]]'' Coquillett, provide typical examples of transovarial transmission of microsporidia.<ref>{{cite journal |vauthors=Andreadis TG, Hall DW |title=Development, ultrastructure, and mode of transmission of Amblyospora sp. (Microspora) in the mosquito |journal=The Journal of Protozoology |volume=26 |issue=3 |pages=444–52 |date=August 1979 |pmid=536933 |doi=10.1111/j.1550-7408.1979.tb04651.x}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |vauthors=Andreadis TG, Hall DW |title=Significance of transovarial infections of Amblyospora sp. (Microspora:Thelohaniidae) in relation to parasite maintenance in the mosquito Culex salinarius |journal=Journal of Invertebrate Pathology |volume=34 |issue=2 |pages=152–7 |date=September 1979 |pmid=536610 |doi=10.1016/0022-2011(79)90095-8}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |vauthors=Jahn GC, Hall DW, Zam SG |year=1986 |title=A comparison of the life cycles of two Amblyospora (Microspora: Amblyosporidae) in the mosquitoes ''Culex salinarius'' and ''Culex tarsalis'' Coquillett |journal=Journal of the Florida Anti-Mosquito Association |volume=57 |issue=1 |pages=24–27}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |vauthors=Becnel JJ, Andreadis TG |title=''Amblyospora salinaria'' n. sp. (Microsporidia: amblyosporidae), parasite of ''Culex salinarius'' (Diptera: culicidae): its life cycle stages in an intermediate host |journal=Journal of Invertebrate Pathology |volume=71 |issue=3 |pages=258–62 |date=May 1998 |pmid=9538031 |doi=10.1006/jipa.1998.4729|url=https://zenodo.org/record/1229866 }}</ref> Microsporidia, specifically the mosquito-infecting ''[[Vavraia culicis]]'', are being explored as a possible 'evolution-proof' malaria-control method.<ref>{{Cite book|first1=Jacob C. |last1=Koella |first2=Lena |last2=Lorenz |first3=Irka |last3=Bargielowski |year=2009 |title=Chapter 12 Microsporidians as Evolution-Proof Agents of Malaria Control?|volume=68|pages=315–327 |pmid=19289199|doi=10.1016/S0065-308X(08)00612-X|series=Advances in Parasitology|isbn=978-0-12-374787-7}}</ref> Microsporidian infection of ''[[Anopheles gambiae]]'' (the principal vector of ''[[Plasmodium falciparum]]'' malaria) reduces malarial infection within the mosquito, and shortens the mosquito lifespan.<ref>{{cite journal |vauthors=Bargielowski I, Koella JC |title=A Possible Mechanism for the Suppression of Plasmodium berghei Development in the Mosquito Anopheles gambiae by the Microsporidian Vavraia culicis |journal=PLOS ONE |volume=4 |issue=3 |pages=e4676 |year=2009 |pmid=19277119 |pmc=2651578 |doi=10.1371/journal.pone.0004676 |editor1-last=Baylis |editor1-first=Matthew|bibcode=2009PLoSO...4.4676B |doi-access=free }}</ref> As the majority of malaria-infected mosquitoes naturally die before the malaria parasite is mature enough to transmit, any increase in mosquito mortality through microsporidian-infection may reduce malaria transmission to humans. In May 2020, researchers reported that ''Microsporidia MB'', a symbiont in the midgut and ovaries of ''[[Anopheles gambiae#Discovery and elements|An. arabiensis]]'', significantly impaired transmission of ''P. falciparum'', had "no overt effect" on the fitness of host mosquitoes, and was transmitted vertically (through inheritance).<ref>{{cite journal |display-authors = etal |last1 = Herren |first1 = JK |last2 = Mbaisi |first2 = L |last3 = Mararo |first3 = E |title=A microsporidian impairs ''Plasmodium falciparum'' transmission in ''Anopheles arabiensis'' mosquitoes |journal=Nature Communications |volume=11 |issue=2187 |year=2020 |page = 2187 |doi=10.1038/s41467-020-16121-y|pmid = 32366903 |pmc = 7198529 |bibcode = 2020NatCo..11.2187H |doi-access = free }}</ref> |
||
| Line 54: | Line 71: | ||
{{Main|Microsporidiosis}} |
{{Main|Microsporidiosis}} |
||
{{expand section|date=November 2013}} |
{{expand section|date=November 2013}} |
||
Microsporidian infections of humans sometimes cause a disease called [[microsporidiosis]]. At least 14 microsporidian species, spread across eight genera, have been recognized as human [[pathogen]]s. These include ''[[Trachipleistophora hominis]]''.<ref>{{cite journal | last1 = Heinz | first1 = E | last2 = Williams | first2 = TA | last3 = Nakjang | first3 = S | last4 = Noël | first4 = CJ | last5 = Swan | first5 = DC | last6 = Goldberg | first6 = AV | last7 = Harris | first7 = SR | last8 = Weinmaier | first8 = T | last9 = Markert | first9 = S |date=Oct 2012 | title = The genome of the obligate intracellular parasite ''Trachipleistophora hominis'': New insights into microsporidian genome dynamics and reductive evolution | journal = PLOS Pathog | volume = 8 | issue = 10| page = e1002979 | doi = 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002979 | pmid = 23133373 | pmc = 3486916 | display-authors = 3 | last10 = Bernhardt | first10 = Jörg | last11 = Dagan | first11 = Tal | last12 = Hacker | first12 = Christian | last13 = Lucocq | first13 = John M. | last14 = Schweder | first14 = Thomas | last15 = Rattei | first15 = Thomas | last16 = Hall | first16 = Neil | last17 = Hirt | first17 = Robert P. | last18 = Embley | first18 = T. Martin }}</ref> |
Microsporidian infections of humans sometimes cause a disease called [[microsporidiosis]]. At least 14 microsporidian species, spread across eight genera, have been recognized as human [[pathogen]]s. These include ''[[Trachipleistophora hominis]]''.<ref>{{cite journal | last1 = Heinz | first1 = E | last2 = Williams | first2 = TA | last3 = Nakjang | first3 = S | last4 = Noël | first4 = CJ | last5 = Swan | first5 = DC | last6 = Goldberg | first6 = AV | last7 = Harris | first7 = SR | last8 = Weinmaier | first8 = T | last9 = Markert | first9 = S |date=Oct 2012 | title = The genome of the obligate intracellular parasite ''Trachipleistophora hominis'': New insights into microsporidian genome dynamics and reductive evolution | journal = PLOS Pathog | volume = 8 | issue = 10| page = e1002979 | doi = 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002979 | pmid = 23133373 | pmc = 3486916 | display-authors = 3 | last10 = Bernhardt | first10 = Jörg | last11 = Dagan | first11 = Tal | last12 = Hacker | first12 = Christian | last13 = Lucocq | first13 = John M. | last14 = Schweder | first14 = Thomas | last15 = Rattei | first15 = Thomas | last16 = Hall | first16 = Neil | last17 = Hirt | first17 = Robert P. | last18 = Embley | first18 = T. Martin | doi-access = free }}</ref> |
||
==As hyperparasites== |
==As hyperparasites== |
||
[[File:Parasite140019-fig4 Nosema podocotyloidis - Hyperparasitic Microsporidia.tif|thumb|A hyperparasitic microsporidian, ''Nosema podocotyloidis'', a parasite of a [[digenea]]n which is itself a parasite of a fish.<ref name=Toguebaye/>]] |
[[File:Parasite140019-fig4 Nosema podocotyloidis - Hyperparasitic Microsporidia.tif|thumb|A hyperparasitic microsporidian, ''Nosema podocotyloidis'', a parasite of a [[digenea]]n which is itself a parasite of a fish.<ref name=Toguebaye/>]] |
||
Microsporidia can infect a variety of hosts, including hosts which are themselves parasites. In that case, the microsporidian species is a [[hyperparasite]], i.e. a parasite of a parasite. As an example, more than eighteen species are known which parasitize [[digenea]]ns (parasitic [[flatworm]]s). These digeneans are themselves parasites in various [[vertebrate]]s and [[mollusc]]s. Eight of these species belong to the genus ''[[Nosema (microsporidian)|Nosema]]''.<ref name=Toguebaye>{{cite journal | last1 = Toguebaye | first1 = B. S. | last2 = Quilichini | first2 = Y. | last3 = Diagne | first3 = P. M. | last4 = Marchand | first4 = B. | year = 2014 | title = Ultrastructure and development of ''Nosema podocotyloidis'' n. sp. (Microsporidia), a hyperparasite of ''Podocotyloides magnatestis'' (Trematoda), a parasite of ''Parapristipoma octolineatum'' (Teleostei) | journal = Parasite | volume = 21 | page = 44 | doi = 10.1051/parasite/2014044 | pmid = 25174849 | pmc = 4150386 }} {{open access}}</ref> Similarly, the microsporidian species ''Toguebayea baccigeri'' is a parasite of a digenean, the faustulid ''Bacciger israelensis'', itself an intestinal parasite of a marine fish, the bogue ''[[Boops boops]]'' (Teleostei, Sparidae).<ref name="Miquel2022">{{cite journal | last1=Miquel | first1=Jordi | last2=Kacem | first2=Hichem | last3=Baz-González | first3=Edgar | last4=Foronda | first4=Pilar | last5=Marchand | first5=Bernard | title=Ultrastructural and molecular study of the microsporidian ''Toguebayea baccigeri'' n. gen., n. sp., a hyperparasite of the digenean trematode ''Bacciger israelensis'' (Faustulidae), a parasite of ''Boops boops'' (Teleostei, Sparidae) | journal=Parasite | publisher=EDP Sciences | volume=29 | year=2022 | issn=1776-1042 | doi=10.1051/parasite/2022007 | page=2| pmid=35103588 | s2cid=246443154 }} {{open access}}</ref> |
Microsporidia can infect a variety of hosts, including hosts which are themselves parasites. In that case, the microsporidian species is a [[hyperparasite]], i.e. a parasite of a parasite. As an example, more than eighteen species are known which parasitize [[digenea]]ns (parasitic [[flatworm]]s). These digeneans are themselves parasites in various [[vertebrate]]s and [[mollusc]]s. Eight of these species belong to the genus ''[[Nosema (microsporidian)|Nosema]]''.<ref name=Toguebaye>{{cite journal | last1 = Toguebaye | first1 = B. S. | last2 = Quilichini | first2 = Y. | last3 = Diagne | first3 = P. M. | last4 = Marchand | first4 = B. | year = 2014 | title = Ultrastructure and development of ''Nosema podocotyloidis'' n. sp. (Microsporidia), a hyperparasite of ''Podocotyloides magnatestis'' (Trematoda), a parasite of ''Parapristipoma octolineatum'' (Teleostei) | journal = Parasite | volume = 21 | page = 44 | doi = 10.1051/parasite/2014044 | pmid = 25174849 | pmc = 4150386 }} {{open access}}</ref> Similarly, the microsporidian species ''Toguebayea baccigeri'' is a parasite of a digenean, the faustulid ''Bacciger israelensis'', itself an intestinal parasite of a marine fish, the bogue ''[[Boops boops]]'' (Teleostei, Sparidae).<ref name="Miquel2022">{{cite journal | last1=Miquel | first1=Jordi | last2=Kacem | first2=Hichem | last3=Baz-González | first3=Edgar | last4=Foronda | first4=Pilar | last5=Marchand | first5=Bernard | title=Ultrastructural and molecular study of the microsporidian ''Toguebayea baccigeri'' n. gen., n. sp., a hyperparasite of the digenean trematode ''Bacciger israelensis'' (Faustulidae), a parasite of ''Boops boops'' (Teleostei, Sparidae) | journal=Parasite | publisher=EDP Sciences | volume=29 | year=2022 | issn=1776-1042 | doi=10.1051/parasite/2022007 | page=2| pmid=35103588 | pmc=8805611 | s2cid=246443154 }} {{open access}}</ref> |
||
==Genomes== |
==Genomes== |
||
| Line 77: | Line 94: | ||
[[Horizontal gene transfer]] (HGT) seems to have occurred many times in microsporidia. For instance, the genomes of ''[[Encephalitozoon romaleae]]'' and ''[[Trachipleistophora hominis]]'' contain genes that derive from animals and bacteria, and some even from fungi.<ref name="Conradi2013" /> |
[[Horizontal gene transfer]] (HGT) seems to have occurred many times in microsporidia. For instance, the genomes of ''[[Encephalitozoon romaleae]]'' and ''[[Trachipleistophora hominis]]'' contain genes that derive from animals and bacteria, and some even from fungi.<ref name="Conradi2013" /> |
||
==DNA repair== |
|||
The [[RAD9A|Rad9]]-[[RAD1 homolog|Rad1]]-Hus1 protein complex (also known as the 9-1-1 complex) in eukaryotes is recruited to sites of [[DNA damage (naturally occurring)|DNA damage]] where it is considered to help trigger the checkpoint-signaling cascade. Genes that code for heterotrimeric 9-1-1 are present in microsporidia.<ref name = Santos2022>{{cite journal|vauthors=Mascarenhas Dos Santos AC, Julian AT, Pombert JF|title=The Rad9-Rad1-Hus1 DNA Repair Clamp is Found in Microsporidia|journal=Genome Biology and Evolution|date=2022-04-10|volume=14|issue=4|pages=evac053|doi=10.1093/gbe/evac053|pmid=35439302|pmc=9053307}}</ref> In addition to the 9-1-1 complex, other components of the [[DNA repair]] machinery are also present indicting that repair of DNA damage likely occurs in microsporidia.<ref name = Santos2022/> |
|||
==Phylogeny== |
|||
Phylogeny of Rozellomycota<ref name="Wijayawardene_2020">{{Cite journal |display-authors=6 |vauthors=Wijayawardene NN, Hyde KD, Al-Ani LK, Tedersoo L, Haelewaters D, Rajeshkumar KC, Zhao RL, Aptroot A, Leontyev DV, Saxena RK, Tokarev YS, Dai DQ, Letcher PM, Stephenson SL, Ertz D, Lumbsch HT, Kukwa M, Issi IV, Madrid H, Phillips AJ, Selbmann L, Pfliegler WP, Horváth E, Bensch K, Kirk PM, Kolaříková K, Raja HA, Radek R, Papp V, Dima B, Ma J, Malosso E, Takamatsu S, Rambold G, Gannibal PB, Triebel D, Gautam AK, Avasthi S, Suetrong S, Timdal E, Fryar SC, Delgado G, Réblová M, Doilom M, Dolatabadi S, Pawłowska J, Humber RA, Kodsueb R, Sánchez-Castro I, Goto BT, Silva DK, de Souza FA, Oehl F, da Silva GA, Silva IR, Błaszkowski J, Jobim K, Maia LC, Barbosa FR, Fiuza PO, Divakar PK, Shenoy BD, Castañeda-Ruiz RF, Somrithipol S, Lateef AA, Karunarathna SC, Tibpromma S, Mortimer PE, Wanasinghe DN, Phookamsak R, Xu J, Wang Y, Tian F, Alvarado P, Li DW, Kušan I, Matočec N, Maharachchikumbura SS, Papizadeh M, Heredia G, Wartchow F, Bakhshi M, Boehm E, Youssef N, Hustad VP, Lawrey JD, Santiago AL, Bezerra JD, Souza-Motta CM, Firmino AL, Tian Q, Houbraken J, Hongsanan S, Tanaka K, Dissanayake AJ, Monteiro JS, Grossart HP, Suija A, Weerakoon G, Etayo J, Tsurykau A, Vázquez V, Mungai P, Damm U, Li QR, Zhang H, Boonmee S, Lu YZ, Becerra AG, Kendrick B, Brearley FQ, Motiejūnaitė J, Sharma B, Khare R, Gaikwad S, Wijesundara DS, Tang LZ, He MQ, Flakus A, Rodriguez-Flakus P, Zhurbenko MP, McKenzie EH, Stadler M, Bhat DJ, Liu JK, Raza M, Jeewon R, Nassonova ES, Prieto M, Jayalal RG, Erdoğdu M, Yurkov A, Schnittler M, Shchepin ON, Novozhilov YK, Silva-Filho AG, Liu P, Cavender JC, Kang Y, Mohammad S, Zhang LF, Xu RF, Li YM, Dayarathne MC, Ekanayaka AH, Wen TC, Deng CY, Pereira OL, Navathe S, Hawksworth DL, Fan XL, Dissanayake LS, Kuhnert E, Grossart HP, Thines M |title = Outline of Fungi and fungus-like taxa |journal=Mycosphere |year=2020 |volume=11 |issue=1 |pages=1060–1456 |url=http://www.mycosphere.org/pdf/MYCOSPHERE_11_1_8-1.pdf |issn=2077-7019 |doi=10.5943/mycosphere/11/1/8 |pmid= |doi-access=free }}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Bojko |first1=Jamie |last2=Reinke |first2=Aaron W. |last3=Stentiford |first3=Grant D. |last4=Williams |first4=Bryony |last5=Rogers |first5=Martin S.J. |last6=Bass |first6=David | title=Microsporidia: a new taxonomic, evolutionary, and ecological synthesis |journal=Trends in Parasitology |year=2022 |volume=38 |issue=8 |pages=642–659 |url= |doi=10.1016/j.pt.2022.05.007 |pmid= |doi-access=free}}</ref> |
|||
{{clade|style=font-size:90%;line-height:100%;width:350px |
|||
|label1=Rozellomyceta |
|||
|1={{clade |
|||
|label1=[[Rozellomycota]] |
|||
|1={{clade |
|||
|label1=Rozellomycetes |
|||
|1=Rozellales |
|||
}} |
|||
|label2=[[Microsporidiomycota]] |
|||
|2={{clade |
|||
|1={{clade |
|||
|label1=Morellosporales |
|||
|1={{clade |
|||
|1=Mitosporidiaceae |
|||
|2=Morellosporaceae |
|||
}} |
|||
}} |
|||
|2={{clade |
|||
|1={{clade |
|||
|label1=Paramicrosporidiales |
|||
|1=Paramicrosporidiaceae |
|||
}} |
|||
|2={{clade |
|||
|label1=Nucleophagales |
|||
|1=Nucleophagaceae |
|||
|label2='''Microsporidia''' |
|||
|2={{clade |
|||
|1={{clade |
|||
|label1=[[Chytridiopsidea]] |
|||
|1=[[Chytridiopsida]] |
|||
}} |
|||
|2={{clade |
|||
|label1=[[Metchnikovellea]] |
|||
|1=Metchnikovellida |
|||
|label2=Microsporidea |
|||
|2={{clade |
|||
|1=Neopereziida |
|||
|2={{clade |
|||
|1=Ovavesiculida |
|||
|2={{clade |
|||
|1=Amblyosporida |
|||
|2={{clade |
|||
|1=Glugeida |
|||
|2=Nosematida |
|||
}} |
|||
}} |
|||
}} |
|||
}} |
|||
}} |
|||
}} |
|||
}} |
|||
}} |
|||
}} |
|||
}} |
|||
}} |
|||
== Classification == |
== Classification == |
||
| Line 82: | Line 161: | ||
The first described microsporidian genus, ''[[Nosema (microsporidian)|Nosema]]'', was initially put by [[Carl Nägeli|Nägeli]] in the fungal group [[Schizomycetes]] together with some [[bacteria]] and [[yeasts]].<ref>{{cite journal | last1 = Nägeli | first1 = C. von | year = 1857 | title = Über die neue Krankheit der Seidenraupe und verwandte Organismen. pp. 760–61. In: Caspary, R. (ed.). Bericht über die Verhandlungen der 33. Versammlung deutscher Naturforscher und Aerzte, gehalten in Bonn von 18 bis 24 September 1857 | url = https://archive.org/stream/botanischezeitun15mohl#page/374/mode/2up | journal = Botanische Zeitung | volume = 15 | pages = 749–776 }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | last1 = Keeling | first1 = P. J. | last2 = Fast | first2 = N. M. | year = 2002 | title = Microsporidia: biology and evolution of highly reduced intracellular parasites | url = http://www3.botany.ubc.ca/keeling/PDF/02microARM.pdf | journal = Annual Review of Microbiology | volume = 56 | issue = 1| pages = 93–116 | doi = 10.1146/annurev.micro.56.012302.160854 | pmid = 12142484 }}</ref> For some time microsporidia were considered as very primitive eukaryotes, placed in the protozoan group [[Cnidospora]].<ref name=corliss /> Later, especially because of the lack of mitochondria, they were placed along with the other [[Protozoa]] such as [[diplomonad]]s, [[parabasalid]]s and [[archamoebae]] in the [[protozoa]]n-group [[Archezoa]].<ref>{{cite journal | last1 = Cavalier-Smith | first1 = T | year = 1993 | title = Kingdom protozoa and its 18 phyla | url= | journal = Microbiological Reviews | volume = 57 | issue = 4| pages = 953–994 | doi = 10.1128/MR.57.4.953-994.1993 | pmid = 8302218 | pmc = 372943 }}</ref> More recent research has falsified this theory of early origin (for all of these). Instead, microsporidia are proposed to be highly developed and specialized organisms, which just dispensed functions that are needed no longer, because they are supplied by the host.<ref name="Keeling">{{cite journal |vauthors=Keeling PJ, Slamovits CH |title=Simplicity and Complexity of Microsporidian Genomes |journal=Eukaryotic Cell |volume=3 |issue=6 |pages=1363–9 |date=December 2004 |pmid=15590811 |pmc=539024 |doi=10.1128/EC.3.6.1363-1369.2004}}</ref> Furthermore, spore-forming organisms in general do have a complex system of reproduction, both sexual and asexual, which look far from primitive. |
The first described microsporidian genus, ''[[Nosema (microsporidian)|Nosema]]'', was initially put by [[Carl Nägeli|Nägeli]] in the fungal group [[Schizomycetes]] together with some [[bacteria]] and [[yeasts]].<ref>{{cite journal | last1 = Nägeli | first1 = C. von | year = 1857 | title = Über die neue Krankheit der Seidenraupe und verwandte Organismen. pp. 760–61. In: Caspary, R. (ed.). Bericht über die Verhandlungen der 33. Versammlung deutscher Naturforscher und Aerzte, gehalten in Bonn von 18 bis 24 September 1857 | url = https://archive.org/stream/botanischezeitun15mohl#page/374/mode/2up | journal = Botanische Zeitung | volume = 15 | pages = 749–776 }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | last1 = Keeling | first1 = P. J. | last2 = Fast | first2 = N. M. | year = 2002 | title = Microsporidia: biology and evolution of highly reduced intracellular parasites | url = http://www3.botany.ubc.ca/keeling/PDF/02microARM.pdf | journal = Annual Review of Microbiology | volume = 56 | issue = 1| pages = 93–116 | doi = 10.1146/annurev.micro.56.012302.160854 | pmid = 12142484 }}</ref> For some time microsporidia were considered as very primitive eukaryotes, placed in the protozoan group [[Cnidospora]].<ref name=corliss /> Later, especially because of the lack of mitochondria, they were placed along with the other [[Protozoa]] such as [[diplomonad]]s, [[parabasalid]]s and [[archamoebae]] in the [[protozoa]]n-group [[Archezoa]].<ref>{{cite journal | last1 = Cavalier-Smith | first1 = T | year = 1993 | title = Kingdom protozoa and its 18 phyla | url= | journal = Microbiological Reviews | volume = 57 | issue = 4| pages = 953–994 | doi = 10.1128/MR.57.4.953-994.1993 | pmid = 8302218 | pmc = 372943 }}</ref> More recent research has falsified this theory of early origin (for all of these). Instead, microsporidia are proposed to be highly developed and specialized organisms, which just dispensed functions that are needed no longer, because they are supplied by the host.<ref name="Keeling">{{cite journal |vauthors=Keeling PJ, Slamovits CH |title=Simplicity and Complexity of Microsporidian Genomes |journal=Eukaryotic Cell |volume=3 |issue=6 |pages=1363–9 |date=December 2004 |pmid=15590811 |pmc=539024 |doi=10.1128/EC.3.6.1363-1369.2004}}</ref> Furthermore, spore-forming organisms in general do have a complex system of reproduction, both sexual and asexual, which look far from primitive. |
||
Since the mid-2000s microsporidia are placed within the Fungi or as a sister-group of the Fungi with a common ancestor.<ref>{{cite journal |vauthors=Fischer WM, Palmer JD |title=Evidence from small-subunit ribosomal RNA sequences for a fungal origin of Microsporidia |journal=Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution |volume=36 |issue=3 |pages=606–22 |date=September 2005 |pmid=15923129 |doi=10.1016/j.ympev.2005.03.031}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |vauthors=Liu YJ, Hodson MC, Hall BD |title=Loss of the flagellum happened only once in the fungal lineage: phylogenetic structure of Kingdom Fungi inferred from RNA polymerase II subunit genes |journal=BMC Evolutionary Biology |volume=6|pages=74 |year=2006 |pmid=17010206 |pmc=1599754 |doi=10.1186/1471-2148-6-74}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |vauthors=Gill EE, Fast NM |title=Assessing the microsporidia-fungi relationship: Combined phylogenetic analysis of eight genes |journal=Gene |volume=375 |pages=103–9 |date=June 2006 |pmid=16626896 |doi=10.1016/j.gene.2006.02.023}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |vauthors=Lee SC, Corradi N, Byrnes EJ, etal |title=Microsporidia evolved from ancestral sexual fungi |journal=Current Biology |volume=18 |issue=21 |pages=1675–9 |date=November 2008 |pmid=18976912 |doi=10.1016/j.cub.2008.09.030 |pmc=2654606 }}</ref> |
Since the mid-2000s microsporidia are placed within the Fungi or as a sister-group of the Fungi with a common ancestor.<ref>{{cite journal |vauthors=Fischer WM, Palmer JD |title=Evidence from small-subunit ribosomal RNA sequences for a fungal origin of Microsporidia |journal=Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution |volume=36 |issue=3 |pages=606–22 |date=September 2005 |pmid=15923129 |doi=10.1016/j.ympev.2005.03.031}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |vauthors=Liu YJ, Hodson MC, Hall BD |title=Loss of the flagellum happened only once in the fungal lineage: phylogenetic structure of Kingdom Fungi inferred from RNA polymerase II subunit genes |journal=BMC Evolutionary Biology |volume=6|pages=74 |year=2006 |pmid=17010206 |pmc=1599754 |doi=10.1186/1471-2148-6-74 |doi-access=free }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |vauthors=Gill EE, Fast NM |title=Assessing the microsporidia-fungi relationship: Combined phylogenetic analysis of eight genes |journal=Gene |volume=375 |pages=103–9 |date=June 2006 |pmid=16626896 |doi=10.1016/j.gene.2006.02.023}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |vauthors=Lee SC, Corradi N, Byrnes EJ, etal |title=Microsporidia evolved from ancestral sexual fungi |journal=Current Biology |volume=18 |issue=21 |pages=1675–9 |date=November 2008 |pmid=18976912 |doi=10.1016/j.cub.2008.09.030 |pmc=2654606 }}</ref> |
||
Work to identify clades is largely based on habitat and host. Three classes of Microsporidia are proposed by Vossbrinck and Debrunner-Vossbrinck, based on the habitat: Aquasporidia, Marinosporidia and Terresporidia.<ref>{{cite journal |vauthors=Vossbrinck CR, Debrunner-Vossbrinck BA |title=Molecular phylogeny of the Microsporidia: ecological, ultrastructural and taxonomic considerations |journal=Folia Parasitologica |volume=52 |issue=1–2 |pages=131–42; discussion 130 |date=May 2005 |pmid=16004372 |doi=10.14411/fp.2005.017|doi-access=free }}</ref> |
Work to identify clades is largely based on habitat and host. Three classes of Microsporidia are proposed by Vossbrinck and Debrunner-Vossbrinck, based on the habitat: Aquasporidia, Marinosporidia and Terresporidia.<ref>{{cite journal |vauthors=Vossbrinck CR, Debrunner-Vossbrinck BA |title=Molecular phylogeny of the Microsporidia: ecological, ultrastructural and taxonomic considerations |journal=Folia Parasitologica |volume=52 |issue=1–2 |pages=131–42; discussion 130 |date=May 2005 |pmid=16004372 |doi=10.14411/fp.2005.017|doi-access=free }}</ref> |
||
| Line 104: | Line 183: | ||
{|class="wikitable" |
{|class="wikitable" |
||
|- |
|- |
||
! colspan=1 |Alimov 2007 <ref>{{cite |
! colspan=1 |Alimov 2007 <ref>{{cite book |editor=Alimov, A. F. |title=Protista 2: Handbook on zoology |publisher=Nauka |pages=1141 |date=May 2007 |isbn=9785020262249 | url=https://books.google.com/books?id=FVFQAAAAYAAJ }}</ref> |
||
! colspan=1 |Wijayawardene et al. 2020<ref name="Wijayawardene_2020">{{Cite journal |display-authors=6 |vauthors=Wijayawardene NN, Hyde KD, Al-Ani LK, Tedersoo L, Haelewaters D, Rajeshkumar KC, Zhao RL, Aptroot A, Leontyev DV, Saxena RK, Tokarev YS, Dai DQ, Letcher PM, Stephenson SL, Ertz D, Lumbsch HT, Kukwa M, Issi IV, Madrid H, Phillips AJ, Selbmann L, Pfliegler WP, Horváth E, Bensch K, Kirk PM, Kolaříková K, Raja HA, Radek R, Papp V, Dima B, Ma J, Malosso E, Takamatsu S, Rambold G, Gannibal PB, Triebel D, Gautam AK, Avasthi S, Suetrong S, Timdal E, Fryar SC, Delgado G, Réblová M, Doilom M, Dolatabadi S, Pawłowska J, Humber RA, Kodsueb R, Sánchez-Castro I, Goto BT, Silva DK, de Souza FA, Oehl F, da Silva GA, Silva IR, Błaszkowski J, Jobim K, Maia LC, Barbosa FR, Fiuza PO, Divakar PK, Shenoy BD, Castañeda-Ruiz RF, Somrithipol S, Lateef AA, Karunarathna SC, Tibpromma S, Mortimer PE, Wanasinghe DN, Phookamsak R, Xu J, Wang Y, Tian F, Alvarado P, Li DW, Kušan I, Matočec N, Maharachchikumbura SS, Papizadeh M, Heredia G, Wartchow F, Bakhshi M, Boehm E, Youssef N, Hustad VP, Lawrey JD, Santiago AL, Bezerra JD, Souza-Motta CM, Firmino AL, Tian Q, Houbraken J, Hongsanan S, Tanaka K, Dissanayake AJ, Monteiro JS, Grossart HP, Suija A, Weerakoon G, Etayo J, Tsurykau A, Vázquez V, Mungai P, Damm U, Li QR, Zhang H, Boonmee S, Lu YZ, Becerra AG, Kendrick B, Brearley FQ, Motiejūnaitė J, Sharma B, Khare R, Gaikwad S, Wijesundara DS, Tang LZ, He MQ, Flakus A, Rodriguez-Flakus P, Zhurbenko MP, McKenzie EH, Stadler M, Bhat DJ, Liu JK, Raza M, Jeewon R, Nassonova ES, Prieto M, Jayalal RG, Erdoğdu M, Yurkov A, Schnittler M, Shchepin ON, Novozhilov YK, Silva-Filho AG, Liu P, Cavender JC, Kang Y, Mohammad S, Zhang LF, Xu RF, Li YM, Dayarathne MC, Ekanayaka AH, Wen TC, Deng CY, Pereira OL, Navathe S, Hawksworth DL, Fan XL, Dissanayake LS, Kuhnert E, Grossart HP, Thines M |title = Outline of Fungi and fungus-like taxa |journal=Mycosphere |year=2020 |volume=11 |issue=1 |pages=1060–1456 |url=http://www.mycosphere.org/pdf/MYCOSPHERE_11_1_8-1.pdf |issn=2077-7019 |doi=10.5943/mycosphere/11/1/8 |pmid= |doi-access=free }}</ref> |
! colspan=1 |Wijayawardene et al. 2020<ref name="Wijayawardene_2020">{{Cite journal |display-authors=6 |vauthors=Wijayawardene NN, Hyde KD, Al-Ani LK, Tedersoo L, Haelewaters D, Rajeshkumar KC, Zhao RL, Aptroot A, Leontyev DV, Saxena RK, Tokarev YS, Dai DQ, Letcher PM, Stephenson SL, Ertz D, Lumbsch HT, Kukwa M, Issi IV, Madrid H, Phillips AJ, Selbmann L, Pfliegler WP, Horváth E, Bensch K, Kirk PM, Kolaříková K, Raja HA, Radek R, Papp V, Dima B, Ma J, Malosso E, Takamatsu S, Rambold G, Gannibal PB, Triebel D, Gautam AK, Avasthi S, Suetrong S, Timdal E, Fryar SC, Delgado G, Réblová M, Doilom M, Dolatabadi S, Pawłowska J, Humber RA, Kodsueb R, Sánchez-Castro I, Goto BT, Silva DK, de Souza FA, Oehl F, da Silva GA, Silva IR, Błaszkowski J, Jobim K, Maia LC, Barbosa FR, Fiuza PO, Divakar PK, Shenoy BD, Castañeda-Ruiz RF, Somrithipol S, Lateef AA, Karunarathna SC, Tibpromma S, Mortimer PE, Wanasinghe DN, Phookamsak R, Xu J, Wang Y, Tian F, Alvarado P, Li DW, Kušan I, Matočec N, Maharachchikumbura SS, Papizadeh M, Heredia G, Wartchow F, Bakhshi M, Boehm E, Youssef N, Hustad VP, Lawrey JD, Santiago AL, Bezerra JD, Souza-Motta CM, Firmino AL, Tian Q, Houbraken J, Hongsanan S, Tanaka K, Dissanayake AJ, Monteiro JS, Grossart HP, Suija A, Weerakoon G, Etayo J, Tsurykau A, Vázquez V, Mungai P, Damm U, Li QR, Zhang H, Boonmee S, Lu YZ, Becerra AG, Kendrick B, Brearley FQ, Motiejūnaitė J, Sharma B, Khare R, Gaikwad S, Wijesundara DS, Tang LZ, He MQ, Flakus A, Rodriguez-Flakus P, Zhurbenko MP, McKenzie EH, Stadler M, Bhat DJ, Liu JK, Raza M, Jeewon R, Nassonova ES, Prieto M, Jayalal RG, Erdoğdu M, Yurkov A, Schnittler M, Shchepin ON, Novozhilov YK, Silva-Filho AG, Liu P, Cavender JC, Kang Y, Mohammad S, Zhang LF, Xu RF, Li YM, Dayarathne MC, Ekanayaka AH, Wen TC, Deng CY, Pereira OL, Navathe S, Hawksworth DL, Fan XL, Dissanayake LS, Kuhnert E, Grossart HP, Thines M |title = Outline of Fungi and fungus-like taxa |journal=Mycosphere |year=2020 |volume=11 |issue=1 |pages=1060–1456 |url=http://www.mycosphere.org/pdf/MYCOSPHERE_11_1_8-1.pdf |issn=2077-7019 |doi=10.5943/mycosphere/11/1/8 |pmid= |doi-access=free }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |display-authors=6 |last1=Wijayawardene |first1=N.N. |last2=Hyde |first2=K.D. |last3=Dai |first3=D.Q. |last4=Sánchez-García |first4=M. |last5=Goto |first5=B.T. |last6=Saxena |first6=R.K. |last7=Erdoğdu |first7=M. |last8=Selçuk |first8=F. |last9=Rajeshkumar |first9=K.C. |last10=Aptroot |first10=A. |last11=Błaszkowski |first11=J. |last12=Boonyuen |first12=N. |last13=da Silva |first13=G. |last14=de Souza |first14=F.A. |last15=Dong |first15=W. |last16=Ertz |first16=D. |last17=Haelewaters |first17=D. |last18=Jones |first18=E.B. |last19=Karunarathna |first19=S.C. |last20=Kirk |first20=P.M. |last21=Kukwa |first21=M. |last22=Kumla |first22=J. |last23=Leontyev |first23=D.V. |last24=Lumbsch |first24=H.T. |last25=Maharachchikumbura |first25=S.S.N. |last26=Marguno |first26=F. |last27=Martínez-Rodríguez |first27=P. |last28=Mešić |first28=A. |last29=Monteiro |first29=J.S. |last30=Oehl |first30=F. |last31=Pawłowska |first31=J. |last32=Pem |first32=D. |last33=Pfliegler |first33=W.P. |last34=Phillips |first34=A.J.L. |last35=Pošta |first35=A. |last36=He |first36=M.Q. |last37=Li |first37=J.X. |last38=Raza |first38=M. |last39=Sruthi |first39=O.P. |last40=Suetrong |first40=S. |last41=Suwannarach |first41=N. |last42=Tedersoo |first42=L. |last43=Thiyagaraja |first43=V. |last44=Tibpromma |first44=S. |last45=Tkalčec |first45=Z. |last46=Tokarev |first46=Y.S. |last47=Wanasinghe |first47=D.N. |last48=Wijesundara |first48=D.S.A. |last49=Wimalaseana |first49=S.D.M.K. |last50=Madrid |first50=H. |last51=Zhang |first51=G.Q. |last52=Gao |first52=Y. |last53=Sánchez-Castro |first53=I. |last54=Tang |first54=L.Z. |last55=Stadler |first55=M. |last56=Yurkov |first56=A. |last57=Thines |first57=M. |year=2022 |title=Outline of Fungi and fungus-like taxa – 2021 |journal=Mycosphere |volume=13 |issue=1 |pages=53–453 |doi=10.5943/mycosphere/13/1/2 |s2cid=249054641 |url=https://www.researchgate.net/publication/358798332|hdl=1854/LU-8754813 |hdl-access=free }}</ref> |
||
|- style="vertical-align:top;" |
|- style="vertical-align:top;" |
||
|style="width:50%;"| |
|style="width:50%;"| |
||
| Line 168: | Line 247: | ||
***** Family [[Tetramicridae]] |
***** Family [[Tetramicridae]] |
||
|style="width:50%;"| |
|style="width:50%;"| |
||
* Order [[Paramicrosporidiales]] <small>Corsaro 2022</small> |
|||
** Family [[Paramicrosporidiaceae]] <small>Corsaro 2022</small> |
|||
* Order [[Morellosporales]] <small>Corsaro 2022</small> |
|||
** Family [[Mitosporidiaceae]] <small>Corsaro 2022</small> |
|||
** Family [[Morellosporaceae]] <small>Corsaro 2022</small> |
|||
* Order [[Nucleophagales]] <small>Corsaro 2022</small> |
|||
** Family [[Nucleophagaceae]] <small>Corsaro 2022</small> |
|||
* Class [[Chytridiopsidea]] Issi 1980 |
* Class [[Chytridiopsidea]] Issi 1980 |
||
** Order [[Hesseida]] <small>Weiser 1977</small> |
|||
*** Family [[Hesseidae]] <small>Ormières & Sprague 1973</small> |
|||
** Order [[Chytridiopsida]] <small>Weiser 1974</small> |
** Order [[Chytridiopsida]] <small>Weiser 1974</small> |
||
*** Family [[Buxtehudeidae]] <small>Larsson 1980</small> |
*** Family [[Buxtehudeidae]] <small>Larsson 1980</small> |
||
*** Family [[ |
*** Family [[Chytridiopsidae]] <small>Sprague, Ormières & Manier 1972</small> |
||
*** Family [[Chytridiopsidae]] <small>Sprague, Ormieres & Manier 1972</small> |
|||
* Class [[Metchnikovellea]] <small>Weiser 1977 em. Cavalier-Smith 1993</small> [Manubrispora <small>Cavalier-Smith 1998</small>] |
* Class [[Metchnikovellea]] <small>Weiser 1977 em. Cavalier-Smith 1993</small> [Manubrispora <small>Cavalier-Smith 1998</small>] |
||
** Order [[Metchnikovellida]] <small>Vivier 1977</small> |
** Order [[Metchnikovellida]] <small>Vivier 1977</small> |
||
| Line 230: | Line 317: | ||
==References== |
==References== |
||
{{Reflist| |
{{Reflist|refs= |
||
<ref name="OOF2022">{{cite journal |display-authors=6 |last1=Wijayawardene |first1=N.N. |last2=Hyde |first2=K.D. |last3=Dai |first3=D.Q. |last4=Sánchez-García |first4=M. |last5=Goto |first5=B.T. |last6=Saxena |first6=R.K. |last7=Erdoğdu |first7=M. |last8=Selçuk |first8=F. |last9=Rajeshkumar |first9=K.C. |last10=Aptroot |first10=A. |last11=Błaszkowski |first11=J. |last12=Boonyuen |first12=N. |last13=da Silva |first13=G. |last14=de Souza |first14=F.A. |last15=Dong |first15=W. |last16=Ertz |first16=D. |last17=Haelewaters |first17=D. |last18=Jones |first18=E.B. |last19=Karunarathna |first19=S.C. |last20=Kirk |first20=P.M. |last21=Kukwa |first21=M. |last22=Kumla |first22=J. |last23=Leontyev |first23=D.V. |last24=Lumbsch |first24=H.T. |last25=Maharachchikumbura |first25=S.S.N. |last26=Marguno |first26=F. |last27=Martínez-Rodríguez |first27=P. |last28=Mešić |first28=A. |last29=Monteiro |first29=J.S. |last30=Oehl |first30=F. |last31=Pawłowska |first31=J. |last32=Pem |first32=D. |last33=Pfliegler |first33=W.P. |last34=Phillips |first34=A.J.L. |last35=Pošta |first35=A. |last36=He |first36=M.Q. |last37=Li |first37=J.X. |last38=Raza |first38=M. |last39=Sruthi |first39=O.P. |last40=Suetrong |first40=S. |last41=Suwannarach |first41=N. |last42=Tedersoo |first42=L. |last43=Thiyagaraja |first43=V. |last44=Tibpromma |first44=S. |last45=Tkalčec |first45=Z. |last46=Tokarev |first46=Y.S. |last47=Wanasinghe |first47=D.N. |last48=Wijesundara |first48=D.S.A. |last49=Wimalaseana |first49=S.D.M.K. |last50=Madrid |first50=H. |last51=Zhang |first51=G.Q. |last52=Gao |first52=Y. |last53=Sánchez-Castro |first53=I. |last54=Tang |first54=L.Z. |last55=Stadler |first55=M. |last56=Yurkov |first56=A. |last57=Thines |first57=M. |year=2022 |title=Outline of Fungi and fungus-like taxa – 2021 |journal=Mycosphere |volume=13 |issue=1 |pages=53–453 |doi=10.5943/mycosphere/13/1/2 |s2cid=249054641 |url=https://www.researchgate.net/publication/358798332|doi-access=free |hdl=10481/76378 |hdl-access=free }}</ref> |
|||
}} |
|||
== External links == |
== External links == |
||
{{ |
{{Commons category|Microsporidia}} |
||
*{{Wikispecies-inline|Microsporidia}} |
|||
*[http://www.biohealthbase.org/microsporidia BioHealthBase Bioinformatics Resource Center] Database of microspordia sequences and related information. |
*[http://www.biohealthbase.org/microsporidia BioHealthBase Bioinformatics Resource Center] Database of microspordia sequences and related information. |
||
*{{MeshName|Microsporidia}} |
*{{MeshName|Microsporidia}} |
||
{{Commons category|position=left|Microsporidia}} |
|||
{{Fungi classification}} |
|||
{{Opisthokont protists}} |
{{Opisthokont protists}} |
||
{{Taxonbar|from=Q132652}} |
{{Taxonbar|from=Q132652}} |
||
{{Authority control}} |
|||
[[Category:Microsporidia| ]] |
[[Category:Microsporidia| ]] |
||
<!-- [[Category:Parasitic fungi]] category:Microsporidia already listed here --> |
<!-- [[Category:Parasitic fungi]] category:Microsporidia already listed here --> |
||
Latest revision as of 08:32, 5 October 2024
| Microsporidia | |
|---|---|

| |
| Sporoblast of Fibrillanosema crangonycis | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Clade: | Amorphea |
| Clade: | Obazoa |
| (unranked): | Opisthokonta |
| Clade: | Holomycota |
| Kingdom: | Fungi |
| Subkingdom: | Rozellomyceta |
| Class: | Microsporidiomycota Benny 2007 |
| Classes & orders[1] | |
| Synonyms | |
Microsporidia are a group of spore-forming unicellular parasites. These spores contain an extrusion apparatus that has a coiled polar tube ending in an anchoring disc at the apical part of the spore.[7] They were once considered protozoans or protists, but are now known to be fungi,[8] or a sister group to true fungi.[9] These fungal microbes are obligate eukaryotic parasites that use a unique mechanism to infect host cells.[7] They have recently been discovered in a 2017 Cornell study to infect Coleoptera on a large scale. So far, about 1500 of the probably more than one million[10] species are named. Microsporidia are restricted to animal hosts, and all major groups of animals host microsporidia. Most infect insects, but they are also responsible for common diseases of crustaceans and fish. The named species of microsporidia usually infect one host species or a group of closely related taxa. Approximately 10 percent of the known species are parasites of vertebrates — several species, most of which are opportunistic, can infect humans, in whom they can cause microsporidiosis.
After infection they influence their hosts in various ways and all organs and tissues are invaded, though generally by different species of specialised microsporidia. Some species are lethal, and a few are used in biological control of insect pests. Parasitic castration, gigantism, or change of host sex are all potential effects of microsporidian parasitism (in insects). In the most advanced cases of parasitism the microsporidium rules the host cell completely and controls its metabolism and reproduction, forming a xenoma.[11]
Replication takes place within the host's cells, which are infected by means of unicellular spores. These vary from 1–40 μm, making them some of the smallest eukaryotes.[citation needed] Microsporidia that infect mammals are 1.0–4.0 μm.[12] They also have the smallest eukaryotic genomes.
The terms "microsporidium" (pl. "microsporidia") and "microsporidian" are used as vernacular names for members of the group. The name Microsporidium Balbiani, 1884[13] is also used as a catchall genus for incertae sedis members.[14]

Morphology
[edit]
Microsporidia lack mitochondria, instead possessing mitosomes. They also lack motile structures, such as flagella.
Microsporidia produce highly resistant spores, capable of surviving outside their host for up to several years. Spore morphology is useful in distinguishing between different species. Spores of most species are oval or pyriform, but rod-shaped or spherical spores are not unusual. A few genera produce spores of unique shape for the genus.
The spore is protected by a wall, consisting of three layers:
- an outer electron-dense exospore
- a median, wide and seemingly structureless endospore, containing chitin
- a thin internal plasma membrane
In most cases there are two closely associated nuclei, forming a diplokaryon, but sometimes there is only one.
The anterior half of the spore contains a harpoon-like apparatus with a long, thread-like polar filament, which is coiled up in the posterior half of the spore. The anterior part of the polar filament is surrounded by a polaroplast, a lamella of membranes. Behind the polar filament, there is a posterior vacuole.[11]
Infection
[edit]In the gut of the host the spore germinates; it builds up osmotic pressure until its rigid wall ruptures at its thinnest point at the apex. The posterior vacuole swells, forcing the polar filament to rapidly eject the infectious content into the cytoplasm of the potential host. Simultaneously the material of the filament is rearranged to form a tube which functions as a hypodermic needle and penetrates the gut epithelium.
Once inside the host cell, a sporoplasm grows, dividing or forming a multinucleate plasmodium, before producing new spores. The life cycle varies considerably. Some have a simple asexual life cycle,[16] while others have a complex life cycle involving multiple hosts and both asexual and sexual reproduction. Different types of spores may be produced at different stages, probably with different functions including autoinfection (transmission within a single host).
Medical implications
[edit]In animals and humans, microsporidia often cause chronic, debilitating diseases rather than lethal infections. Effects on the host include reduced longevity, fertility, weight, and general vigor. Vertical transmission of microsporidia is frequently reported.
In the case of insect hosts, vertical transmission often occurs as transovarial transmission, where the microsporidian parasites pass from the ovaries of the female host into eggs and eventually multiply in the infected larvae. Amblyospora salinaria n. sp. which infects the mosquito Culex salinarius Coquillett, and Amblyospora californica which infects the mosquito Culex tarsalis Coquillett, provide typical examples of transovarial transmission of microsporidia.[17][18][19][20] Microsporidia, specifically the mosquito-infecting Vavraia culicis, are being explored as a possible 'evolution-proof' malaria-control method.[21] Microsporidian infection of Anopheles gambiae (the principal vector of Plasmodium falciparum malaria) reduces malarial infection within the mosquito, and shortens the mosquito lifespan.[22] As the majority of malaria-infected mosquitoes naturally die before the malaria parasite is mature enough to transmit, any increase in mosquito mortality through microsporidian-infection may reduce malaria transmission to humans. In May 2020, researchers reported that Microsporidia MB, a symbiont in the midgut and ovaries of An. arabiensis, significantly impaired transmission of P. falciparum, had "no overt effect" on the fitness of host mosquitoes, and was transmitted vertically (through inheritance).[23]
Clinical
[edit]This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (November 2013) |
Microsporidian infections of humans sometimes cause a disease called microsporidiosis. At least 14 microsporidian species, spread across eight genera, have been recognized as human pathogens. These include Trachipleistophora hominis.[24]
As hyperparasites
[edit]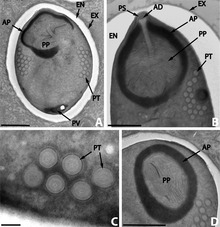
Microsporidia can infect a variety of hosts, including hosts which are themselves parasites. In that case, the microsporidian species is a hyperparasite, i.e. a parasite of a parasite. As an example, more than eighteen species are known which parasitize digeneans (parasitic flatworms). These digeneans are themselves parasites in various vertebrates and molluscs. Eight of these species belong to the genus Nosema.[25] Similarly, the microsporidian species Toguebayea baccigeri is a parasite of a digenean, the faustulid Bacciger israelensis, itself an intestinal parasite of a marine fish, the bogue Boops boops (Teleostei, Sparidae).[26]
Genomes
[edit]Microsporidia have the smallest known (nuclear) eukaryotic genomes. The parasitic lifestyle of microsporidia has led to a loss of many mitochondrial and Golgi genes, and even their ribosomal RNAs are reduced in size compared with those of most eukaryotes. As a consequence, the genomes of microsporidia are much smaller than those of other eukaryotes. Currently known microsporidial genomes are 2.5 to 11.6 Mb in size, encoding from 1,848 to 3,266 proteins which is in the same range as many bacteria.[27]
Horizontal gene transfer (HGT) seems to have occurred many times in microsporidia. For instance, the genomes of Encephalitozoon romaleae and Trachipleistophora hominis contain genes that derive from animals and bacteria, and some even from fungi.[27]
DNA repair
[edit]The Rad9-Rad1-Hus1 protein complex (also known as the 9-1-1 complex) in eukaryotes is recruited to sites of DNA damage where it is considered to help trigger the checkpoint-signaling cascade. Genes that code for heterotrimeric 9-1-1 are present in microsporidia.[28] In addition to the 9-1-1 complex, other components of the DNA repair machinery are also present indicting that repair of DNA damage likely occurs in microsporidia.[28]
Phylogeny
[edit]Phylogeny of Rozellomycota[29][30]
| Rozellomyceta |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Classification
[edit]The first described microsporidian genus, Nosema, was initially put by Nägeli in the fungal group Schizomycetes together with some bacteria and yeasts.[31][32] For some time microsporidia were considered as very primitive eukaryotes, placed in the protozoan group Cnidospora.[5] Later, especially because of the lack of mitochondria, they were placed along with the other Protozoa such as diplomonads, parabasalids and archamoebae in the protozoan-group Archezoa.[33] More recent research has falsified this theory of early origin (for all of these). Instead, microsporidia are proposed to be highly developed and specialized organisms, which just dispensed functions that are needed no longer, because they are supplied by the host.[34] Furthermore, spore-forming organisms in general do have a complex system of reproduction, both sexual and asexual, which look far from primitive.
Since the mid-2000s microsporidia are placed within the Fungi or as a sister-group of the Fungi with a common ancestor.[35][36][37][38]
Work to identify clades is largely based on habitat and host. Three classes of Microsporidia are proposed by Vossbrinck and Debrunner-Vossbrinck, based on the habitat: Aquasporidia, Marinosporidia and Terresporidia.[39]
A second classification by Cavalier-Smith 1993:[40]
- Subphyla Rudimicrospora Cavalier-Smith 1993
- Class Minisporea Cavalier-Smith 1993
- Order Minisporida Sprague, 1972
- Class Metchnikovellea Weiser, 1977
- Order Metchnikovellida Vivier, 1975
- Class Minisporea Cavalier-Smith 1993
- Subphyla Polaroplasta Cavalier-Smith 1993
- Class Pleistophoridea Cavalier-Smith 1993
- Order Pleistophorida Stempell 1906
- Class Disporea Cavalier-Smith 1993
- Subclass Unikaryotia Cavalier-Smith 1993
- Subclass Diplokaryotia Cavalier-Smith 1993
- Class Pleistophoridea Cavalier-Smith 1993
|
See also
[edit]- List of Microsporidian genera
- Glugea, a genus of microsporidia
- Nosema apis, a microsporidian parasite of bees
References
[edit]- ^ Wijayawardene, N.N.; Hyde, K.D.; Dai, D.Q.; Sánchez-García, M.; Goto, B.T.; Saxena, R.K.; et al. (2022). "Outline of Fungi and fungus-like taxa – 2021". Mycosphere. 13 (1): 53–453. doi:10.5943/mycosphere/13/1/2. hdl:10481/76378. S2CID 249054641.
- ^ Balbiani, G (1882). "Sur les microsporidies ou psorospermies des Articulés". C. R. Acad. Sci. 95: 1168–71.
- ^ Delphy, J. 1936. Sous-règne des Protozoaires. In: Perrier, R. (ed.). La Faune de la France en tableaux synoptiques illustrés, vol 1A. Delagrave: Paris.
- ^ Levine, N. D.; et al. (1980). "A Newly Revised Classification of the Protozoa". The Journal of Protozoology. 27 (1): 37–58. doi:10.1111/j.1550-7408.1980.tb04228.x. PMID 6989987.
- ^ a b Corliss JO, Levine ND (1963). "Establishment of the Microsporidea as a new class in the protozoan subphylum Cnidospora". The Journal of Protozoology. 10 (Suppl): 26–27. doi:10.1111/jeu.1963.10.issue-s3.
- ^ Sprague, V. (1977). Classification and phylogeny of the Microsporidia. In: Comparative pathobiology. vol. 2, Systematics of the Microsporidia. Lee A. Bulla & Thomas C. Cheng (ed.). pp. 1–30. New York: Plenum Press, [1].
- ^ a b Franzen, C. (2005). How do Microsporidia invade cells?. Folia Parasitologica, 52(1–2), 36–40. doi.org/10.14411/fp.2005.005
- ^ Hibbett, D.S.; et al. (2007). "A higher level phylogenetic classification of the Fungi" (PDF). Mycological Research. 111 (5): 509–47. doi:10.1016/j.mycres.2007.03.004. PMID 17572334. S2CID 4686378.
- ^ Silar, Philippe (2016). Protistes Eucaryotes : Origine, Evolution et Biologie des Microbes Eucaryotes. HAL. p. 462. ISBN 978-2-9555841-0-1.
- ^ Hawksworth, David (2001). "The magnitude of fungal diversity: The 1.5 million spices estimate revisited". Mycological Research. 105 (12): 1422. doi:10.1017/S0953756201004725.
- ^ a b Ronny Larsson, Lund University (Department of Cell and Organism Biology) Cytology and taxonomy of the microsporidia Archived 2009-09-12 at the Wayback Machine 2004.
- ^ Didier, ES. (Apr 2005). "Microsporidiosis: an emerging and opportunistic infection in humans and animals". Acta Trop. 94 (1): 61–76. doi:10.1016/j.actatropica.2005.01.010. PMID 15777637.
- ^ Balbiani, G. 1884. Les Psorospermies des Articulés ou Microsporidies, pp. 150-168, 184. In: Leçons sur les sporozoaires. Paris: Doin, [2].
- ^ Hoffman, G. (1999). Parasites of North American Freshwater Fishes, 2nd edn, University of California Press, Berkeley, California, USA, p. 89, [3].
- ^ Winters, A. D.; Faisal, M. (2014). "Molecular and ultrastructural characterization of Dictyocoela diporeiae n. sp. (Microsporidia), a parasite of Diporeia spp. (Amphipoda, Gammaridea)". Parasite. 21: 26. doi:10.1051/parasite/2014028. PMC 4059264. PMID 24934702.
- ^ Ironside JE (2007). "Multiple losses of sex within a single genus of Microsporidia". BMC Evolutionary Biology. 7: 48. doi:10.1186/1471-2148-7-48. PMC 1853083. PMID 17394631.
- ^ Andreadis TG, Hall DW (August 1979). "Development, ultrastructure, and mode of transmission of Amblyospora sp. (Microspora) in the mosquito". The Journal of Protozoology. 26 (3): 444–52. doi:10.1111/j.1550-7408.1979.tb04651.x. PMID 536933.
- ^ Andreadis TG, Hall DW (September 1979). "Significance of transovarial infections of Amblyospora sp. (Microspora:Thelohaniidae) in relation to parasite maintenance in the mosquito Culex salinarius". Journal of Invertebrate Pathology. 34 (2): 152–7. doi:10.1016/0022-2011(79)90095-8. PMID 536610.
- ^ Jahn GC, Hall DW, Zam SG (1986). "A comparison of the life cycles of two Amblyospora (Microspora: Amblyosporidae) in the mosquitoes Culex salinarius and Culex tarsalis Coquillett". Journal of the Florida Anti-Mosquito Association. 57 (1): 24–27.
- ^ Becnel JJ, Andreadis TG (May 1998). "Amblyospora salinaria n. sp. (Microsporidia: amblyosporidae), parasite of Culex salinarius (Diptera: culicidae): its life cycle stages in an intermediate host". Journal of Invertebrate Pathology. 71 (3): 258–62. doi:10.1006/jipa.1998.4729. PMID 9538031.
- ^ Koella, Jacob C.; Lorenz, Lena; Bargielowski, Irka (2009). Chapter 12 Microsporidians as Evolution-Proof Agents of Malaria Control?. Advances in Parasitology. Vol. 68. pp. 315–327. doi:10.1016/S0065-308X(08)00612-X. ISBN 978-0-12-374787-7. PMID 19289199.
- ^ Bargielowski I, Koella JC (2009). Baylis M (ed.). "A Possible Mechanism for the Suppression of Plasmodium berghei Development in the Mosquito Anopheles gambiae by the Microsporidian Vavraia culicis". PLOS ONE. 4 (3): e4676. Bibcode:2009PLoSO...4.4676B. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0004676. PMC 2651578. PMID 19277119.
- ^ Herren, JK; Mbaisi, L; Mararo, E; et al. (2020). "A microsporidian impairs Plasmodium falciparum transmission in Anopheles arabiensis mosquitoes". Nature Communications. 11 (2187): 2187. Bibcode:2020NatCo..11.2187H. doi:10.1038/s41467-020-16121-y. PMC 7198529. PMID 32366903.
- ^ Heinz, E; Williams, TA; Nakjang, S; et al. (Oct 2012). "The genome of the obligate intracellular parasite Trachipleistophora hominis: New insights into microsporidian genome dynamics and reductive evolution". PLOS Pathog. 8 (10): e1002979. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1002979. PMC 3486916. PMID 23133373.
- ^ a b Toguebaye, B. S.; Quilichini, Y.; Diagne, P. M.; Marchand, B. (2014). "Ultrastructure and development of Nosema podocotyloidis n. sp. (Microsporidia), a hyperparasite of Podocotyloides magnatestis (Trematoda), a parasite of Parapristipoma octolineatum (Teleostei)". Parasite. 21: 44. doi:10.1051/parasite/2014044. PMC 4150386. PMID 25174849.

- ^ Miquel, Jordi; Kacem, Hichem; Baz-González, Edgar; Foronda, Pilar; Marchand, Bernard (2022). "Ultrastructural and molecular study of the microsporidian Toguebayea baccigeri n. gen., n. sp., a hyperparasite of the digenean trematode Bacciger israelensis (Faustulidae), a parasite of Boops boops (Teleostei, Sparidae)". Parasite. 29. EDP Sciences: 2. doi:10.1051/parasite/2022007. ISSN 1776-1042. PMC 8805611. PMID 35103588. S2CID 246443154.

- ^ a b Corradi, N.; Selman, M. (2013). "Latest Progress in Microsporidian Genome Research". Journal of Eukaryotic Microbiology. 60 (3): 309–312. doi:10.1111/jeu.12030. PMID 23445243. S2CID 24504235.
- ^ a b Mascarenhas Dos Santos AC, Julian AT, Pombert JF (2022-04-10). "The Rad9-Rad1-Hus1 DNA Repair Clamp is Found in Microsporidia". Genome Biology and Evolution. 14 (4): evac053. doi:10.1093/gbe/evac053. PMC 9053307. PMID 35439302.
- ^ a b Wijayawardene NN, Hyde KD, Al-Ani LK, Tedersoo L, Haelewaters D, Rajeshkumar KC, et al. (2020). "Outline of Fungi and fungus-like taxa" (PDF). Mycosphere. 11 (1): 1060–1456. doi:10.5943/mycosphere/11/1/8. ISSN 2077-7019.
- ^ Bojko, Jamie; Reinke, Aaron W.; Stentiford, Grant D.; Williams, Bryony; Rogers, Martin S.J.; Bass, David (2022). "Microsporidia: a new taxonomic, evolutionary, and ecological synthesis". Trends in Parasitology. 38 (8): 642–659. doi:10.1016/j.pt.2022.05.007.
- ^ Nägeli, C. von (1857). "Über die neue Krankheit der Seidenraupe und verwandte Organismen. pp. 760–61. In: Caspary, R. (ed.). Bericht über die Verhandlungen der 33. Versammlung deutscher Naturforscher und Aerzte, gehalten in Bonn von 18 bis 24 September 1857". Botanische Zeitung. 15: 749–776.
- ^ Keeling, P. J.; Fast, N. M. (2002). "Microsporidia: biology and evolution of highly reduced intracellular parasites" (PDF). Annual Review of Microbiology. 56 (1): 93–116. doi:10.1146/annurev.micro.56.012302.160854. PMID 12142484.
- ^ Cavalier-Smith, T (1993). "Kingdom protozoa and its 18 phyla". Microbiological Reviews. 57 (4): 953–994. doi:10.1128/MR.57.4.953-994.1993. PMC 372943. PMID 8302218.
- ^ Keeling PJ, Slamovits CH (December 2004). "Simplicity and Complexity of Microsporidian Genomes". Eukaryotic Cell. 3 (6): 1363–9. doi:10.1128/EC.3.6.1363-1369.2004. PMC 539024. PMID 15590811.
- ^ Fischer WM, Palmer JD (September 2005). "Evidence from small-subunit ribosomal RNA sequences for a fungal origin of Microsporidia". Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution. 36 (3): 606–22. doi:10.1016/j.ympev.2005.03.031. PMID 15923129.
- ^ Liu YJ, Hodson MC, Hall BD (2006). "Loss of the flagellum happened only once in the fungal lineage: phylogenetic structure of Kingdom Fungi inferred from RNA polymerase II subunit genes". BMC Evolutionary Biology. 6: 74. doi:10.1186/1471-2148-6-74. PMC 1599754. PMID 17010206.
- ^ Gill EE, Fast NM (June 2006). "Assessing the microsporidia-fungi relationship: Combined phylogenetic analysis of eight genes". Gene. 375: 103–9. doi:10.1016/j.gene.2006.02.023. PMID 16626896.
- ^ Lee SC, Corradi N, Byrnes EJ, et al. (November 2008). "Microsporidia evolved from ancestral sexual fungi". Current Biology. 18 (21): 1675–9. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2008.09.030. PMC 2654606. PMID 18976912.
- ^ Vossbrinck CR, Debrunner-Vossbrinck BA (May 2005). "Molecular phylogeny of the Microsporidia: ecological, ultrastructural and taxonomic considerations". Folia Parasitologica. 52 (1–2): 131–42, discussion 130. doi:10.14411/fp.2005.017. PMID 16004372.
- ^ Cavalier-Smith (1993). "Kingdom Protozoa and its 18 phyla". Microbiological Reviews. 57 (4): 953–94. doi:10.1128/MR.57.4.953-994.1993. PMC 372943. PMID 8302218.
- ^ Alimov, A. F., ed. (May 2007). Protista 2: Handbook on zoology. Nauka. p. 1141. ISBN 9785020262249.
- ^ Wijayawardene, N.N.; Hyde, K.D.; Dai, D.Q.; Sánchez-García, M.; Goto, B.T.; Saxena, R.K.; et al. (2022). "Outline of Fungi and fungus-like taxa – 2021". Mycosphere. 13 (1): 53–453. doi:10.5943/mycosphere/13/1/2. hdl:1854/LU-8754813. S2CID 249054641.
External links
[edit] Data related to Microsporidia at Wikispecies
Data related to Microsporidia at Wikispecies- BioHealthBase Bioinformatics Resource Center Database of microspordia sequences and related information.
- Microsporidia at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
