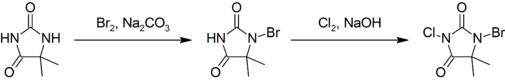BCDMH: Difference between revisions
Rifleman 82 (talk | contribs) →Preparation: +image |
No edit summary |
||
| (40 intermediate revisions by 27 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{chembox |
{{chembox |
||
| Watchedfields = changed |
|||
| verifiedrevid = |
| verifiedrevid = 439489418 |
||
| Name = BCDMH |
| Name = BCDMH |
||
| ImageFile = BCDMH |
| ImageFile = BCDMH.png |
||
| ImageSize = |
| ImageSize = 180px |
||
| |
| ImageAlt = Skeletal formula of BCDMH |
||
| ImageFile1 = BCDMH.png |
| ImageFile1 = BCDMH-3D-balls.png |
||
| ImageSize1 = |
| ImageSize1 = 180 |
||
| |
| ImageAlt1 = Ball-and-stick model of BCDMH |
||
| ImageFile2 = BCDMH 100g.jpg |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ImageSize2 = 150px |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ImageAlt2 = Laboratory sample of BCDMH |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| InChI = 1/C5H6BrClN2O2/c1-5(2)3(10)8(6)4(11)9(5)7/h1-2H3 |
| InChI = 1/C5H6BrClN2O2/c1-5(2)3(10)8(6)4(11)9(5)7/h1-2H3 |
||
| InChIKey = PQRDTUFVDILINV-UHFFFAOYAT |
| InChIKey = PQRDTUFVDILINV-UHFFFAOYAT |
||
| Line 18: | Line 22: | ||
| StdInChIKey_Ref = {{stdinchicite|correct|chemspider}} |
| StdInChIKey_Ref = {{stdinchicite|correct|chemspider}} |
||
| StdInChIKey = PQRDTUFVDILINV-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| StdInChIKey = PQRDTUFVDILINV-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
||
| CASNo_Ref = {{cascite|correct| |
| CASNo_Ref = {{cascite|correct|CAS}} |
||
| CASNo = |
| CASNo = 32718-18-6 |
||
| |
| SMILES = O=C1N(Br)C(=O)N(Cl)C1(C)C |
||
| ChemSpiderID_Ref = {{chemspidercite|correct|chemspider}} |
| ChemSpiderID_Ref = {{chemspidercite|correct|chemspider}} |
||
| ChemSpiderID=29069 |
| ChemSpiderID =29069 |
||
| EINECS = 204-766-9 |
|||
| UNII_Ref = {{fdacite|correct|FDA}} |
|||
| UNII = W18O2G87ND |
|||
| ChEMBL = 1895319 |
|||
}} |
}} |
||
| |
|Section2={{Chembox Properties |
||
| |
| Formula = C<sub>5</sub>H<sub>6</sub>BrClN<sub>2</sub>O<sub>2</sub> |
||
| |
| MolarMass = 241.47 g/mol |
||
| |
| Appearance = White solid |
||
| |
| Density = 1.9 g/cm<sup>3</sup> |
||
| |
| Solubility = 0.15 g/100 ml (25 °C) |
||
| MeltingPtC = 159 to 163 |
|||
| MeltingPt = 159–163 °C |
|||
| |
| MeltingPt_notes = |
||
| BoilingPt = |
|||
}} |
}} |
||
| |
|Section7={{Chembox Hazards |
||
| |
| ExternalSDS = [http://physchem.ox.ac.uk/MSDS/BR/1-bromo-3-chloro-5,5-dimethyl-2,4-imidazolidinedione.html External MSDS] |
||
| |
| MainHazards = Flamability, Inhalation |
||
| |
| NFPA-H = 3 |
||
| |
| NFPA-R = 1 |
||
| |
| NFPA-F = 1 |
||
| |
| FlashPt = Decomposes at 160°C |
||
| |
| GHSPictograms = {{GHS03}}{{GHS05}}{{GHS07}}{{GHS09}} |
||
| GHSSignalWord = Danger |
|||
| HPhrases = {{H-phrases|272|302|312|314|317|332|400}} |
|||
| PPhrases = {{P-phrases|210|220|221|260|261|264|270|271|272|273|280|301+312|301+330+331|302+352|303+361+353|304+312|304+340|305+351+338|310|312|321|322|330|333+313|363|370+378|391|405|501}} |
|||
}} |
}} |
||
}} |
}} |
||
'''1-Bromo-3-chloro-5,5-dimethylhydantoin''' ('''BCDMH''') is a chemical structurally related to [[hydantoin]]. It is a white crystalline compound with a slight [[bromine]] and [[acetone]] odor and is insoluble in water, but soluble in [[acetone]]. |
'''1-Bromo-3-chloro-5,5-dimethylhydantoin''' ('''BCDMH''' or '''bromochlorodimethylhydantoin''') is a chemical structurally related to [[hydantoin]]. It is a white crystalline compound with a slight [[bromine]] and [[acetone]] odor and is insoluble in water, but soluble in [[acetone]]. |
||
BCDMH is an excellent source of both chlorine and bromine as it reacts slowly with water releasing [[hypochlorous acid]] and [[hypobromous acid]]. It used as a chemical [[disinfectant]] |
BCDMH is an excellent source of both [[chlorine]] and [[bromine]] as it reacts slowly with water releasing [[hypochlorous acid]] and [[hypobromous acid]]. It used as a chemical [[disinfectant]] for [[Swimming pool sanitation#Chlorine and bromine methods|recreational water sanitation]] and drinking [[water purification]].<ref name=NSF>{{Cite web |
||
| url = http://info.nsf.org/Certified/PwsChemicals/Listings.asp?=&ChemicalName=Bromochlorodimethylhydantoin |
|||
| title = NSF/ANSI 60 - Drinking Water Treatment Chemicals - Health Effects |
|||
| access-date = November 14, 2018 |
|||
| author = NSF International |
|||
| author-link = NSF International |
|||
| year = 2012 |
|||
| work = NSF Product and Service Listings |
|||
| publisher = [[NSF International]] |
|||
| quote = Bromochlorodimethylhydantoin[CL] - Bromicide Tablets - Algicide - Disinfection & Oxidation. [CL] The residual levels of chlorine ([[hypochlorite]] ion and [[hypochlorous acid]]), [[chlorine dioxide]], chlorate ion, [[monochloramine]] and disinfection by-products shall be monitored in the finished drinking water to ensure compliance to all applicable regulations.}}</ref> BCDMH works in the following manner:<ref>South Australian Health Commission, "Standard for the Operation of Swimming Pools and Spa Pools in South Australia", [http://www.dh.sa.gov.au/pehs/publications/code-bromine.pdf Supplement C: Bromine Disinfection] {{Webarchive|url=http://webarchive.loc.gov/all/20090521114852/http://www.dh.sa.gov.au/pehs/publications/code-bromine.pdf |date=2009-05-21 }}, page 8. Retrieved on 2009-05-12.</ref> |
|||
The initial BCDMH reacts with water (R = Dimethylhydantoin): |
The initial BCDMH reacts with water (R = Dimethylhydantoin): |
||
| Line 54: | Line 75: | ||
Hypobromous acid partially dissociates in water: |
Hypobromous acid partially dissociates in water: |
||
: HOBr → H<sup>+</sup> + OBr<sup> |
: HOBr → H<sup>+</sup> + OBr<sup>−</sup> |
||
Hypobromous acid oxidizes the substrate, itself being reduced to bromide: |
Hypobromous acid oxidizes the substrate, itself being reduced to bromide: |
||
: HOBr + Live pathogens → Br<sup> |
: HOBr + Live pathogens → Br<sup>−</sup> + Dead pathogens |
||
The bromide ions are oxidized with the hypochlorous acid that was formed from the initial BCDMH: |
The bromide ions are oxidized with the hypochlorous acid that was formed from the initial BCDMH: |
||
: Br<sup> |
: Br<sup>−</sup> + HOCl → HOBr + Cl<sup>−</sup> |
||
This produces more hypobromous acid |
This produces more hypobromous acid; the hypochlorous acid itself act directly as a disinfectant in the process. |
||
==Preparation== |
==Preparation== |
||
This compound is prepared by first brominating, then chlorinating 5,5-dimethylhydantoin:<ref>{{Ullmann | title = Chloroamines | Yasukazu Ura, Gozyo Sakata | doi = 10.1002/14356007.a06_553}}</ref> |
This compound is prepared by first [[brominating]], then [[Chlorination reaction|chlorinating]] 5,5-dimethylhydantoin:<ref>{{Ullmann | title = Chloroamines | author = Yasukazu Ura, Gozyo Sakata | doi = 10.1002/14356007.a06_553}}</ref> |
||
:[[ |
:[[File:Preparation of BCDMH.png|505px]] |
||
==References== |
==References== |
||
{{ |
{{Reflist}} |
||
== External links == |
== External links == |
||
* [ |
* [https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/summary/summary.cgi?cid=61828&loc=ec_rcs PubChem Public Chemical Database (nih.gov)] |
||
* [http://www.e1.greatlakes.com/common/msdspdf/00255.pdf External MSDS] |
* [https://web.archive.org/web/20070928060017/http://www.e1.greatlakes.com/common/msdspdf/00255.pdf External MSDS] |
||
[[Category:Disinfectants]] |
[[Category:Disinfectants]] |
||
| Line 81: | Line 102: | ||
[[Category:Organochlorides]] |
[[Category:Organochlorides]] |
||
[[Category:Hydantoins]] |
[[Category:Hydantoins]] |
||
[[ja:1-ブロモ-3-クロロ-5,5-ジメチルヒダントイン]] |
|||
[[ru:1-бром-3-хлор-5,5-диметилгидантоин]] |
|||
Latest revision as of 22:21, 4 February 2024

| |

| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1-Bromo-3-chloro-5,5-dimethylimidazolidine-2,4-dione | |
| Other names
bromochloro-5,5-dimethylhydantoin, BCDMH, agribrom, aquabrom, aquabrome, bromicide, bromochlorodimethylhydantoin, di-halo, halogene T30, HarvestCide, nylate, photobrome, slimicide 78P
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.334 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C5H6BrClN2O2 | |
| Molar mass | 241.47 g/mol |
| Appearance | White solid |
| Density | 1.9 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 159 to 163 °C (318 to 325 °F; 432 to 436 K) |
| 0.15 g/100 ml (25 °C) | |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards
|
Flamability, Inhalation |
| GHS labelling: | |
   
| |
| Danger | |
| H272, H302, H312, H314, H317, H332, H400 | |
| P210, P220, P221, P260, P261, P264, P270, P271, P272, P273, P280, P301+P312, P301+P330+P331, P302+P352, P303+P361+P353, P304+P312, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P310, P312, P321, P322, P330, P333+P313, P363, P370+P378, P391, P405, P501 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | Decomposes at 160°C |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | External MSDS |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
1-Bromo-3-chloro-5,5-dimethylhydantoin (BCDMH or bromochlorodimethylhydantoin) is a chemical structurally related to hydantoin. It is a white crystalline compound with a slight bromine and acetone odor and is insoluble in water, but soluble in acetone.
BCDMH is an excellent source of both chlorine and bromine as it reacts slowly with water releasing hypochlorous acid and hypobromous acid. It used as a chemical disinfectant for recreational water sanitation and drinking water purification.[1] BCDMH works in the following manner:[2]
The initial BCDMH reacts with water (R = Dimethylhydantoin):
Hypobromous acid partially dissociates in water:
- HOBr → H+ + OBr−
Hypobromous acid oxidizes the substrate, itself being reduced to bromide:
- HOBr + Live pathogens → Br− + Dead pathogens
The bromide ions are oxidized with the hypochlorous acid that was formed from the initial BCDMH:
- Br− + HOCl → HOBr + Cl−
This produces more hypobromous acid; the hypochlorous acid itself act directly as a disinfectant in the process.
Preparation
[edit]This compound is prepared by first brominating, then chlorinating 5,5-dimethylhydantoin:[3]
References
[edit]- ^ NSF International (2012). "NSF/ANSI 60 - Drinking Water Treatment Chemicals - Health Effects". NSF Product and Service Listings. NSF International. Retrieved November 14, 2018.
Bromochlorodimethylhydantoin[CL] - Bromicide Tablets - Algicide - Disinfection & Oxidation. [CL] The residual levels of chlorine (hypochlorite ion and hypochlorous acid), chlorine dioxide, chlorate ion, monochloramine and disinfection by-products shall be monitored in the finished drinking water to ensure compliance to all applicable regulations.
- ^ South Australian Health Commission, "Standard for the Operation of Swimming Pools and Spa Pools in South Australia", Supplement C: Bromine Disinfection Archived 2009-05-21 at the Library of Congress Web Archives, page 8. Retrieved on 2009-05-12.
- ^ Yasukazu Ura, Gozyo Sakata. "Chloroamines". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a06_553. ISBN 978-3527306732.