Fritzing: Difference between revisions
No edit summary Tags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit |
Tom.Reding (talk | contribs) m WP:STUBSPACING followup |
||
| (35 intermediate revisions by 31 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|Open source CAD system for electronic design, aimed at hobbyists}} |
|||
{{Infobox |
{{Infobox software |
||
| name |
| name = Fritzing Software |
||
| logo = |
|||
| logo = |
|||
| screenshot = fritzing breadboard view.jpg |
|||
| |
| screenshot = fritzing breadboard view.jpg |
||
| caption = Fritzing's breadboard view |
|||
| developer |
| developer = Interaction Design Lab Potsdam |
||
| latest release version = 0.9.3b |
|||
| latest release |
| latest release version = {{wikidata|property|edit|reference|Q2463610|P548=Q2804309|P348}} |
||
| latest release date = {{start date and age|{{wikidata|qualifier|Q2463610|P548=Q2804309|P348|P577}}}} |
|||
| operating system = [[Mac OS X]], [[Unix]], [[Microsoft Windows|Windows]] |
|||
| programming language = [[C++]] |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| operating system = [[Microsoft Windows|Windows]], [[macOS]], [[Linux]] |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
}} |
}} |
||
'''Fritzing''' is an [[open source]] initiative<ref>{{cite book|last=McRoberts|first=Michael|title=Beginning Arduino|year=2010|publisher=APress|isbn=978-1-4302-3240-7|pages=xx|url=https:// |
'''Fritzing''' is an [[open-source software|open-source]] initiative<ref>{{cite book|last=McRoberts|first=Michael|title=Beginning Arduino|year=2010|publisher=APress|isbn=978-1-4302-3240-7|pages=xx|url=https://archive.org/details/beginningarduino00mcro_0|url-access=registration}}</ref> to develop amateur or hobby [[CAD software]] for the [[Electronic design automation|design of electronics hardware]], intended to allow designers and artists to build more permanent circuits from prototypes. It was developed at the [[University of Applied Sciences Potsdam]].<ref>{{cite book|last=Brühlmann|first=Thomas|title=Arduino: Praxiseinstieg|year=2010|publisher=Hüthig Jehle Rehm|isbn=978-3-8266-5605-7|pages=270|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=hIdBwUaSfWsC&pg=PA270}}</ref> Fritzing is [[free software]] under the [[GNU General Public License|GPL 3.0 or later]] license, with the source code available on GitHub and the binaries at a monetary cost, which is allowed by the GPL.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.gnu.org/licenses/gpl-faq.en.html#DoesTheGPLAllowMoney|title=Frequently Asked Questions about the GNU Licenses}}</ref> |
||
== Goals == |
== Goals == |
||
[[File:fritzing schematic view.jpg|thumb|left|Fritzing's schematic view]] |
[[File:fritzing schematic view.jpg|thumb|left|Fritzing's schematic view]] |
||
The software |
The software was created with inspiration from the [[Processing (programming language)|Processing]] programming language and the [[Arduino]] microcontroller<ref>{{cite news|last=Gläser |author2=Markus Jaritz |author3=Philipp Sackl|first=Thomas|title=Hardware-Hacking: So baut man einen Tentakel-Roboter für 100 Euro|url=http://www.spiegel.de/netzwelt/games/0,1518,647596,00.html|access-date=14 April 2011|newspaper=[[Der Spiegel]]|date=13 September 2009}}</ref> and allows a designer, artist, researcher, or hobbyist to document their Arduino-based prototype and create a [[Printed circuit board|PCB]] layout for manufacturing. The associated website helps users share and discuss drafts and experiences as well as to reduce manufacturing costs. |
||
Fritzing can be seen as an [[electronic design automation]] (EDA) tool for non-engineers: the input metaphor is inspired by the environment of designers (the [[breadboard]]-based prototype), while the output is focused on accessible means of production. As of December 2, 2014 Fritzing has made a code view option, where one can modify code and upload it directly to an Arduino device.<ref>http://blog.fritzing.org/2014/12/02/its-fritzmas-new-fritzing-code-view-release-and-a-little-present.</ref> |
Fritzing can be seen as an [[electronic design automation]] (EDA) tool for non-engineers: the input metaphor is inspired by the environment of designers (the [[breadboard]]-based prototype), while the output is focused on accessible means of production. As of December 2, 2014 Fritzing has made a code view option, where one can modify code and upload it directly to an Arduino device.<ref>http://blog.fritzing.org/2014/12/02/its-fritzmas-new-fritzing-code-view-release-and-a-little-present. {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210506181007/https://blog.fritzing.org/2014/12/02/its-fritzmas-new-fritzing-code-view-release-and-a-little-present |date=2021-05-06 }}</ref> |
||
Component images are distributed under [[CC |
Component images are distributed under [[Creative Commons license|CC BY-SA 3.0]], which will also be the license for any generated breadboard views. |
||
{| |
{| |
||
| Line 30: | Line 32: | ||
|} |
|} |
||
{{Clear}} |
{{Clear}} |
||
== Developer == |
|||
The Fritzing source code is written in [[C++]] using the [[Qt (software)|Qt]]-framework. The source code can be downloaded |
|||
and edited via the [[GitHub]] repositories. The source is split in two main repositories: Fritzing-App and Fritzing-Parts. |
|||
== Maker == |
== Maker == |
||
Fritzing allows for easy creation of [[printed circuit board]]s. |
|||
FritzingFab enables users to order PCBs with designs made on the Fritzing software. |
|||
Fritzing allows for creation of [[printed circuit board]]s. Fritzing provides access to a commercial service known as ‘FritzingFab’ to order PCBs created with designs made on the Fritzing software. |
|||
Additionally, the [http://www.fritzing.org website] contains a [http://forum.fritzing.org/ forum] where users can share and comment on each other's designs. |
|||
== Simulator == |
|||
Since version 0.9.10, Fritzing incorporates a basic simulator,<ref>{{Cite web |last=Faíña |first=Andrés |date=27 June 2022 |title=Simulating Circuits with Fritzing |url=https://blog.fritzing.org/2022/06/27/Simulating-Circuits-with-Fritzing |website=Fritzing}}</ref> which is still in beta. The main aim of the simulator is to teach electronics to beginners, and Fritzing version 0.9.10 only supports analysis of DC circuits. The simulator works on the breadboard and schematic views. In addition, it checks that the parts are working within their specifications (otherwise, a smoke symbol appears). The simulator provides multimeters to read voltages and currents and it attempts to recreate a realistic laboratory session. |
|||
==See also== |
==See also== |
||
{{Portal|Electronics}} |
{{Portal|Electronics}} |
||
* [[Comparison of EDA software]] |
* [[Comparison of EDA software]] |
||
*[[List of free and open-source software packages|List of free and open source software packages]] |
|||
* [[List of free electronics circuit simulators]] |
* [[List of free electronics circuit simulators]] |
||
| Line 51: | Line 51: | ||
== External links == |
== External links == |
||
{{commons category}} |
{{commons category}} |
||
* {{official website| |
* {{official website|https://fritzing.org}} |
||
* [http://forum.fritzing.org/ User Forum] |
* [http://forum.fritzing.org/ User Forum] |
||
* [http://fab.fritzing.org FabService] |
* [http://fab.fritzing.org FabService] |
||
| Line 64: | Line 64: | ||
[[Category:Electronic design automation software for Linux]] |
[[Category:Electronic design automation software for Linux]] |
||
[[Category:Engineering software that uses Qt]] |
[[Category:Engineering software that uses Qt]] |
||
[[Category:Free software programmed in C++]] |
|||
[[Category:Arduino]] |
|||
Latest revision as of 12:17, 24 September 2024
 Fritzing's breadboard view | |
| Developer(s) | Interaction Design Lab Potsdam |
|---|---|
| Stable release | 1.0.4[1] |
| Repository | |
| Written in | C++ |
| Operating system | Windows, macOS, Linux |
| Type | EDA |
| License | GPL 3.0 or later (software) CC BY-SA 3.0 (component images)[2] |
| Website | fritzing |
Fritzing is an open-source initiative[3] to develop amateur or hobby CAD software for the design of electronics hardware, intended to allow designers and artists to build more permanent circuits from prototypes. It was developed at the University of Applied Sciences Potsdam.[4] Fritzing is free software under the GPL 3.0 or later license, with the source code available on GitHub and the binaries at a monetary cost, which is allowed by the GPL.[5]
Goals
[edit]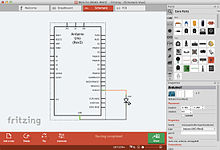
The software was created with inspiration from the Processing programming language and the Arduino microcontroller[6] and allows a designer, artist, researcher, or hobbyist to document their Arduino-based prototype and create a PCB layout for manufacturing. The associated website helps users share and discuss drafts and experiences as well as to reduce manufacturing costs.
Fritzing can be seen as an electronic design automation (EDA) tool for non-engineers: the input metaphor is inspired by the environment of designers (the breadboard-based prototype), while the output is focused on accessible means of production. As of December 2, 2014 Fritzing has made a code view option, where one can modify code and upload it directly to an Arduino device.[7]
Component images are distributed under CC BY-SA 3.0, which will also be the license for any generated breadboard views.
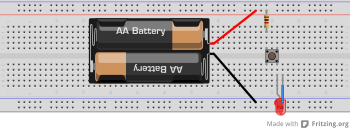 |
 |
Maker
[edit]Fritzing allows for creation of printed circuit boards. Fritzing provides access to a commercial service known as ‘FritzingFab’ to order PCBs created with designs made on the Fritzing software.
Simulator
[edit]Since version 0.9.10, Fritzing incorporates a basic simulator,[8] which is still in beta. The main aim of the simulator is to teach electronics to beginners, and Fritzing version 0.9.10 only supports analysis of DC circuits. The simulator works on the breadboard and schematic views. In addition, it checks that the parts are working within their specifications (otherwise, a smoke symbol appears). The simulator provides multimeters to read voltages and currents and it attempts to recreate a realistic laboratory session.
See also
[edit]- Comparison of EDA software
- List of free and open source software packages
- List of free electronics circuit simulators
References
[edit]- ^ https://blog.fritzing.org/2024/10/08/fritzing-1-0-4.
{{cite web}}: Missing or empty|title=(help) - ^ What license is Fritzing released under? FAQ
- ^ McRoberts, Michael (2010). Beginning Arduino. APress. pp. xx. ISBN 978-1-4302-3240-7.
- ^ Brühlmann, Thomas (2010). Arduino: Praxiseinstieg. Hüthig Jehle Rehm. p. 270. ISBN 978-3-8266-5605-7.
- ^ "Frequently Asked Questions about the GNU Licenses".
- ^ Gläser, Thomas; Markus Jaritz; Philipp Sackl (13 September 2009). "Hardware-Hacking: So baut man einen Tentakel-Roboter für 100 Euro". Der Spiegel. Retrieved 14 April 2011.
- ^ http://blog.fritzing.org/2014/12/02/its-fritzmas-new-fritzing-code-view-release-and-a-little-present. Archived 2021-05-06 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Faíña, Andrés (27 June 2022). "Simulating Circuits with Fritzing". Fritzing.
External links
[edit]- Official website
- User Forum
- FabService
- Fritzing-App on GitHub
- Fritzing-Parts on GitHub
- Fritzing overview
