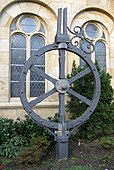St. Peter's Cathedral, Osnabrück: Difference between revisions
Disambiguated: Romanesque → Romanesque architecture (2), Gothic → Gothic architecture (2) |
|||
| (32 intermediate revisions by 24 users not shown) | |||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
| landscape = |
| landscape = |
||
| caption = Osnabrück Cathedral. To the right is the southwest tower with the ringing bells. |
| caption = Osnabrück Cathedral. To the right is the southwest tower with the ringing bells. |
||
| pushpin map = Germany |
| pushpin map = Lower Saxony#Germany |
||
| pushpin label position = |
| pushpin label position = |
||
| pushpin map alt = |
| pushpin map alt = |
||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
| relief = |
| relief = |
||
| map caption = |
| map caption = |
||
| |
| coordinates = {{coord|52.27755|N|8.04498|E|display=inline,title|format=dms}} |
||
| latm = 17 |
|||
| lats = |
|||
| latNS = N |
|||
| longd = 8 |
|||
| longm = 3 |
|||
| longs = |
|||
| longEW = E |
|||
| coordinates = <!-- {{coord| LAT| LONG| region:ZZ_type:landmark| display=inline,title}} --> |
|||
| osgraw = <!-- TEXT --> |
| osgraw = <!-- TEXT --> |
||
| osgridref = <!-- {{gbmappingsmall| TEXT}} --> |
| osgridref = <!-- {{gbmappingsmall| TEXT}} --> |
||
| Line 36: | Line 28: | ||
| membership = |
| membership = |
||
| attendance = |
| attendance = |
||
| website = |
| website = {{URL|http://www.dom-osnabrueck.de/}} |
||
| former name = |
| former name = |
||
| Line 51: | Line 43: | ||
| people = |
| people = |
||
| status = |
| status = [[Cathedral]] |
||
| functional status = |
| functional status = Active |
||
| heritage designation = |
| heritage designation = |
||
| designated date = |
| designated date = |
||
| architect = |
| architect = |
||
| architectural type = [[Romanesque architecture|Romanesque]], [[Gothic architecture|Gothic]] |
| architectural type = |
||
| style = [[Romanesque architecture|Romanesque]], [[Gothic architecture|Gothic]] |
|||
| style = |
|||
| groundbreaking = |
| groundbreaking = |
||
| completed date = <br>11th century (enlarged)<br>13th century (renovations)<br>1946 ([[Reconstruction of Germany|reconstruction]] of tower) |
|||
| completed date = |
|||
| construction cost = |
| construction cost = |
||
| closed date = |
| closed date = |
||
| Line 81: | Line 73: | ||
| spire height = <!-- {{convert| }} --> |
| spire height = <!-- {{convert| }} --> |
||
| materials = |
| materials = |
||
| bells = |
| bells = 6 |
||
| bells hung = |
| bells hung = |
||
| bell weight = <!-- {{CwtQtrLb to kg| }} --> |
| bell weight = <!-- {{CwtQtrLb to kg| }} --> |
||
| Line 91: | Line 83: | ||
| archdiocese = |
| archdiocese = |
||
| metropolis = |
| metropolis = |
||
| diocese = [[Roman Catholic Diocese of Osnabrück]] |
| diocese = [[Roman Catholic Diocese of Osnabrück|Osnabrück]] |
||
| province = |
| province = |
||
| presbytery = |
| presbytery = |
||
| Line 101: | Line 93: | ||
| archbishop = |
| archbishop = |
||
| bishop = |
| bishop = [[sede vacante]] |
||
| dean = |
| dean = [[Johannes Wübbe]] |
||
| provost = |
| provost = |
||
| provost-rector = |
| provost-rector = |
||
| Line 110: | Line 102: | ||
| archpriest = |
| archpriest = |
||
| chancellor = |
| chancellor = |
||
| canonchancellor = |
| canonchancellor = [[Johannes Wübbe]] |
||
| canon = |
| canon = |
||
Ulrich Beckwermert |
|||
Ansgar Lüttel |
|||
Reinhard Molitor |
|||
Theodor Paul |
|||
Martin Schomaker |
|||
Hermann Wieh |
|||
Bernhard Stecker |
|||
Alfons Strodt |
|||
| canonmissioner = |
| canonmissioner = |
||
| canonpastor = |
| canonpastor = |
||
| Line 135: | Line 135: | ||
| chaplain = |
| chaplain = |
||
| sacristan = |
| sacristan = |
||
| reader = |
| reader = |
||
| Line 161: | Line 162: | ||
| logoalt = |
| logoalt = |
||
}} |
}} |
||
{{citations|date=February 2018}} |
|||
'''St. Peter's Cathedral''' in [[Osnabrück]], [[Germany]] is the cathedral of the [[Roman Catholic Diocese of Osnabrück]]. The cathedral is a late [[Romanesque architecture|Romanesque]] building and dominates the city's [[skyline]]. |
'''St. Peter's Cathedral''' in [[Osnabrück]], [[Germany]] is the cathedral of the [[Roman Catholic Diocese of Osnabrück]]. The cathedral is a late [[Romanesque architecture|Romanesque]] building and dominates the city's [[skyline]]. |
||
| Line 170: | Line 171: | ||
The oldest parts of the present-day church are the Romanesque [[crossing tower]], the northern facade and the Romanesque-[[Gothic architecture|Gothic]] west facade. The dome in the middle part of the three-[[aisle]]d [[nave]] is as high as the [[column|pillar]]s on which it rests. |
The oldest parts of the present-day church are the Romanesque [[crossing tower]], the northern facade and the Romanesque-[[Gothic architecture|Gothic]] west facade. The dome in the middle part of the three-[[aisle]]d [[nave]] is as high as the [[column|pillar]]s on which it rests. |
||
The oldest pieces of equipment that have survived to this day are the [[baptismal font]] from 1220 and the [[triumphal cross]] from 1230. The broken [[rood screen]] from 1664 has also survived. Twelve statues received from the [[Münster]] sculptor [[Heinrich Brabender]] remain preserved to this day, including figures of the [[Christ]] and of the [[Apostles]], and also a smaller number of statues received from [[Eric of Saxe-Lauenburg (prince-bishop)|Duke Erich II of Saxe-Lauenburg]], [[Prince-Bishopric of Münster|Bishop of Münster]]. These are on display at the Diocesan Museum of Osnabrück. |
The oldest pieces of equipment that have survived to this day are the [[baptismal font]] from 1220 and the [[triumphal cross]] from 1230. The broken [[rood screen]] from 1664 has also survived. Twelve statues received from the [[Münster]] sculptor [[Heinrich Brabender]] remain preserved to this day, including figures of the [[Christ]] and of the [[Apostles in the New Testament|Apostles]], and also a smaller number of statues received from [[Eric of Saxe-Lauenburg (prince-bishop)|Duke Erich II of Saxe-Lauenburg]], [[Prince-Bishopric of Münster|Bishop of Münster]]. These are on display at the Diocesan Museum of Osnabrück. |
||
Over the centuries, the cathedral changed in appearance - the interior primarily during the [[Baroque period]], to which the [[altar]]s, figures, and [[epitaph]]s bear testimony, and the exterior during the major restoration in 1882-1910 under [[Alexander Behnes]] through renovations and building of annexes. During the [[Second World War]] the cathedral roof with baroque domes and some church annexes were destroyed by [[Incendiary device|incendiary bombs]]. The cathedral has since been rebuilt and is still a major attraction for the Christians of the city and the diocese as well as people interested in [[art history]] from around the world. The Osnabrück Wheel, which on September 13, 1944 fell from the larger of the towers due to bombing, has been re-erected at the side of the cathedral. |
Over the centuries, the cathedral changed in appearance - the interior primarily during the [[Baroque period]], to which the [[altar]]s, figures, and [[epitaph]]s bear testimony, and the exterior during the major restoration in 1882-1910 under [[Alexander Behnes]] through renovations and building of annexes. During the [[Second World War]] the cathedral roof with baroque domes and some church annexes were destroyed by [[Incendiary device|incendiary bombs]]. The cathedral has since been rebuilt and is still a major attraction for the Christians of the city and the diocese as well as people interested in [[art history]] from around the world. The Osnabrück Wheel, which on September 13, 1944 fell from the larger of the towers due to bombing, has been re-erected at the side of the cathedral. |
||
The [[cloister]] is attached to the church at south of the nave. It has open pillar-[[arcade (architecture)|arcade]]s on the remaining three sides. [[Capital (architecture)#Western Romanesque and Gothic capitals|Cushion capital]]s, which correspond to those in the former west [[choir]] of 1140, are present in the east wing. The [[barrel vault]] in the eastern part of the cloister features [[lunette]]s but no [[belt bow]]s; the vaults in the south and west wings are supported by belt bows and [[ |
The [[cloister]] is attached to the church at south of the nave. It has open pillar-[[arcade (architecture)|arcade]]s on the remaining three sides. [[Capital (architecture)#Western Romanesque and Gothic capitals|Cushion capital]]s, which correspond to those in the former west [[choir]] of 1140, are present in the east wing. The [[barrel vault]] in the eastern part of the cloister features [[lunette]]s but no [[belt bow]]s; the vaults in the south and west wings are supported by belt bows and [[Ogival arch#Architecture|ogival arch]]es (built in the second quarter of the 13th century). During the Second World War the cloister, which had been walled towards the courtyard, served as an [[air raid shelter]]. |
||
== Bells == |
== Bells == |
||
The [[belfry (architecture)|belfry]] in the southwest tower houses a [[Ring of bells|ring]] of six [[cast steel]] bells, one of the |
The [[belfry (architecture)|belfry]] in the southwest tower houses a [[Ring of bells|ring]] of six [[cast steel]] bells all cast in 1954, one of the [[Bochumer Verein]]'s best works. The bells were built in the so-called experimental V7 shape, a minor octave shape cast. The 1951 cast steel bells of the [[Paderborn Cathedral]] also ring in the same disposition, and were considered the first major bells ringing in the then newly developed V7 shape. The largest bell or [[Bourdon (bell)|bourdon]] is called " Maria Immaculata" and it weighs 5 tons. The 5 smaller bells are named “Petrus”, “Crispinus and Crispinianus”, “Wiho”, “Gosbert” and “Adolf von Tecklenburg”. In Germany, the bells are always numbered from largest to smallest, Bell 1 is always the [[Tenor bell|tenor]] or [[Bourdon (bell)|bourdon]]. |
||
{| class="wikitable sortable" |
|||
|+Bells of St. Peter's Cathedral |
|||
!Bell |
|||
!Mass (kg) |
|||
|- |
|||
|Maria Immaculata (Bourdon Bell) |
|||
|4830 |
|||
|- |
|||
|Petrus |
|||
|2805 |
|||
|- |
|||
|Crispinus & Crispinianus |
|||
|2115 |
|||
|- |
|||
|Wiho |
|||
|1560 |
|||
|- |
|||
|Gosbert |
|||
|935 |
|||
|- |
|||
|Adolf von Tecklenburg |
|||
|625 |
|||
|} |
|||
== Organs == |
== Organs == |
||
| Line 209: | Line 233: | ||
== References == |
== References == |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
== External links == |
|||
*[http://www.bistum-osnabrueck.de/kultur/dom-st-petrus.html Information] – Diocese of Osnabrück website |
|||
{{Authority control}} |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
{{DEFAULTSORT:Saint Peters Cathedral, Osnabruck}} |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
[[Category: |
[[Category:8th-century churches in Germany|Osnabruck Cathedral]] |
||
[[Category:12th-century |
[[Category:12th-century churches in Germany|Osnabruck Cathedral]] |
||
[[Category: |
[[Category:Roman Catholic cathedrals in Germany|Osnabruck]] |
||
| ⚫ | |||
[[Category:Churches in Osnabrück|Cathedral]] |
|||
[[Category:Tourist attractions in Osnabrück]] |
|||
Latest revision as of 14:54, 23 September 2024
| St. Peter's Cathedral | |
|---|---|
Dom St. Peter | |
 Osnabrück Cathedral. To the right is the southwest tower with the ringing bells. | |
| 52°16′39″N 8°02′42″E / 52.27755°N 8.04498°E | |
| Location | Osnabrück, Lower Saxony |
| Country | Germany |
| Denomination | Roman Catholic |
| Website | www |
| History | |
| Status | Cathedral |
| Founded | 785 |
| Architecture | |
| Functional status | Active |
| Style | Romanesque, Gothic |
| Completed | 11th century (enlarged) 13th century (renovations) 1946 (reconstruction of tower) |
| Specifications | |
| Bells | 6 |
| Administration | |
| Diocese | Osnabrück |
| Clergy | |
| Bishop(s) | sede vacante |
| Dean | Johannes Wübbe |
| Canon Chancellor | Johannes Wübbe |
| Canon(s) | Ulrich Beckwermert
Ansgar Lüttel Reinhard Molitor Theodor Paul Martin Schomaker Hermann Wieh Bernhard Stecker Alfons Strodt |
This article includes a list of references, related reading, or external links, but its sources remain unclear because it lacks inline citations. (February 2018) |
St. Peter's Cathedral in Osnabrück, Germany is the cathedral of the Roman Catholic Diocese of Osnabrück. The cathedral is a late Romanesque building and dominates the city's skyline.
History, interior architecture, and equipment
[edit]The first version of St. Peter's Cathedral was built in the year 785, 15 years after the diocese was founded by Charlemagne. The Normans destroyed the church 100 years later, and the present version of the church developed only gradually after a fire around 1100.
The oldest parts of the present-day church are the Romanesque crossing tower, the northern facade and the Romanesque-Gothic west facade. The dome in the middle part of the three-aisled nave is as high as the pillars on which it rests.
The oldest pieces of equipment that have survived to this day are the baptismal font from 1220 and the triumphal cross from 1230. The broken rood screen from 1664 has also survived. Twelve statues received from the Münster sculptor Heinrich Brabender remain preserved to this day, including figures of the Christ and of the Apostles, and also a smaller number of statues received from Duke Erich II of Saxe-Lauenburg, Bishop of Münster. These are on display at the Diocesan Museum of Osnabrück.
Over the centuries, the cathedral changed in appearance - the interior primarily during the Baroque period, to which the altars, figures, and epitaphs bear testimony, and the exterior during the major restoration in 1882-1910 under Alexander Behnes through renovations and building of annexes. During the Second World War the cathedral roof with baroque domes and some church annexes were destroyed by incendiary bombs. The cathedral has since been rebuilt and is still a major attraction for the Christians of the city and the diocese as well as people interested in art history from around the world. The Osnabrück Wheel, which on September 13, 1944 fell from the larger of the towers due to bombing, has been re-erected at the side of the cathedral.
The cloister is attached to the church at south of the nave. It has open pillar-arcades on the remaining three sides. Cushion capitals, which correspond to those in the former west choir of 1140, are present in the east wing. The barrel vault in the eastern part of the cloister features lunettes but no belt bows; the vaults in the south and west wings are supported by belt bows and ogival arches (built in the second quarter of the 13th century). During the Second World War the cloister, which had been walled towards the courtyard, served as an air raid shelter.
Bells
[edit]The belfry in the southwest tower houses a ring of six cast steel bells all cast in 1954, one of the Bochumer Verein's best works. The bells were built in the so-called experimental V7 shape, a minor octave shape cast. The 1951 cast steel bells of the Paderborn Cathedral also ring in the same disposition, and were considered the first major bells ringing in the then newly developed V7 shape. The largest bell or bourdon is called " Maria Immaculata" and it weighs 5 tons. The 5 smaller bells are named “Petrus”, “Crispinus and Crispinianus”, “Wiho”, “Gosbert” and “Adolf von Tecklenburg”. In Germany, the bells are always numbered from largest to smallest, Bell 1 is always the tenor or bourdon.
| Bell | Mass (kg) |
|---|---|
| Maria Immaculata (Bourdon Bell) | 4830 |
| Petrus | 2805 |
| Crispinus & Crispinianus | 2115 |
| Wiho | 1560 |
| Gosbert | 935 |
| Adolf von Tecklenburg | 625 |
Organs
[edit]The cathedral has two organs: the main organ in the west, and a small choir organ in the north transept .
Main organ
[edit]The main organ was built in 2003 by the organ maker Kuhn AG of Männedorf, Switzerland. It stands above the main portal under the west rose window. The console is "in" the organ, centered over the back wall of the organ, facing towards the altar. It is electrically connected to a small tower organ chamber with four registers (cone chests), which is housed on the first floor of the large west tower. The organ chamber is swellable and has a sound-absorbing chamber.
Mutin-Cavaillé-Coll
[edit]The cathedral has an additional rare organ - on the north wall of the transept is a choir organ from the workshop of Mutin-Cavaillé-Coll. Built in 1898, the organ has 12 stops with three additional transmissions to the pedal. All the sounding pipes are swellable.
Gallery
[edit]-
View from the east
-
Crossing tower of the cathedral, viewed from the northwest
-
Baptismal font of 1220
-
Interior with triumphal cross of 1230
-
Altarpiece
-
The main organ
-
Osnabrück wheel, originally on the large southwest tower
-
Cloister surrounding the courtyard of the cathedral
-
Cloister
-
The Löwenpudel ("lion poodle") in front of the cathedral
References
[edit]- Feldwisch-Dentrup, Heinrich; Jung, Andreas (1980). Osnabrück – Dom und Domschatz [Osnabrück - Cathedral and the Cathedral Treasury] (in German). Königstein im Taunus: Verlag Langewiesche.
- Thümmler, Hans (1954). "Der Dom zu Osnabrück" [The Cathedral of Osnabrück]. Deutsche Lande – Deutsche Kunst [German lands - German art] (in German). Munich / Berlin: Deutscher Kunstverlag.
External links
[edit]- Information – Diocese of Osnabrück website